Unpacking the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting 16/8 for Diabetics
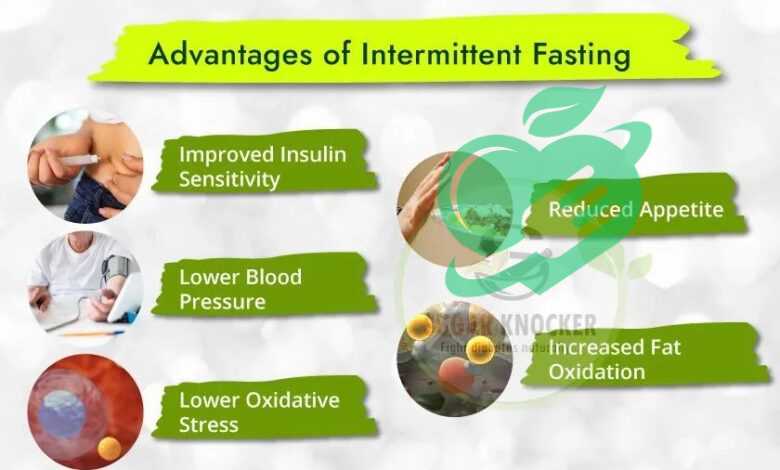
Definition and Basics of Intermittent Fasting16/8
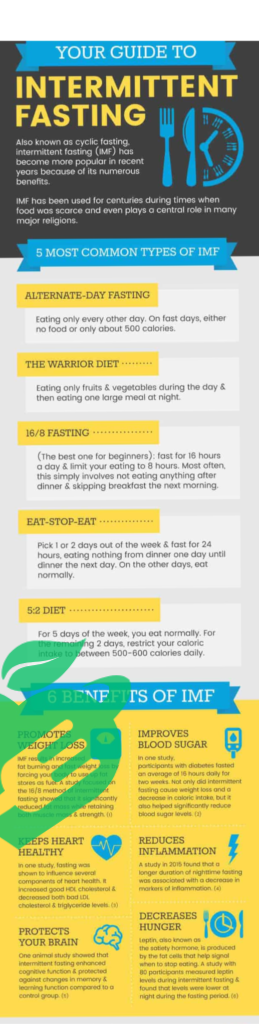
Intermittent fasting16/8 (IF) is more than just a trendy dietary approach; it is a strategic eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Unlike traditional diets that often dictate what you eat, intermittent fasting focuses on when you eat. There are several popular methods, including:
- 16/8 Method: Fasting for 16 hours and eating during an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 Diet: Eating normally for five days a week and limiting calories to about 500-600 on two non-consecutive days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: A 24-hour fast once or twice a week.
For diabetics, this approach can simplify meal planning while potentially aiding in blood sugar management and weight loss.
Prevalence of Diabetes and Importance of Management
Diabetes is a significant public health concern, affecting millions globally. According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults were living with diabetes in 2021, with numbers projected to rise dramatically over the next decade. This growing epidemic necessitates effective management strategies to mitigate complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve issues. Personalized management plans, which may include intermittent fasting, can be beneficial for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Consider Sarah, a busy professional diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. After struggling with her diet and weight, she decided to try intermittent fasting. By restricting her eating to an 8-hour window, she found not only an easier way to manage her meals but also noticed improved energy levels and better control of her blood sugar. Understanding the principles of intermittent fasting can empower diabetics to take the first step toward potentially enhancing their health and well-being.
Read also: Unlocking the Secrets of Alzheimer’s and Diabetes 3: A Comprehensive Guide.
