Unveiling the Secrets of ECG Readings for Better Health

What is ECG?
Electrocardiography, commonly known as ECG Readings, is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart over some time. Using electrodes placed on the skin, an ECG provides a visual representation of the heart’s electrical signals. This method is non-invasive, quick, and vital for assessing heart health. Imagine you’re at the doctor’s office for a routine check-up. You casually mention some occasional heart palpitations. The doctor nods and quickly hooks you up to an ECG machine. In just a few minutes, you can see your heart’s rhythm displayed on the monitor, along with any irregularities. That’s the power of ECG!
Importance of ECG Readings
ECG readings are pivotal for several reasons:
- Diagnosis: They help diagnose heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and ischemic heart disease.
- Monitoring: ECGs allow healthcare providers to continuously monitor a patient’s heart health, especially during surgeries or in emergencies.
- Risk Assessment: By examining the ECG waves, doctors can evaluate the risk of potential heart diseases in apparently healthy individuals.
The ability to catch anomalies early can be life-saving. For instance, atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder, can lead to serious complications like stroke if not detected promptly. Regular ECG screenings empower patients by promoting proactive heart health measures. In conclusion, understanding ECG readings is crucial for anyone who values their cardiovascular health. It serves as a window into the heart’s functioning, revealing insights that can guide treatment and prevention efforts.
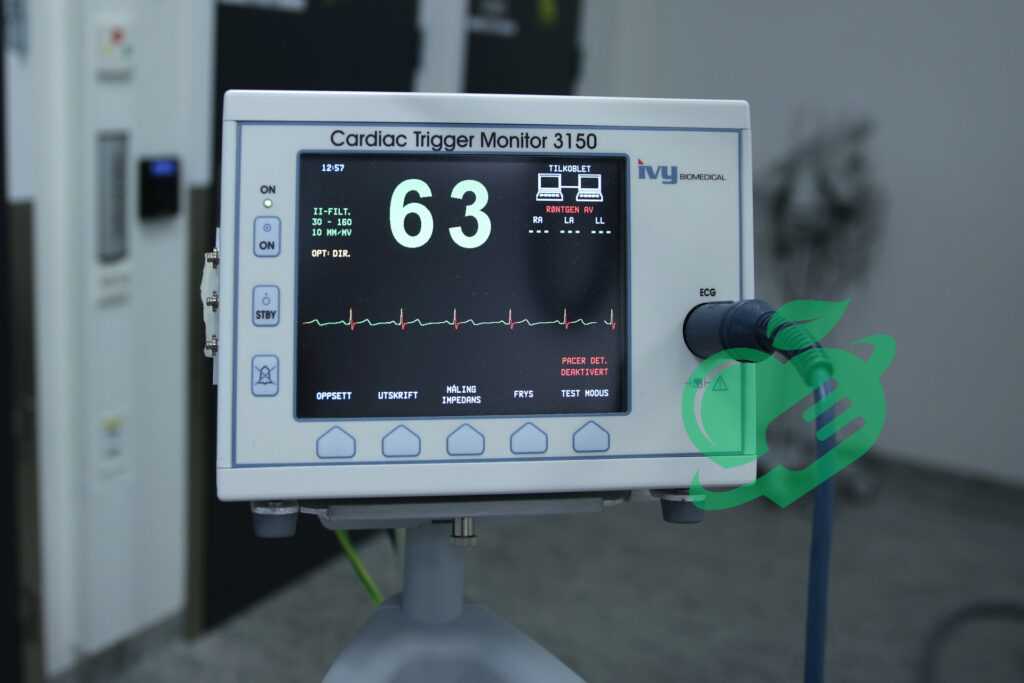
How ECG Works
Now that we’ve explored the significance of ECG readings, it’s essential to understand how ECGs are conducted. The first step involves the strategic placement of electrodes on the patient’s body. These small, sticky pads are responsible for capturing the electrical signals emitted by the heart. During an ECG test, typically 10 electrodes are placed:
- Standard 12-lead configuration: This includes
- 4 limb electrodes: One on each arm and leg.
- 6 chest electrodes: Positioned across the chest to monitor the heart from various angles.
You might feel a brief tingling sensation as the electrodes adhere to your skin, but it’s painless. The electrodes pick up electrical impulses and send them to a machine that translates these signals into a visual graph, known as an electrocardiogram.
ECG readings of the heart’s electrical activity
The heart functions like a finely-tuned electrical circuit. At the core of this circuit is the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s natural pacemaker. When the SA node sends out electrical impulses:
- Atria Contract: The upper chambers of the heart contract and pump blood into the lower chambers.
