Vaginitis Unveiled: Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention

Definition of Vaginitis
Vaginitis is a common condition that refers to the inflammation of the vagina, often causing discomfort and requiring attention. This inflammation can lead to changes in vaginal discharge, itching, and irritation. Many women experience vaginitis at some point in their lives, and understanding it is crucial for maintaining reproductive health. Imagine a woman who, after a long day, feels an unusual itch and irritation. She might dismiss it as a minor annoyance. However, this could be a sign of vaginitis that warrants further investigation. Recognizing the signs can lead to early intervention and relief.
Types of Vaginitis
There are several types of vaginitis, each with distinct causes and symptoms. Here are the most common:
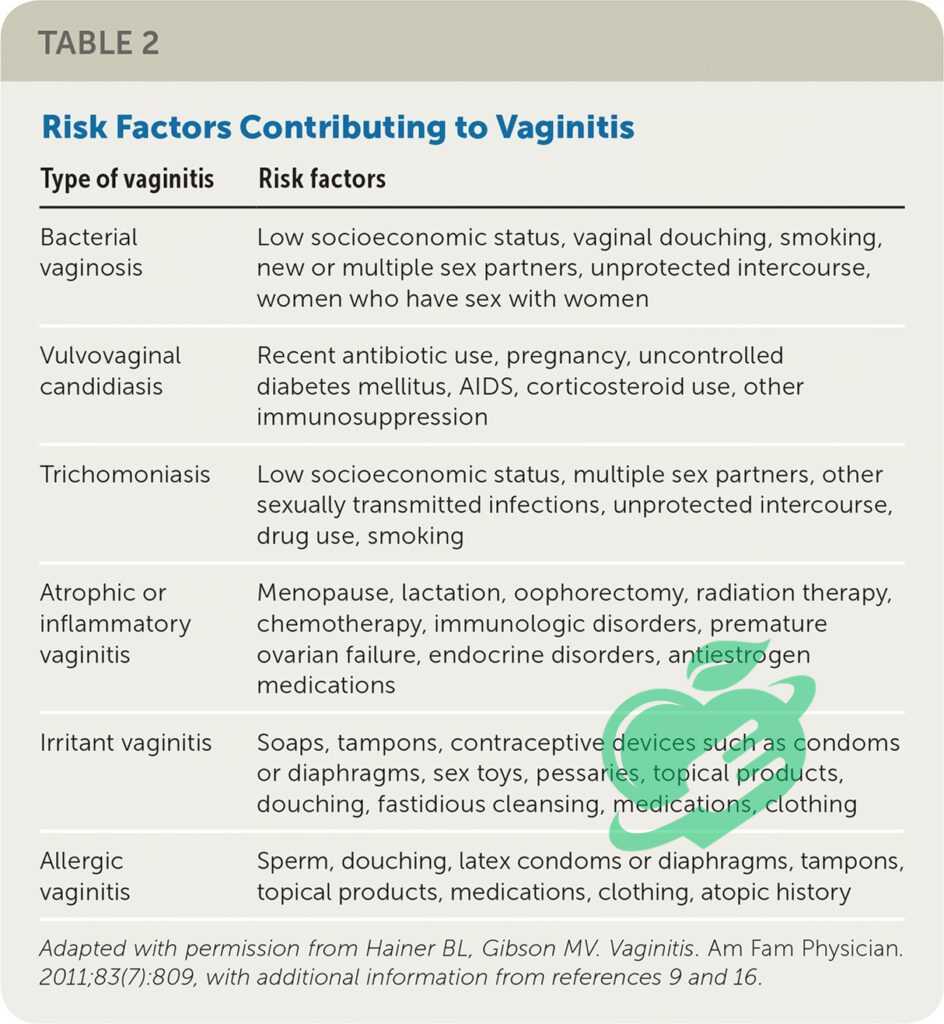
- Bacterial Vaginosis: A result of an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina.
- Yeast Infections: Often caused by an overgrowth of Candida, leading to intense itching and thick discharge.
- Trichomoniasis: A sexually transmitted infection caused by a protozoan parasite.
- Atrophic Vaginitis: Occurs due to decreased estrogen levels, commonly affecting postmenopausal women.
Understanding these types empowers women to seek appropriate treatment and maintain their health.
Read also: Say Goodbye to Itchy Skin with Antihistamine Cream!