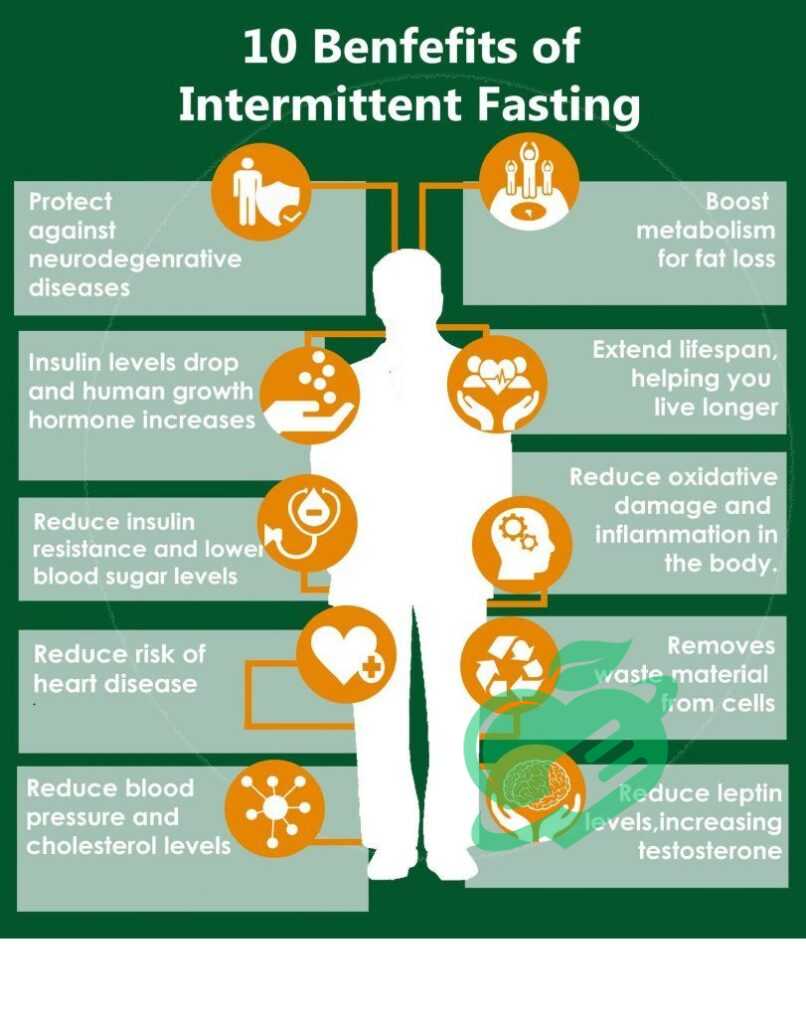
Impact of Intermittent Fasting16/8 on Diabetes
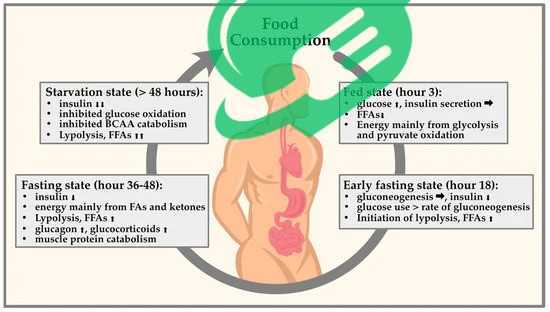
Intermittent fasting can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, which is particularly important for diabetics. When practiced correctly, intermittent fasting can lead to improved glycemic control. During fasting periods, the body shifts from using glucose as its primary energy source to burning stored fat. This transition can result in lower blood sugar spikes and more stable levels.
Read also: Supercharge Your Health with Hawthorn: Everything You Need to Know.
- Simplified Eating Patterns: With fewer meals to plan, diabetics may find it easier to monitor their carbohydrate intake and portion sizes.
- Reduced Levels of Insulin: Fasting can promote lower insulin levels, which is beneficial for those managing diabetes.
Take Mike, for example. After implementing a 16/8 fasting method, he noticed his fasting blood sugar levels reduced from an average of 150 mg/dL to about 120 mg/dL over a few months. This gradual improvement helped him feel more in control of his health.
Influence on Insulin Sensitivity
Another crucial aspect of intermittent fasting is its positive influence on insulin sensitivity. Enhanced insulin sensitivity means that the body’s cells can utilize insulin more effectively, allowing for better glucose uptake. Research indicates that intermittent fasting can:
- Increase Insulin Sensitivity: Regular fasting periods may help cells respond more effectively to insulin, especially in individuals with insulin resistance.