- Ventricles Contract: The impulses travel to the ventricles, causing them to contract and push blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
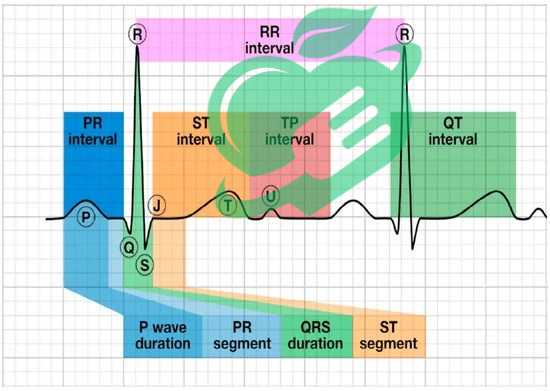
This electrical activity creates distinct waves—P, QRS, and T waves on the ECG. Understanding these patterns is essential for interpreting the heart’s function effectively. For instance, a healthy heart rhythm shows a clear and consistent pattern, like a well-rehearsed symphony. Any irregularities can indicate underlying conditions that may require further investigation. So, the next time you see an ECG, remember: it’s not just lines on paper—it’s the story of your heart’s health unfolding!
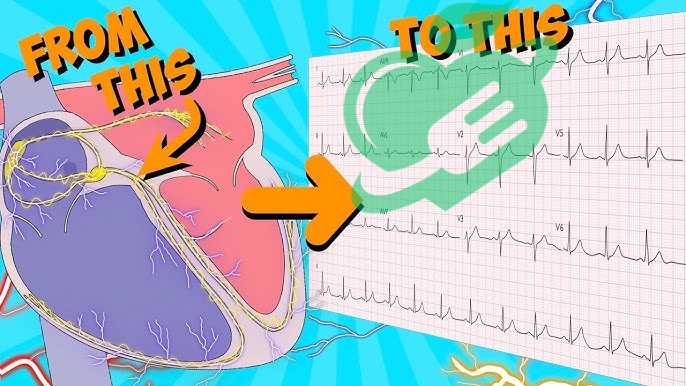
Interpretation of ECG Waves
Understanding ECG waves is like reading a novel where your heart tells the story of its rhythm and health. Each wave provides unique information, shedding light on the electrical impulses driving your heartbeat. Let’s dive into the three main components of the ECG trace: the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave.
P wave
The P-wave presents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the atria, the heart’s upper chambers. Imagine it as the opening chapter of your heart’s story—short and sweet, setting the pace for what follows.
- Normal Characteristics: The P P-wave should be small, rounded, and positive in shape.
- Clinical Significance: Abnormalities in the P P-wave indicate issues such as atrial enlargement or atrial fibrillation. If your doctor notices alterations here, it may warrant further tests or concerns.
QRS complex – ECG Readings
Next up is the QRS complex, which represents the electrical activity of the ventricles, the heart’s lower chambers. This is like the climax of the heart’s story—intense and vital for circulation.
- Normal Characteristics: The QRS complex is typically sharp and narrow.
- Clinical Significance: A wider QRS complex can suggest issues such as ventricular hypertrophy or blockages in heart conduction pathways. Observing these patterns gives valuable insights into the heart’s pumping efficiency.
T wave – ECG Readings
Lastly, we have the T wave, which corresponds to the repolarization of the ventricles. Think of it as the resolution chapter of your heart’s saga.
- Normal Characteristics: The T wave should be smooth and rounded, typically positive in most leads.
- Clinical Significance: Inverted T waves could indicate repolarization issues or even ischemia (reduced blood flow) to the heart muscle.
Each component of the ECG reading serves as a clue, helping healthcare professionals piece together the story of your heart’s health. Recognizing these waves can empower you to take an active role in understanding your cardiovascular well-being. So, the next time you’re faced with an ECG, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor to walk you through the plot twists and turns of your heart’s rhythm!