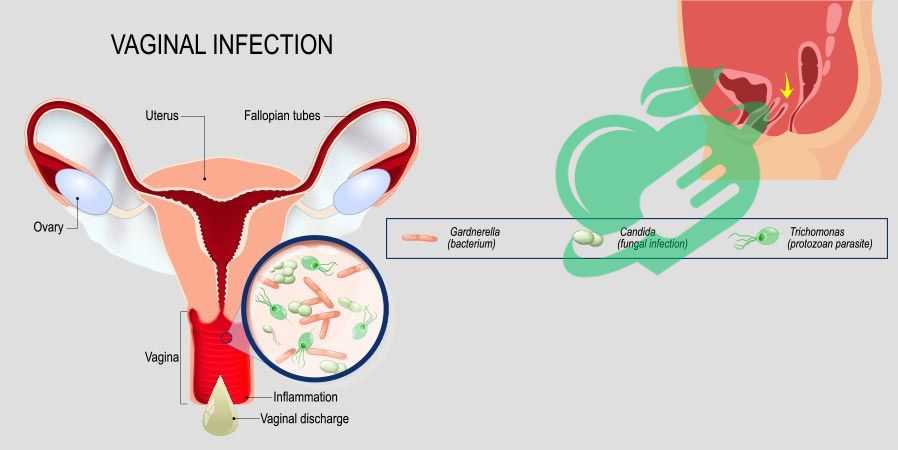
Symptoms of Vaginitis
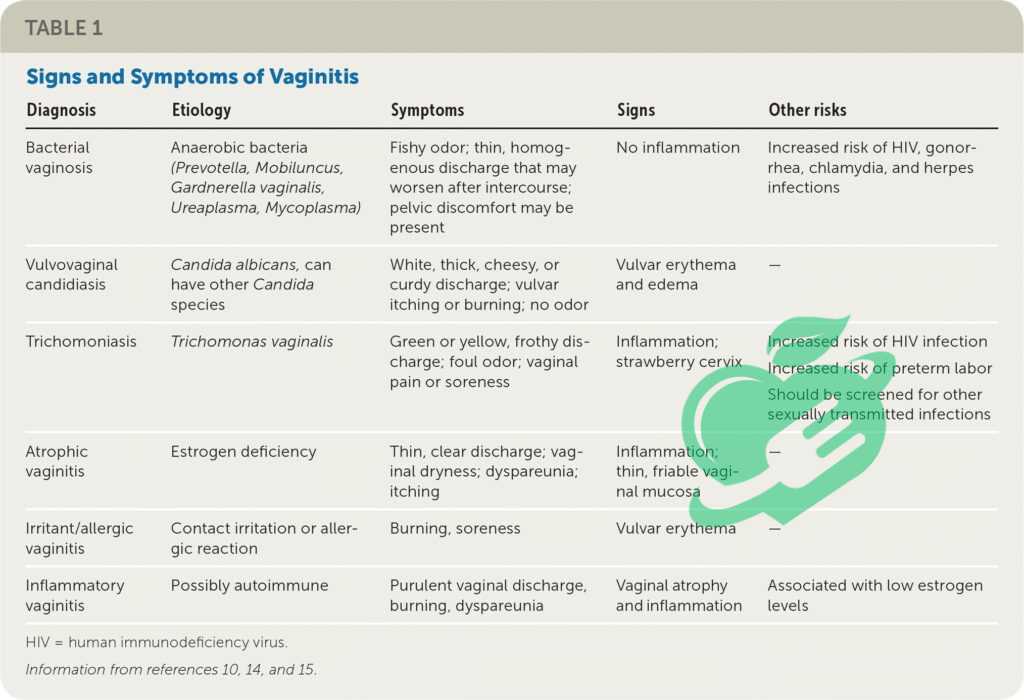
Identifying the symptoms of vaginitis is essential for seeking timely treatment. Women experiencing vaginitis may notice a variety of symptoms, which can vary based on the type of infection. Some of the most common signs include:
- Itching or irritation: A persistent itch can be troubling and difficult to ignore.
- Unusual discharge: The color, odor, and consistency of vaginal discharge may change.
- Burning sensation: This can occur during urination or sexual intercourse.
- Redness or swelling: The vaginal area might appear inflamed.