- Promote Weight Loss: As insulin sensitivity improves, weight management becomes more attainable, which is vital for diabetics.
For instance, Emily, a young woman diagnosed with prediabetes, adopted intermittent fasting and witnessed a remarkable change. Not only did her overall health improve, but her insulin sensitivity also increased, making it easier for her to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Through fostering better blood sugar control and improving insulin sensitivity, intermittent fasting can serve as a valuable tool in diabetes management, aiding individuals in achieving their health goals.
Read also: Optimizing Your A1C Levels: Strategies for Success.
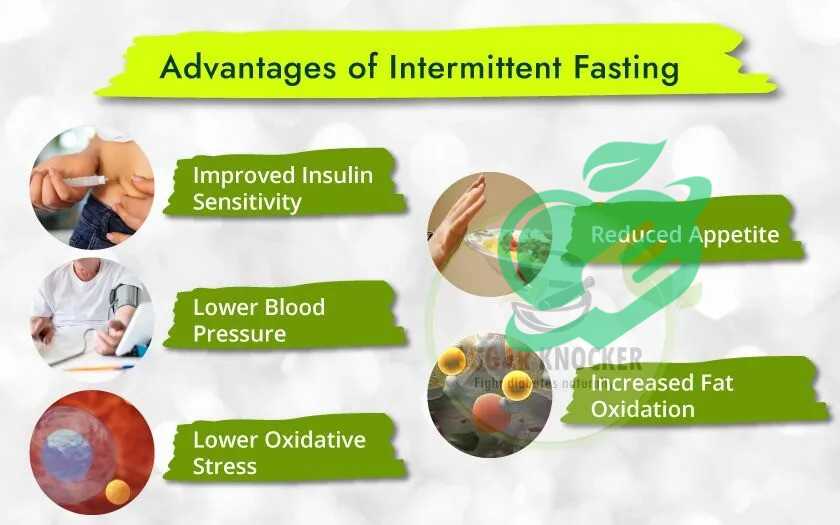
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting16/8 for Diabetics
Weight Management and Metabolic Health
One of the primary benefits of intermittent fasting for diabetics lies in its potential for effective weight management. Weight control is essential for those with diabetes, as excess body weight can exacerbate insulin resistance and complicate blood sugar regulation. Intermittent fasting offers several advantages for weight management:
- Caloric Restriction: By limiting the eating window, many individuals unintentionally reduce their overall calorie intake, which can lead to weight loss.
- Enhanced Fat Oxidation: Fasting periods encourage the body to tap into fat reserves for energy, aiding in fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass.
Consider Tom, who struggled for years with his weight and diabetes. After starting a 5:2 intermittent fasting plan, where he limited his caloric intake two days a week, he experienced significant weight loss and felt more energetic throughout the day. His success not only helped him manage his diabetes but also improved his overall metabolic health.
Potential Reduction of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Beyond weight management, intermittent fasting has shown promise in reducing cardiovascular risk factors, which is particularly crucial for diabetics who are at a higher risk for heart disease. Research indicates that intermittent fasting can lead to:
- Lowered Blood Pressure: Regular fasting may contribute to reductions in blood pressure, lowering stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Improved Cholesterol Levels: Fasting can lead to decreased levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides while helping to increase HDL (good) cholesterol.
For instance, Maria, a 55-year-old diabetic, noticed after six months of intermittent fasting that her cholesterol levels improved significantly, along with her blood pressure. This transformation not only gave her peace of mind but also brought her closer to achieving her long-term health goals. In summary, the benefits of intermittent fasting for diabetics extend beyond just managing blood sugar levels. By facilitating weight management and reducing cardiovascular risk factors, this approach can lead to a more robust, healthier lifestyle.