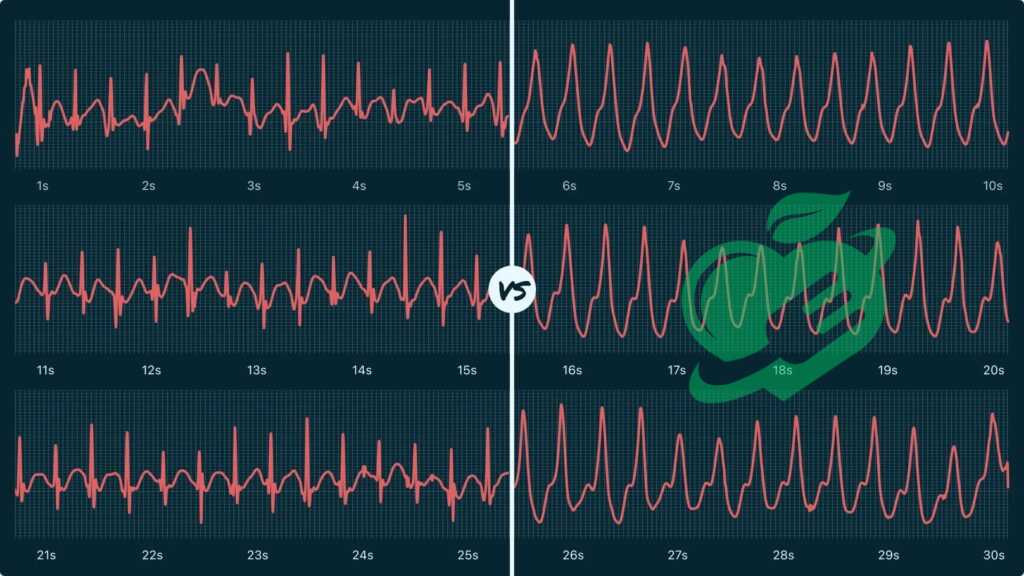
Common ECG Patterns and Abnormalities
As we delve deeper into ECG readings, it becomes crucial to recognize some common patterns and their potential abnormalities. Understanding these can help in identifying issues early on. Let’s explore three prominent patterns: Normal Sinus Rhythm, Atrial Fibrillation, and Ventricular Tachycardia.
ECG readings for normal sinus rhythm
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) is the heart’s ideal rhythm, a melody that indicates a healthy heart function. In this pattern, the heart beats between 60 to 100 beats per minute, showcasing a consistent and organized sequence of waves.
- Characteristics:
- Regular intervals between beats.
- Clear P wave preceding each QRS complex.
Think of it as a well-orchestrated performance where all musicians are in sync. If your ECG shows NSR, it signals that your heart is functioning properly, nd blood is flowing effectively throughout your body.
Read also: Thyroid Troubles? Find Relief with Effective Hypothyroidism Treatments
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is a common yet concerning arrhythmia characterized by a chaotic and irregular heart rhythm. It occurs when the electrical impulses in the atria misfire, leading to ineffective contractions.
- Characteristics:
- Absence of distinct P waves.
- Irregularly spaced QRS complexes.
Imagine a jazz band where every musician starts improvising at once—exciting but chaotic! AFib can lead to blood clots and increase the risk of stroke, making it essential to manage and monitor.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) is potentially life-threatening, defined by an abnormally fast heart rate originating from the ventricles. This condition often results from structural or electrical issues within the heart.
- Characteristics:
- A fast heart rate, usually more than 100 beats per minute.
- A wide QRS complex.
Picture a racing engine that has gone out of control—VT can compromise the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, requiring immediate medical intervention. Identifying these common ECG patterns can lead to timely and effective treatments. As with any important diagnostic tool, knowing what to look for can empower patients and caregivers alike, reinforcing the importance of regular check-ups and awareness of heart health.
Read also: Cardiomyopathy Ischemic ICD 10: What You Need to Know.
Clinical Applications of ECG
With a solid understanding of common ECG patterns, it’s time to explore their practical applications in clinical settings. ECGs serve two fundamental purposes: diagnosing heart diseases and monitoring overall cardiac health. Let’s break these down further.
Diagnosing Heart Diseases
One of the most critical roles of an ECG is diagnosing various heart diseases. A simple, quick test can reveal significant information about a patient’s heart health, which may not be obvious through physical examinations alone.
- Common Conditions Identified:
- Coronary Artery Disease: ECG abnormalities can indicate reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can be diagnosed swiftly through distinct waveform changes.
- Heart Attacks: An acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) often shows up clearly on an ECG with specific patterns.
Consider a scenario where a person older than 70 visits a clinic complaining of chest pain. A quick ECG can help the doctor assess if there’s a possible heart attack in progress, guiding immediate treatment and preventing further complications.
Monitoring Cardiac Health
In addition to diagnostics, ECGs are invaluable for ongoing cardiac health monitoring. Patients with known heart conditions or those undergoing treatment for heart-related issues often require regular ECG assessments.
