Exploring the Link Between Hypothyroidism and Autoimmune Disorders

Definition of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, often referred to as an underactive thyroid, is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. These hormones are critical for regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall bodily functions. When these hormone levels drop, individuals can experience a wide range of symptoms that can significantly affect their quality of life.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
The causes of hypothyroidism can vary, but several common factors contribute to this condition:
- Autoimmune Disorders: The most prevalent cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Surgery: Surgical removal of the thyroid can lead to a deficiency in hormone production.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatments for cancers in the head and neck can damage the thyroid.
- Medications: Certain medications can interfere with thyroid hormone production.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for hormone production; a deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism.
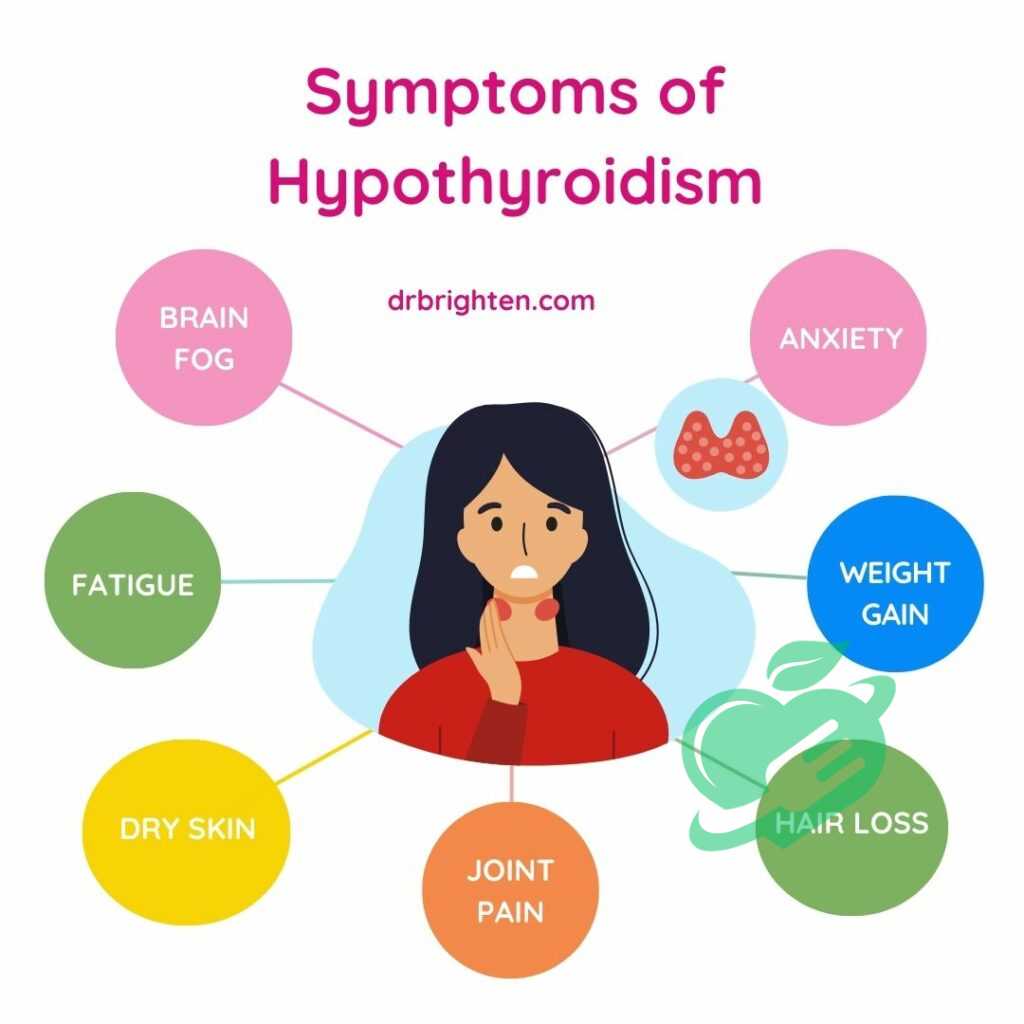
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Detecting hypothyroidism can sometimes be tricky due to its subtle symptoms. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and sluggishness