Read also: Headaches on Repeat: A Guide to Your Daily Struggle
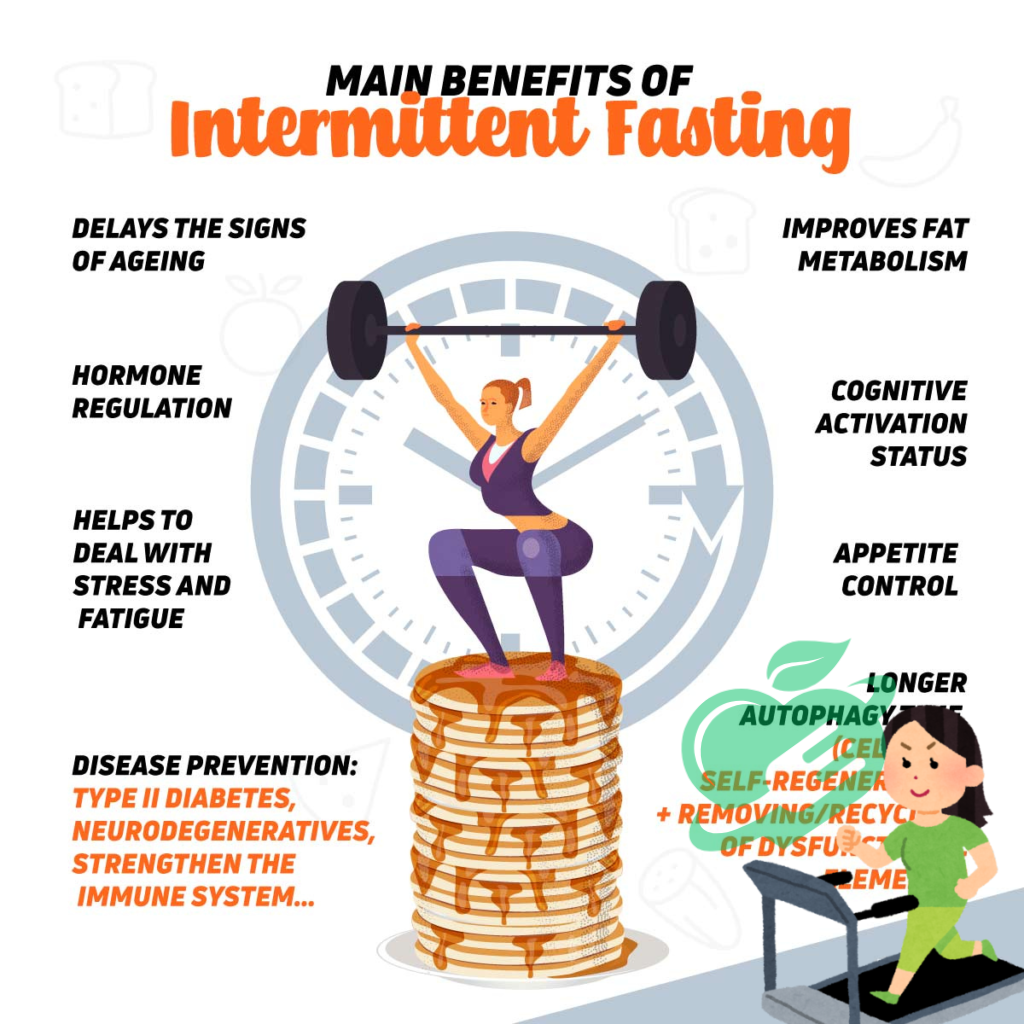
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Before diving into intermittent fasting, diabetics need to consult with healthcare providers. This step helps ensure that the fasting method chosen aligns with individual health needs. Each person’s diabetes management plan is unique, and a healthcare provider can offer insight tailored to specific situations. Here are a few reasons why this consultation is crucial:
- Personalized Guidance: Healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate fasting protocols based on medical history and current medications.
- Risk Assessment: A doctor can help assess any potential risks related to fasting, especially if diabetes medications are involved, which may need adjustments.
Take Lisa’s example. As a newly diagnosed diabetic, she felt overwhelmed by dietary choices. After discussing her interest in intermittent fasting with her healthcare team, they collaboratively established a safe fasting schedule that supported her glucose control while catering to her lifestyle.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels during intermittent fasting is another critical component of safely implementing this dietary approach. Regular checks help ensure that blood sugar remains within target ranges and allow diabetics to respond to changes as necessary. Consider these effective monitoring strategies:
- Frequent Checks: Especially during the initial stages of fasting, it’s essential to check blood sugar levels more frequently to understand how the body responds.
