Optimizing Your A1C Levels: Strategies for Success
What is A1C?
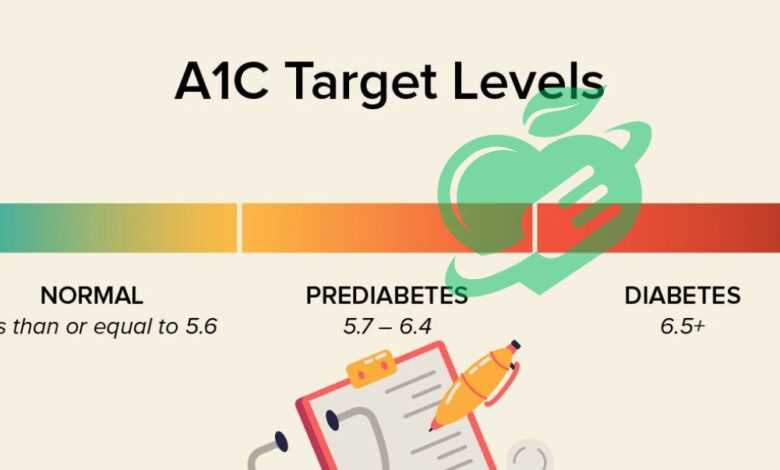
A1C Good levels, or hemoglobin A1C, is a blood test that measures the average blood glucose levels over the previous two to three months. This test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. Essentially, A1C provides a broader view of a person’s blood sugar management, rather than just a snapshot taken at a specific moment, which is what a standard blood glucose test does. When glucose levels are elevated, glucose molecules bind to hemoglobin in red blood cells, forming A1C. The higher the blood sugar, the more A1C is formed. For individuals without diabetes, a normal A1C level is typically below 5.7%. Levels of 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.5% or higher generally confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
Significance of Managing A1C Levels
Properly managing A1C levels is crucial for long-term health, especially for those living with diabetes. Maintaining A1C within target ranges can help in:
- Reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
- Minimizing symptoms of high blood sugar, like fatigue, excessive thirst, and frequent urination.
- Improving overall quality of life—better control can lead to more stable energy levels and mood.
Consider Jane, a 55-year-old diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. By monitoring her A1C Good levels regularly and making dietary changes, she reduced her levels from 8% to 6.5% over six months. This not only improved her energy levels but also significantly decreased her medication needs. Ultimately, understanding and managing A1C levels is not just about numbers; it’s about a proactive approach to health and longevity.
Impact of Diet on A1C
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing A1C levels. The foods consumed directly affect blood sugar levels, and making informed choices can have a significant impact on diabetes management. For instance, incorporating more whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Conversely, highly processed foods high in sugars and refined carbs can cause spikes in glucose levels. Here are some dietary tips:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in fiber, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, help regulate blood sugar.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Consumption: Keep a check on portion sizes and choose complex carbohydrates over simple sugars.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water throughout the day can help maintain optimal glucose levels.
Role of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another essential factor in controlling A1C levels. Engaging in exercise can enhance insulin sensitivity and allow the body to use glucose more effectively. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking or cycling. For example, Mark, a father of two, found that incorporating family walks after dinner not only helped lower his A1C but also improved family bonding time. Key benefits of physical activity include:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: The body becomes more efficient at using insulin following exercise.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for controlling blood sugar levels.
Stress and A1C Control
Lastly, stress is a significant factor that can negatively impact A1C levels. When stressed, the body releases hormones that can increase blood sugar levels, making it harder to manage diabetes. Understanding how to manage stress can lead to better control of A1C. Consider practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or even taking short breaks throughout the day. Techniques that can help include:
- Meditation or Yoga: These practices can provide relaxation and lower stress levels.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help ground you during stressful moments.
In summary, diet, physical activity, and stress management are interconnected factors that significantly influence A1C levels. Taking proactive steps in these areas can lead to meaningful improvements in diabetes management.