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Sensitivity to cold
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Depression or mood swings
- Muscle weakness
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
Read also: From Theory to Reality: Exploring the Feasibility of Blood Tests for Anxiety Disorders
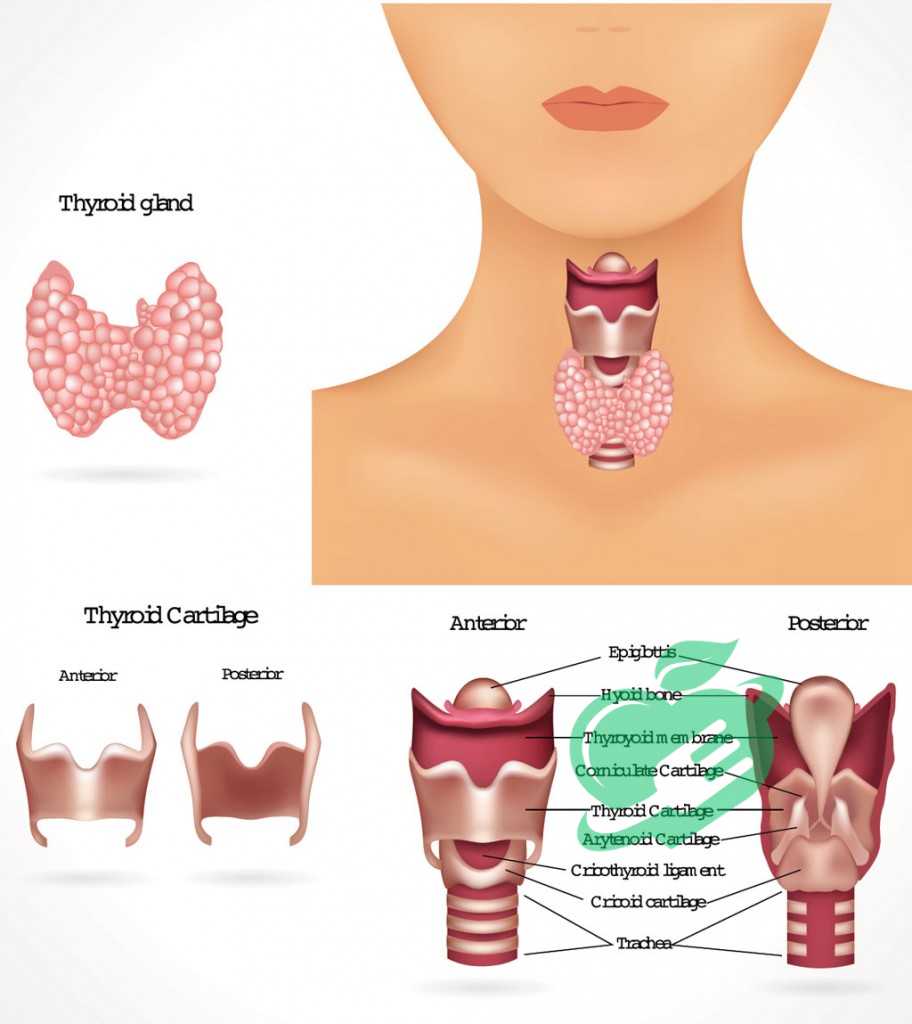
Common Diagnostic Tests for Hypothyroidism
When it comes to diagnosing hypothyroidism, healthcare providers typically rely on a few specific tests. The most common include:
- TSH Test (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): This is usually the first test performed. Elevated TSH levels indicate that the thyroid isn’t producing enough hormones.
- Free T4 Test: This measures the level of free thyroxine in your blood, which should be low if hypothyroidism is present.
- Free T3 Test: Occasionally, a Free T3 test is also conducted for a comprehensive view of thyroid function.
These tests are straightforward, involve a simple blood draw, and provide essential insight into thyroid performance.
Interpreting Thyroid Function Test Results
Interpreting the results can feel overwhelming, but understanding the numbers is crucial. Generally, the following guidelines apply:
- Normal TSH Levels: 0.4 to 4.0 mIU/L
- Elevated TSH: Indicates a potential underactive thyroid.