- Key Monitoring Aspects:
- Effectiveness of Medication: Doctors can track how well heart medications are working by observing changes in ECG readings.
- Patient Rehabilitation: After procedures like angioplasty or surgery, ECGs help monitor recovery and heart function over time.
Think of a marathon runner who trains rigorously. Just as they measure progress and adjust training schedules based on performance metrics, healthcare providers rely on ECGs to fine-tune treatments and ensure patients are on the right path toward recovery. In conclusion, ECGs are more than just a diagnostic tool; they play a vital role in managing cardiac health throughout a patient’s journey. Being aware of their clinical applications can encourage informed discussions between patients and healthcare providers, highlighting the importance of proactive heart health.
ECG Reading Tips
As we continue our journey through ECGs, it’s essential to equip ourselves with practical tips for accurate reading and interpretation. Two critical skills in ECG analysis are artifact recognition and calculating heart rate. Let’s dive into these aspects to enhance our understanding.
Artifact Recognition
Artifact recognition refers to identifying unwanted signals on an ECG that can obscure the true electrical activity of the heart. These artifacts may arise from various sources, such as movement, electrical interference, or poor electrode contact.
- Common Causes of Artifacts:
- Patient Movement: Shivering or fidgeting can create irregular waveforms.
- Loose Electrodes: Poor adhesion can result in fluctuating readings.
- Electrical Interference: Nearby electronic devices can introduce noise into the signals.
Imagine you’re at a concert, trying to enjoy the music, but someone nearby keeps tapping their feet noisily. Just like that distraction, artifacts can make it hard to focus on the underlying heart rhythm. Learning to identify these artifacts means you can disregard misleading signals and hone in on what truly matters in the ECG reading.
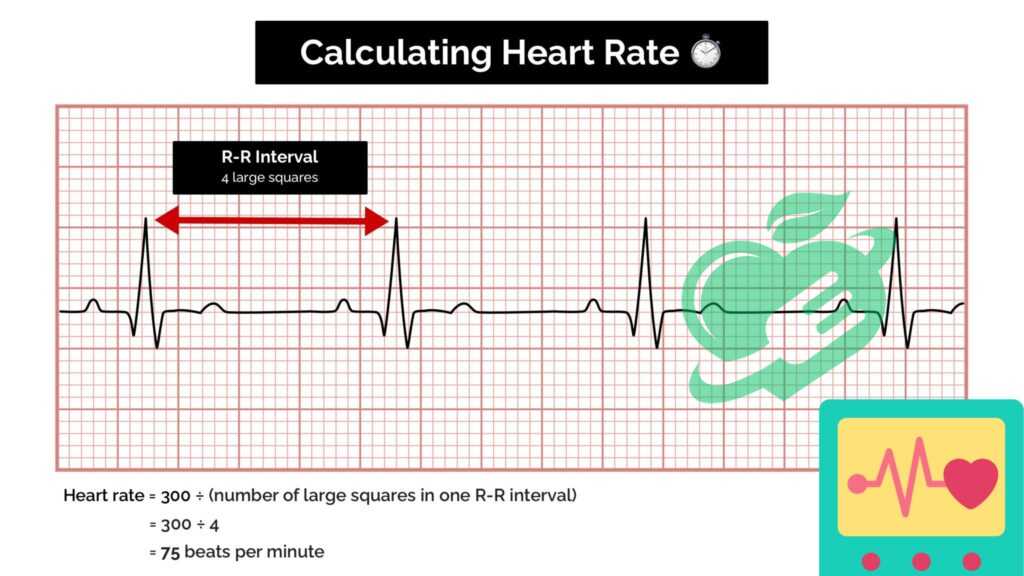
Calculating Heart Rate from ECG Readings
Another fundamental skill in reading an ECG is calculating the heart rate. The heart rate indicates how many times the heart beats in a minute; knowing how to measure it correctly can provide important insights into a person’s cardiovascular health.
- Methods for Calculation:
- The 300 Method: Count the number of large squares between R-waves in the ECG and divide 300 by that number.
- The 1500 Method: Count the number of small squares between two R R-waves and divide 1500 by that number.
For example, if there are five large squares between two R peaks, then the heart rate is 300/5 = 60 beats per minute. Just like a coach analyzing an athlete’s performance, understanding heart rate allows healthcare providers to assess the heart’s efficiency during different physical activities or stress levels. By mastering artifact recognition and heart rate calculation, one can navigate the complexities of ECG readings with confidence. These skills not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also empower patients to engage actively in their cardiovascular health journey.