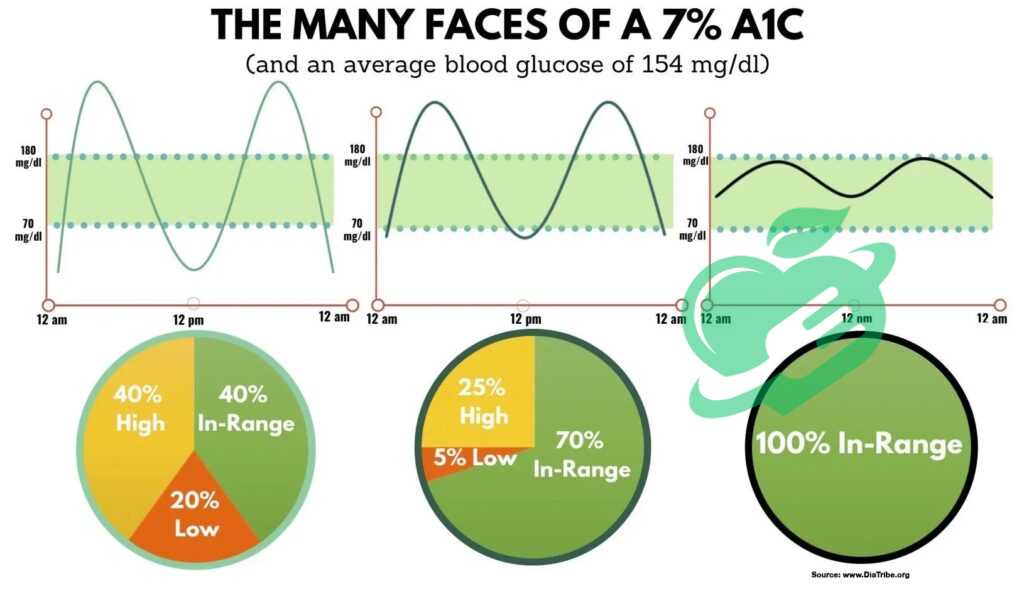
Monitoring and Measuring A1C
Monitoring A1C levels is crucial for individuals managing diabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with diabetes get their A1C checked at least twice a year if their blood sugar levels are stable. However, more frequent testing—every three months—may be necessary for those whose A1C levels are not within the target range or who are adjusting their treatment plans. Mary, a 40-year-old living with type 1 diabetes, found that by closely monitoring her A1C every three months, she was able to identify patterns in her blood sugar fluctuations related to meal choices and stress levels. Regular testing equips individuals with the necessary insights to make informed lifestyle changes. Consider these points when determining testing frequency:
- Stable A1C Levels: Test every 6 months.
- Fluctuating Levels or New Treatment: Test every 3 months.
- Pregnancy or Other Health Changes: Consult with your healthcare provider for recommendations.
Interpreting A1C Results
Understanding A1C results is vital for effective diabetes management. The results are expressed as a percentage, representing the proportion of hemoglobin coated with glucose. Here’s a quick guide to interpreting A1C results:
- Under 5.7%: Normal
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diagnosis of diabetes
When Sarah received her A1C results of 7.2%, it prompted a conversation with her healthcare provider about adjusting her medication and lifestyle changes. Having a clear understanding of A1C ranges helps in setting specific goals for improvement. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals when interpreting these results—they can provide tailored advice and support. Regularly reviewing A1C levels not only aids in managing diabetes but also empowers individuals to take charge of their health.

Lifestyle Changes for A1C Optimization
Adopting healthy eating habits is fundamental for optimizing A1C levels. Making mindful food choices can stabilize blood sugar and improve overall health. For instance, Julia, a 35-year-old diagnosed with prediabetes, transformed her diet by focusing on whole foods. She opted for:
- Colorful Vegetables: Filling her plate with a variety of vegetables ensures nutrient density.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating avocados and nuts provides essential fatty acids.
- Portion Control: Using smaller plates helped Julia manage portion sizes and reduce overeating.
By simplifying her meal planning and reading food labels, she was able to make informed decisions that kept her A1C in check.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Exercise is another critical pillar in managing A1C levels. Regular physical activity not only aids in weight management but also enhances insulin sensitivity. Strive for a mixture of aerobic and strength-training exercises. Donald, a 50-year-old office worker, started walking during his lunch breaks and found that:
- Increased Energy Levels: He felt more energized throughout the day.
- Better Sleep Quality: Exercising helped him sleep more soundly at night.
Recommended activities include brisk walking, running, cycling, or even dancing—whatever brings joy and engagement to the routine.
Quality Sleep for A1C Management
Lastly, quality sleep is often an overlooked aspect of A1C management. Poor sleep can lead to insulin resistance and increased cravings for unhealthy foods. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Consider adopting a bedtime routine, such as:
- Limiting Screen Time: Reducing exposure to blue light an hour before bed.
- Creating a Relaxing Environment: Ensuring the bedroom is dark and cool.
Emily, a sleep enthusiast, enhanced her sleep quality by practicing mindfulness and setting a consistent sleep schedule. As a result, she noticed improved A1C levels and overall mood. By making intentional lifestyle changes in diet, exercise, and sleep, individuals can effectively optimize their A1C levels and promote long-term health. The journey may require effort, but the benefits are certainly worth it.
Read also: What leads to Type 2 Diabetes?

Medication and Treatment Options
When lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough, many individuals with diabetes may require medications to assist in managing their A1C levels. Oral medications can be an effective way to help control blood sugar, and there are several classes available, including:
- Metformin: Often the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, it works by reducing glucose production in the liver and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: They work by increasing incretin levels, which help lower blood sugar levels after meals.
Mark, a 45-year-old with type 2 diabetes, found success with Metformin after struggling to manage his A1C through diet and exercise alone. He appreciated that it helped stabilize his glucose without significant side effects.
Insulin Therapy
For some, particularly those with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and there are various types to consider:
- Rapid-acting Insulin: This type is taken before meals to manage spikes in blood sugar.