- Keeping a Log: Maintaining a log of blood glucose readings alongside fasting times can help identify patterns or triggers that impact blood sugar.
- Adjusting Medications: If fasting leads to lower blood sugar levels, healthcare providers may need to adjust medication dosages accordingly.
For instance, David started intermittent fasting and diligently monitored his blood sugar levels. By doing so, he discovered that fasting improved his overall readings, which prompted him to continue with confidence. In conclusion, implementing intermittent fasting safely requires collaboration with healthcare providers and diligent monitoring of blood glucose levels. These practices can greatly enhance the effectiveness of fasting while minimizing potential risks, leading to a healthier lifestyle for diabetics.
Read also: Understanding the New Diabetes Criteria: What You Need to Know.

Tips for Successful Intermittent Fasting16/8 with Diabetes
Choosing the Right Fasting Protocol
Choosing the right intermittent fasting protocol is crucial for success, especially for diabetics. With various methods available, it’s essential to select one that aligns with personal preferences, lifestyle, and health conditions. Some popular fasting protocols include:
- 16/8 Method: Fast for 16 hours and eat in an 8-hour window. This can be a flexible approach that fits nicely into daily routines.
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally for five days and restrict caloric intake on two non-consecutive days. This allows for creativity in meal planning while promoting a structured approach.
Sarah found success with the 16/8 method, which allowed her to enjoy breakfast at 10 AM and finish eating by 6 PM. By choosing a method that felt natural to her daily routine, she could focus on managing her diabetes without overwhelming herself.
Incorporating Nutrient-Dense Foods
Another key element to successful intermittent fasting is incorporating nutrient-dense foods during eating periods. Choosing foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and keep energy high. Here are some tips for selecting the right foods:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These support overall health while managing blood sugar.
- Watch Portion Sizes: While fasting can reduce calorie intake, portion control remains vital to ensure that meals are satisfying yet nutritious.
- Plan Meals: Consider meal prepping to ensure easy access to healthy options during eating windows, making it less likely to grab unhealthy snacks.
For example, when Jennifer began her intermittent fasting journey, she made it a point to prepare meals rich in vegetables and lean proteins. Not only did this help her feel full and satisfied, but it also contributed to more consistent blood sugar control. By choosing the right fasting protocol and focusing on nutrient-dense foods, diabetics can thrive while implementing intermittent fasting. These thoughtful choices empower individuals to take charge of their health and find harmony within their eating habits.
Read also: What leads to Type 2 Diabetes?
Hypoglycemia Risks and Precautions
While intermittent fasting can be beneficial for many diabetics, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks, particularly the danger of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. This condition can occur when insulin levels remain high and food intake is restricted, causing glucose levels to drop dangerously low. To mitigate these risks, consider these precautions:
- Awareness of Symptoms: Familiarize yourself with the signs of hypoglycemia, such as dizziness, weakness, hunger, and irritability.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring during fasting periods allows for timely interventions if levels begin to drop. Keeping glucose tablets or snacks on hand can be lifesaving.
- Gradual Adjustment: If transitioning into intermittent fasting, start with shorter fasting periods. Gradually increasing the fasting duration helps the body adapt more comfortably.
For instance, after adopting intermittent fasting, Mark experienced low blood sugar one afternoon. By having glucose tablets readily available, he quickly stabilized his levels. This experience underscored the importance of preparation and awareness.
Interactions with Medications
Another crucial consideration for diabetics practicing intermittent fasting is the potential for interactions with medications. Many diabetes medications, particularly insulin and sulfonylureas, can cause blood sugar levels to drop significantly if not appropriately managed during fasting. Here are the steps to take:
- Consult with Healthcare Providers: It’s vital to communicate with doctors about any fasting plans to adjust medication dosages if necessary. Regular follow-ups can ensure that both diet and medication work harmoniously.