Read also: Innovative Therapies for Treating Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Challenges in ECG Interpretation
While ECGs are invaluable in assessing heart health, interpreting these readings isn’t always a straightforward task. Healthcare providers often encounter challenges, especially with artifact interference and differentiating between various arrhythmias. Let’s explore these hurdles.
ECG readings due to interference with artifacts
Artifact interference can complicate the interpretation of ECG readings as it disguises the true electrical activity of the heart. These artifacts can stem from numerous sources, making them sometimes difficult to detect.
- Common Sources of Artifacts:
- Electrode Issues: Loose or poorly placed electrodes can introduce noise into the ECG.
- Patient Movement: If a patient is anxious or unable to remain still, the resulting movements can distort the readings.
- Electrical Interference: External electronic devices may introduce unwanted signals into the ECG trace.
Think of it as listening to a loved one speaking in a crowded café; background noise can distort the message. Similarly, recognizing and mitigating artifacts is essential for an accurate interpretation. Ignoring these distractions is crucial for deriving meaningful clinical insights from the ECG.
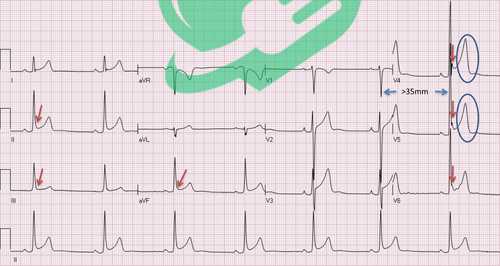
Differentiating between Arrhythmias
Another significant challenge in ECG interpretation is differentiating between various types of arrhythmias. The heart can exhibit a wide array of rhythms, and distinguishing between them requires experience and keen observation.
- Common Arrhythmias to Differentiate:
- Atrial Fibrillation: An irregular rhythm with no distinct P waves.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Rapid, wide QRS complexes indicate a fast heartbeat originating from the ventricles.
- Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs): Irregular heartbeats that might appear sporadically.
Imagine trying to solve a puzzle with similar-looking pieces; recognizing subtle differences is crucial to fitting everything together correctly. Misinterpreting arrhythmias can result in incorrect diagnoses or inappropriate treatments, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive training and experience. In summary, navigating the challenges posed by artifact interference and distinguishing between arrhythmias underscores the need for careful analysis and a thorough understanding of ECG patterns. By tackling these issues head-on, healthcare providers can enhance their diagnostic capabilities and ultimately improve patient care.
Advances in ECG Technology
As we embrace the digital age, advances in ECG technology are reshaping how we monitor and analyze heart health. Two remarkable innovations leading this charge are mobile ECG devices and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in ECG analysis. Let’s take a closer look at these developments.
Mobile ECG Devices
Mobile ECG devices have revolutionized cardiac monitoring, bringing the capabilities of traditional ECG machines into the palm of our hands. These portable devices allow users to record their heart rhythm anywhere and anytime, making heart health more accessible than ever.
- Key Benefits:
- Convenience: Users can conduct tests at home, reducing the need for frequent clinic visits.
- Real-time Monitoring: Many devices can sync with smartphones, providing immediate feedback and insights.
- Empowerment: Patients can take charge of their heart health, tracking their conditions and sharing data with healthcare providers effortlessly.
Picture a busy professional who experiences occasional palpitations. With a mobile ECG device, they can quickly record their ECG during those episodes and send the data to their doctor for immediate evaluation, ensuring timely care.
Artificial Intelligence in ECG Analysis
Artificial intelligence is also making waves in ECG interpretation. By utilizing algorithms and machine learning, AI can analyze ECG readings, identify abnormalities, and even predict potential heart issues with incredible accuracy.
- Applications of AI:
- Real-time Analysis: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data quickly, offering instant feedback during tests.
- Improved Accuracy: With AI’s ability to learn from previous readings, diagnostic accuracy is significantly enhanced, reducing the potential for human error.
Imagine having a highly intelligent assistant reviewing your ECG results alongside a medical professional. This collaboration not only augments the clinician’s ability to make informed decisions but also increases confidence in the diagnostic process. In conclusion, the integration of mobile ECG devices and AI technology is transforming heart health monitoring. With these advancements, individuals can enjoy greater convenience, accuracy, and proactive engagement in their cardiovascular health journey, paving the way to a healthier future.
Read also: The Ultimate Sinus fess Surgery Survival Guide: Tips for a Smooth Recovery.