For instance, Sarah, a 29-year-old, suddenly found herself with a thick, white discharge accompanied by severe itching. Her experience highlights the importance of paying attention to changes in one’s body.
When to See a Doctor
While some cases of vaginitis can resolve on their own, it’s crucial to know when to seek medical advice. Consider consulting a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Symptoms lasting more than a few days
- Severe discomfort that affects daily activities
- A recurring pattern of infections
- Unpleasant or strong-smelling discharge
Prompt consultation not only offers relief but can also help address underlying issues effectively. Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to health!
Causes of Vaginitis
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is one of the primary causes of vaginitis and arises from an imbalance in the natural bacteria present in the vagina. When “good” bacteria like Lactobacillus are low, harmful bacteria can multiply, leading to inflammation. Factors such as douching, new sexual partners, and inconsistent condom use may contribute to this imbalance. For example, Jessica, a 34-year-old, experienced BV after changing her contraceptive method, leading to discomfort and unusual discharge.
Yeast Infections
Yeast infections, often caused by the overgrowth of Candida fungi, are another common culprit. Various factors can trigger this, including antibiotic use, hormonal changes, or even diet high in sugar. When Nathan, a 28-year-old, noticed itching and a thick, white discharge, he realized it was time to address his recent antibiotic course—a known risk factor for yeast overgrowth.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by a parasite, can also result in vaginitis. It’s spread through sexual contact and may present as itching, burning, and foamy discharge. This condition can affect anyone, regardless of gender, highlighting the importance of safe sex practices. If someone suspects exposure, seeking medical attention is essential to prevent complications and further spread. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment!
Diagnosing Vaginitis
Diagnosing vaginitis typically starts with a thorough medical history and physical exam. During the consultation, healthcare providers may ask about symptoms, recent sexual activity, hygiene practices, and any medications or changes in health. For instance, when Lisa, a 27-year-old, visited her doctor due to vaginal discomfort, her provider asked about her menstrual cycle and any changes in routine, which helped pinpoint potential causes. A physical exam often includes a pelvic exam to evaluate the vaginal area for signs of inflammation or abnormalities. Observing any unusual discharge can make it easier to determine the type of vaginitis.
Read also : The Ultimate Vitex Agnus Castus Handbook: Tips and Tricks Revealed
Lab Tests and Procedures
Once the initial assessment is complete, lab tests may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis. These tests can include:
- Vaginal swab: Samples are taken and analyzed for bacteria, yeast, and other pathogens.
- Microscopic examination: This allows doctors to identify the specific cause of the infection.
- pH testing: Measuring the vaginal pH can help differentiate between bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections.
Confirming the diagnosis through these tests ensures the most effective treatment plan is put in place, providing relief and promoting a return to health.
Read also: How does diabetes affect your mood?
Medications for Vaginitis
When it comes to treating vaginitis, the approach often depends on the underlying cause. For bacterial vaginosis, healthcare providers typically prescribe antibiotics, such as metronidazole or clindamycin, to restore the natural balance of bacteria. In the case of yeast infections, antifungal medications like fluconazole or topical treatments such as clotrimazole work effectively to relieve symptoms. For instance, when Emily, a 31-year-old, struggled with recurrent yeast infections, her doctor prescribed a course of oral fluconazole, which finally helped her find relief. Meanwhile, trichomoniasis is treated with specific antibiotics like metronidazole or tinidazole, and it’s essential for partners to be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
In addition to medications, many women find relief through home remedies and self-care practices. Some effective strategies include:
- Probiotics: Consuming yogurt or supplements may help restore the natural balance of bacteria.
- Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress can alleviate discomfort and inflammation.
- Avoiding irritants: Steering clear of scented products or harsh soaps can prevent further irritation.
Embracing a proactive approach to self-care enables women to manage symptoms while collaborating with healthcare professionals for comprehensive treatment.
Preventive Measures for Vaginitis
Hygiene Practices
When it comes to preventing vaginitis, maintaining proper hygiene is key. Simple yet effective practices can go a long way in reducing the risk. Here are some helpful tips:
- Daily washing: Use mild, unscented soap and water to gently clean the vaginal area.
- Avoid douching: Douching can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and lead to infections.
- Wear breathable fabrics: Opt for cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing to promote ventilation.