- Free T4 Level: Low levels may confirm the diagnosis alongside high TSH levels.
Understanding these results helps patients and doctors make informed decisions about treatment options.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of hypothyroidism. Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis can lead to prolonged symptoms, affecting daily life. For example, Andrea, a busy mother, experienced brain fog and fatigue, mistaking these symptoms for regular stress. Timely testing revealed her hypothyroidism, leading to effective treatment and a renewed sense of energy. Emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice when experiencing symptoms is critical for anyone suspecting thyroid issues.
Risk factors
Although anyone can develop hypothyroidism, your risk is higher if you are:
- Women.
- Have a family history of thyroid disease.
- Have an autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes or celiac disease.
- Have been treated for hyperthyroidism.
- Have had radiation therapy to the neck or upper chest.
- Have had thyroid surgery.

Synthetic Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
For many patients, synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the cornerstone of treatment. The most commonly prescribed medication is levothyroxine, which replicates the natural thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). This therapy aims to restore hormone levels to normal, alleviating symptoms. Here’s what you need to know:
- Dosage: Physicians tailor the dosage based on individual needs, often starting low and adjusting as necessary.
- Timing: It is typically recommended to take the medication on an empty stomach to enhance absorption.
Patients often report significant improvements in energy levels and mood shortly after starting treatment, as was the case for Jack, a 43-year-old accountant who finally regained his zest for life after starting levothyroxine.
Read also: Innovative Therapies for Treating Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Hypothyroidism
In addition to medication, some individuals explore natural remedies and supplements. These can include:
- Iodine: Essential for thyroid function but should be taken under medical supervision.
- Selenium: This may help support thyroid hormone production.
- Vitamin D: Enhances overall wellness and can improve immune function.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements to avoid potential interactions.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Thyroid Health
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing hypothyroidism. Consider these changes:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating whole foods rich in nutrients supports thyroid function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity can boost energy levels and help manage weight.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga and meditation can reduce stress, benefiting overall thyroid health.
Making these lifestyle adjustments can complement medical treatments, leading to a holistic approach to managing hypothyroidism effectively.
Read also: Black Seed: The Miracle Cure You Need Toda
Monitoring Thyroid Hormone Levels
Once diagnosed and on treatment, regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels becomes essential. Typically, healthcare providers will recommend testing every six to twelve months. Here’s why it matters:
- Adjustment of Dosage: Hormone levels may fluctuate, requiring medication adjustments.
- Symptom Tracking: Regular tests help align symptoms with hormone levels, ensuring effective management.
For example, Lisa found that after a few months on levothyroxine, her energy levels dipped again. Her doctor recommended a blood test, revealing that her TSH levels had risen, prompting an increase in her dosage, leading to renewed vigor.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Establishing a strong partnership with healthcare providers is crucial in managing hypothyroidism. Patients should:
- Communicate Openly: Share any new symptoms or concerns promptly.
- Educate Themselves: Understanding the condition aids in discussions about treatment options.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Schedule routine appointments to check on progress.
Regular communication helps ensure that personalized care is maintained, adapting treatment as necessary.
Read also: Unpacking the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Diabetics
Long-Term Management Strategies
Long-term management of hypothyroidism involves a blend of medical therapy and healthy lifestyle choices. Some effective strategies include:
- Consistent Medication Routine: Take medications regularly and as prescribed.
- Diet and Nutrition: Focus on a thyroid-friendly diet rich in whole foods.
- Routine Exercise: Maintaining an active lifestyle supports overall health.
By integrating these strategies, patients can effectively manage their hypothyroidism, leading to a happier and healthier life.
Potential Complications of Untreated Hypothyroidism
If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to other health problems, including:
- Goiter. Hypothyroidism can cause an enlarged thyroid gland. This condition is called a goiter. A large goiter can cause problems with swallowing or breathing.
- Heart problems. Hypothyroidism can increase your risk of heart disease and heart failure. This is mainly because people with an underactive thyroid often have high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol).
- Peripheral neuropathy. If left untreated for a long time, hypothyroidism can damage the peripheral nerves that carry information from your brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body. Peripheral neuropathy can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in your arms and legs.