Importance of Regular ECG Monitoring
With the advances in ECG technology making heart health monitoring more accessible, it’s crucial to recognize the importance of regular ECG monitoring. Keeping tabs on your heart’s electrical activity opens the door to proactive healthcare, especially in the realms of early detection of heart conditions and preventive measures.
Early detection of heart disease through ECG readings
Regular ECG monitoring plays a pivotal role in identifying potential heart issues before they escalate. Catching problems early can be the difference between a minor corrective action and a more severe medical intervention.
- Key Advantages:
- Identifying Anomalies: Regular checks can help spot arrhythmias, ischemic changes, or signs of hypertrophy.
- Timely Intervention: Prompt detection allows healthcare providers to initiate treatment earlier, significantly improving outcomes and reducing complications.
Consider a middle-aged individual who experiences occasional fatigue. Routine ECG monitoring might reveal subtle changes suggestive of an impending heart condition, prompting the doctor to recommend lifestyle adjustments or medical interventions well ahead of serious consequences.
Preventive Healthcare Measures
Regular ECGs also serve as a cornerstone for preventive healthcare measures. By monitoring their heart health, patients become active participants in their wellness journey.
- Proactive Lifestyle Changes: Awareness of heart health metrics encourages individuals to adopt healthier lifestyle choices, such as improved diet and increased physical activity.
- Informed Decision-Making: Data from regular ECGs can guide discussions between patients and healthcare providers, allowing them to make informed decisions about treatments or preventive strategies.
Think of a person who, after noticing slight irregularities in their ECG readings, decides to consult a nutritionist and embark on a tailored fitness regimen. This proactive approach can lead to healthier living and potentially avert serious complications down the line. In conclusion, regular ECG monitoring is a vital tool for the early detection of heart conditions and encouraging preventive healthcare measures. Embracing this practice not only fosters greater awareness but also empowers individuals to take charge of their cardiovascular health, paving the way for a longer, healthier life.
Read also: Life After Open Heart Surgery: Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Recap of ECG Insights
Throughout this journey, we’ve discovered that ECGs are invaluable for assessing heart health. From understanding the key components of ECG waves to recognizing common patterns and abnormalities, we’ve highlighted their importance in diagnosing heart diseases and monitoring cardiac health. Regular ECG monitoring stands out as crucial for the early detection of heart conditions and implementing preventive measures.
- Understanding ECG Waves: Each wave has its significance, contributing to a comprehensive overview of heart function.
- Clinical Applications: ECGs are essential tools for both diagnosis and ongoing health management.
- Technological Advances: Mobile ECG devices and AI-driven analysis are enhancing accessibility and accuracy in heart health monitoring.
In short, ECGs are more than just diagnostic tests; they are gateways to understanding and improving cardiovascular health.
Future Trends in ECG Technology
Looking ahead, the future of ECG technology is promising and filled with innovative trends. As healthcare becomes increasingly personalized, we can expect the following:
- Enhanced Mobile Devices: Continued development of more sophisticated, user-friendly mobile ECG devices will empower individuals to monitor their heart health seamlessly.
- AI Integration: The use of AI in ECG analysis will grow, leading to more precise diagnostics and quicker decision-making by healthcare professionals.
- Wearable Technology: The rise of wearable ECG monitors will allow for continuous heart monitoring, alerting users to potential issues in real time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 in ECG?
V1 and V2 are positioned on either side of the sternum at the fourth rib (count down from the sternal angle, where the second rib connects). V4 is placed at the heart’s apex (locate it by touch). V3 is located halfway between V2 and V4. V5 and V6 are positioned horizontally to the side of V4 (not directed toward the armpit). 1.
What is a normal RV5 SV1 in ECG?
Deviation of the QRS axis to the left or right (normal range is -30° to +90°) and an elevated amplitude of SV1 + RV5 (known as the Sokolow-Lyon index, with a normal value below 3.5 mV) assist healthcare professionals in identifying ventricular hypertrophy. 1.
What is a normal RR interval?
Typical ECG readings for waves and intervals are as follows: RR interval: 0.6 to 1.2 seconds; P wave duration: 80 milliseconds; PR interval: 120 to 200 milliseconds. 2
What does RV5 mean in ECG?
RV5/V6 indicates the elevated voltage from the RV5 and RV6 leads. For each lead, four to six cardiac cycles were captured, and the average was determined from three consecutive stable baseline cycles. The ECG measurements for SV1, SV3, SV4, RaVL, RV5/V6, SD, and QRS were documented for all participants. 28/06/2023 3
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.



2 Comments