For instance, Angela, a 26-year-old, noticed a significant decline in her irritation after switching to more breathable fabrics, enabling her skin to breathe and reducing moisture buildup.
Read also : The Pelvic Exam: What Every Woman Should Know
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to hygiene, lifestyle changes can also help prevent vaginitis. Consider incorporating these practices into your routine:
- Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support your immune system.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated helps maintain overall health and can reduce dryness.
- Safe sex: Using condoms can lower the risk of sexually transmitted infections that contribute to vaginitis.
Making these lifestyle adjustments not only fosters a healthier body but can also significantly contribute to improved vaginal health, empowering women to take control of their well-being.
Read also: Headaches on Repeat: A Guide to Your Daily Struggle

Frequently asked questions
What does BV discharge look like?
Bacterial vaginosis happens when there is an overgrowth of specific bacteria in the vagina. While it can be spread through sexual activity, that is not always the case. Individuals with BV often experience a white or gray discharge that has a strong, fishy odor. The condition is typically treated with antibiotics. 1
Why does my boyfriend keep giving me BV?
In essence, the pH levels of a healthy vagina and penis differ, and research has shown that the harmful bacteria from a penis can disrupt the vaginal pH, making it more vulnerable to recurrent bacterial vaginosis infections. 2
What causes vaginitis?
Vaginitis can be caused by bacteria, yeast, viruses, chemicals found in creams or sprays, and even clothing. It can also arise from organisms transmitted between sexual partners. Additionally, various factors can influence the health of your vagina. 3
What does vaginitis smell like?
The symptoms of vaginitis vary based on the specific type. In the case of bacterial vaginosis (BV), you might not experience any symptoms at all. If symptoms do occur, you could notice a thin discharge that is white or gray in color. Additionally, there may be a strong fishy odor, particularly after sexual intercourse. 4
How do you tell if a woman has a bacterial infection?
Bacterial vaginosis leads to a thin discharge that can be yellow-green or gray in color, often occurring in large amounts and having a fishy smell. When symptoms indicate a vaginal infection, physicians will analyze a sample of the discharge or cervical fluid to check for infectious agents.5
When to Consult a Doctor
Red Flags
While some mild symptoms of vaginitis may resolve on their own, it’s essential to be vigilant about certain red flags. Recognizing when to consult a doctor is crucial for ensuring proper care. Here are some warning signs that should prompt you to seek medical attention:
- Severe pain: If you experience intense itching or pain that disrupts your daily life.
- Foul odor: An unusual, strong odor accompanying vaginal discharge can indicate an infection.
- Unusual discharge: If the discharge changes in color (yellow, green) or consistency (frothy).
- Recurrent infections: Frequent episodes of vaginitis may signal an underlying condition.
For example, when Kelly, a 23-year-old, noticed a persistent foul odor and worsening discomfort, she recognized it was time to visit her doctor.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you identify any of these red flags, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can provide valuable insights and diagnostic testing to determine the cause of your symptoms. Early intervention is key to preventing complications and ensuring proper treatment, which can ultimately lead to relief and a return to daily activities. Remember, your health is a priority, and proactive steps can make all the difference!
Read also: Empower Your Health: Recognizing and Addressing 8 Triggers of Vaginal Pain
Recap of Key Points
In summary, vaginitis is a common condition that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. It’s essential to be aware of the different types, including bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, and trichomoniasis. Recognizing symptoms such as itching, unusual discharge, and discomfort serves as a vital first step in addressing the issue. Key takeaways include:
- Prevention: Hygiene practices and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of vaginitis.
- Diagnosis: Understanding the importance of medical history, physical exams, and lab tests will help in obtaining a proper diagnosis.
- Treatment: Prompt treatment options, including medications and home remedies, can alleviate symptoms effectively.
Importance of Vaginitis Awareness
Awareness of vaginitis and its symptoms is crucial for women’s health. Many women may feel embarrassed to discuss their symptoms, but it’s essential to remember that these are common health concerns that can easily be treated. By educating ourselves and others about vaginitis, we empower women to seek help without stigma and promote open conversations around vaginal health. Taking charge of one’s health is not just about treatment; it’s also about prevention and awareness!
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.
- Reference
- clevelandclinic ((↩))
- intimaterose ((↩))
- hopkinsmedicine ((↩))
- medlineplus ((↩))
- msdmanuals ((↩))




2 Comments