- Infertility. Low levels of thyroid hormone can affect ovulation, which can reduce fertility. Some causes of hypothyroidism, such as autoimmune disorders, can also harm fertility.
- Birth defects. Babies whose mothers have untreated hypothyroidism may have a higher risk of birth defects than babies whose mothers do not have the condition.
- Untreated hypothyroidism can cause serious problems with physical and mental development. But if it is detected within the first few months of life, their chances of normal development are excellent.
Myxedema coma. This rare, potentially fatal condition can occur when hypothyroidism is left untreated for a long time. Sedatives, inflammation, or other stresses on the body can cause myxedema coma. Symptoms include intolerance to cold, drowsiness followed by a lack of energy, and then loss of consciousness. Myxedema coma requires emergency medical treatment. that could have been prevented with timely treatment.
Risks of Inadequate Treatment
Inadequate treatment can also bring its own set of challenges. If hormone levels are not properly managed:
- Persistent Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, and depression may continue to disrupt daily life.
- Increased Risk of Other Diseases: A poorly managed thyroid condition can lead to autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Importance of Regular Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up care with healthcare providers plays a vital role in preventing complications. Patients should:
- Schedule Routine Blood Tests: This helps keep hormone levels in check and adjust treatment as necessary.
- Maintain Open Lines of Communication: Report any new symptoms immediately to facilitate therapy adjustments.
By prioritizing follow-up care, patients can effectively manage their hypothyroidism and reduce the risk of complications, ensuring a healthier future.
Read also: Empowering Your Health Journey with an Endocrinologist’s Care

Investigational Treatments for Hypothyroidism
As the understanding of hypothyroidism evolves, researchers continue to explore innovative treatment options beyond conventional hormone replacement therapy. Some investigational treatments include:
- Thyroid Hormone Combinations: Combining T4 and T3 for those who do not respond adequately to standard therapy.
- Gene Therapy: Targeting the genetic causes of thyroid dysfunction, potentially offering a more tailored treatment approach.
For instance, a clinical trial is currently evaluating the effectiveness of a synthetic hormone that mimics natural hormone production, showing promise in preliminary studies.
Complementary Therapies and Alternative Approaches
Many individuals seek complementary therapies to support their thyroid health alongside traditional treatments. Some popular methods include:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest it may help balance hormone levels.
- Herbal Supplements: Adaptogens like ashwagandha are thought to support thyroid function, but should always be taken under medical guidance.
Emily, a long-time hypothyroidism sufferer, combined her medication with yoga and herbal supplements, enhancing her overall well-being and energy levels.
Future Directions in Hypothyroidism Treatment
The future of hypothyroidism treatment may revolve around personalized medicine. Advances in genetics and technology could lead to treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles and lifestyle needs. Continued research and clinical trials play a crucial role in developing these innovative therapies. For patients, staying informed about emerging developments empowers them to make choices that may enhance their treatment journey.
Read also : Supercharge Your Health with Hawthorn: Everything You Need to Know
Summary of Effective Hypothyroidism Treatments
Managing hypothyroidism effectively requires a multifaceted approach. The cornerstone of treatment typically includes:
- Synthetic Thyroid Hormone Replacement: Medications like levothyroxine remain the gold standard.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment as needed.
- Lifestyle Changes: Incorporating a healthy diet and regular exercise supports overall thyroid health.
Patients like Rachel, who diligently follow their treatment plan and monitor their health, often report feeling significantly better and enjoying enhanced vitality.
Promising Developments in Thyroid Health
As research advances, promising developments in thyroid health continue to emerge. Investigational therapies and personalized medicine strategies are on the horizon, potentially offering tailored treatment options for individual genetic profiles. These innovations could revolutionize how healthcare providers approach hypothyroidism treatment soon.
When to see a doctor
You should see your doctor if you feel tired for no reason or if you have other symptoms of hypothyroidism.
If you are taking thyroid hormone medication to treat hypothyroidism, follow your doctor’s advice about how many appointments you need. At first, you may need regular appointments to make sure you are getting the right dose of medication. Over time, you may need tests so your doctor can monitor your condition and medication.



3 Comments