- Educate yourself: Understand how your specific medications work and how fasting may influence their effectiveness.
- Keep a Medication Log: Tracking when and how much medication is taken can help identify patterns related to fasting and blood sugar levels, informing necessary adjustments.
Read also: Everything you care about dry skin.
For example, when Angela started intermittent fasting, her doctor advised adjusting her insulin dosage to avoid hypoglycemia. By staying informed and connected with her healthcare team, she managed to incorporate fasting safely. By addressing these potential concerns regarding hypoglycemia and medication interactions, diabetics can navigate the world of intermittent fasting more safely, ensuring a positive and health-promoting experience.
Read also: How does diabetes affect your mood?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it OK to do 16/8 intermittent fasting every day?
While 16/8 intermittent fasting is usually regarded as safe for healthy adults, it’s important to consult your doctor if you have any pre-existing health issues. This is especially crucial if you are on medication, have diabetes, experience low blood pressure, or have a background of eating disorders. 1
What are the rules for 16/8 intermittent fasting?
This approach consists of a 16-hour daily fast, allowing for an 8-hour period to eat normally. Some people prefer to forgo breakfast and have lunch and dinner, while others opt for breakfast and lunch, skipping dinner instead. Many individuals find it manageable to maintain this routine over an extended period. 2.
Do you lose weight on the 16/8 intermittent fasting?
The 16:8 intermittent fasting method is a type of time-restricted eating pattern. It allows for an 8-hour period during which food can be eaten, followed by 16 hours of fasting. This approach may offer benefits such as weight loss, fat reduction, and a lower risk of certain diseases. 3
What are the best times for 16/8 intermittent fasting?
The 16/8 intermittent fasting schedule is similar to the 14/10 schedule, except that you fast for an additional 2 hours. As a result, your eating window is 2 hours shorter. For instance, you could eat between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m., or you might opt to fast until noon and finish your last meal by 8 p.m. 4.
Which meal is best to skip for intermittent fasting?
Individuals practicing intermittent fasting often miss either breakfast or dinner. However, experts recommend that if one has to choose between the two, it’s better to skip dinner. 5.
Tailoring Fasting16/8 Patterns to Individual Needs
Intermittent fasting isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, especially for diabetics. Personalizing the fasting approach is crucial for sustainability and effectiveness. Every individual has unique health needs, lifestyles, and preferences, so tailoring fasting patterns can make the journey much smoother. Here are some effective ways to customize a fasting plan:
- Assess Your Lifestyle: Consider your daily schedule, work commitments, and social activities. For instance, if you often have social lunches, a fasting method that allows an earlier eating window might suit you better.
- Prioritize Comfort: Choose a fasting protocol that feels manageable. Some may prefer the 16/8 method, which allows for regular meals within an 8-hour window, while others might find more success with the 5:2 approach.
For example, David found that a 14/10 fasting schedule fit seamlessly into his busy life, allowing him to have breakfast with his family while still reaping the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting as Necessary
Tracking progress plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of any fasting regimen. Monitoring not just weight but also blood sugar levels, energy, and overall well-being can provide valuable feedback. Here are some tips for effective tracking:
- Keep a Journal: Documenting daily feelings, blood sugar levels, and any challenges can help identify patterns and issues over time.
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish measurable and achievable goals. Celebrate small victories, such as a consistent blood sugar target or successfully adhering to the fasting schedule for a month.
Take Emma, who meticulously tracked her blood glucose levels while fasting. By logging her results weekly, she noticed that certain fasting days led to improved blood sugar readings. With this data, she and her healthcare provider made informed adjustments to her fasting schedule and meal plan, leading to even better outcomes. By personalizing fasting patterns and actively tracking progress, diabetics can create a flexible, effective, intermittent fasting plan that enhances their health journey and empowers them to achieve lasting results.
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.
- healthline ((↩))
- healthxchange ((↩))
- medicalnewstoday ((↩))
- zoe ((↩))
- hindustantimes ((↩))



2 Comments