- Long-acting Insulin: Used to provide a baseline level of insulin throughout the day and night.
- Combination Therapies: Involving both rapid and long-acting insulins for flexible management.
Samantha, who manages her type 1 diabetes with insulin therapy, uses a combination approach and has successfully balanced her lifestyle, finding that it gives her the control she needs.
Other Pharmacological Interventions
Apart from oral medications and insulin, other pharmacological interventions can aid in managing diabetes:
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These medications can reduce appetite and promote weight loss while also lowering blood sugar.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: They help the kidneys eliminate excess glucose through urine, providing a dual benefit in weight management and heart health.
Michael, who struggled with weight loss in conjunction with diabetes, found success by incorporating a GLP-1 receptor agonist into his treatment plan, which not only helped control his A1C but also contributed to significant weight reduction. In summary, a variety of medication and treatment options exist to help individuals manage their A1C levels. Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential to tailor a personalized plan that fits one’s unique health needs and lifestyle. With the right treatments, individuals can achieve better control over their diabetes and improve their overall quality of life.
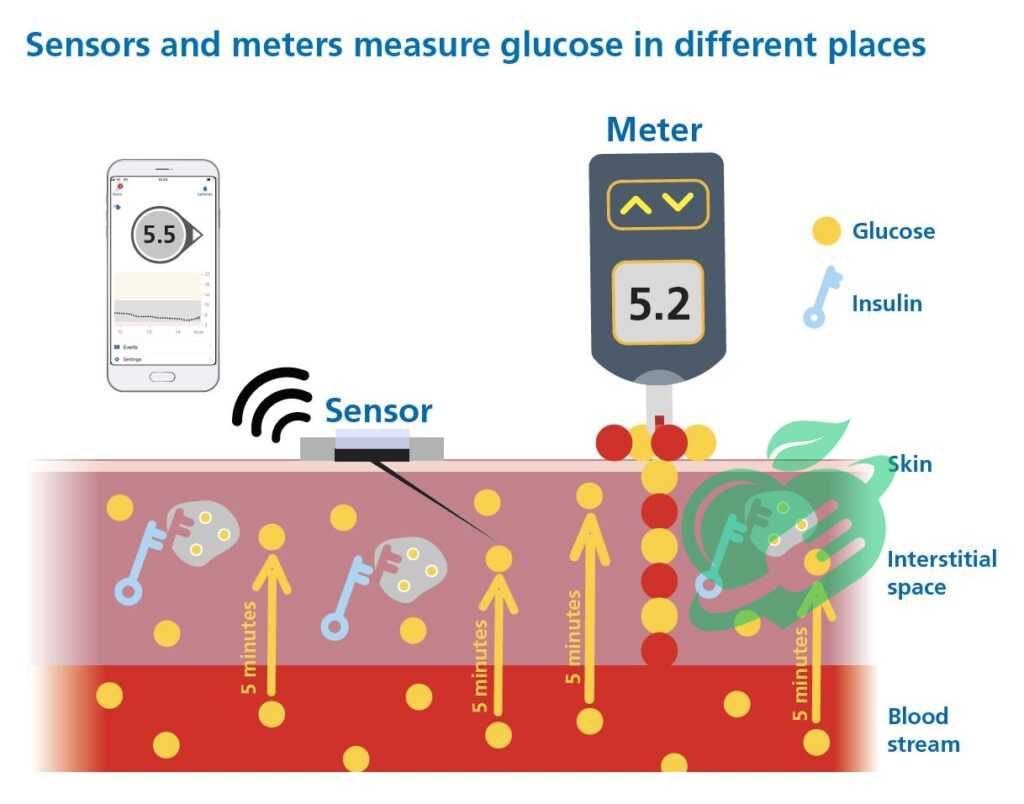
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a game-changer for many individuals managing diabetes. Unlike traditional blood glucose monitoring, which only provides a snapshot of glucose levels, CGM offers real-time glucose data throughout the day and night. This technology has several key benefits:
- Real-Time Alerts: CGM devices alert users to high and low blood sugar levels, allowing for quicker adjustments and reducing the risk of severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Trends and Patterns: Users can spot trends in glucose levels that correlate with their habits, such as diet and exercise. This data helps in making informed decisions regarding management strategies.
- Enhanced Decision Making: With constant feedback, individuals can optimize their insulin doses and meal timing, which can lead to improved overall blood sugar control.
For example, Emily, a long-time diabetes patient, adopted a CGM device and was amazed at the insights it provided. She found that a specific snack raised her glucose levels unexpectedly, prompting her to rethink her choices.
Integration with A1C Management
The integration of CGM technology with A1C management offers a more comprehensive approach to diabetes care. By consistently monitoring glucose levels, users can gain insights to refine their treatment plans effectively. Here’s how CGM can aid in this process:
- A1C Predictions: CGM data can help estimate anticipated A1C levels, allowing for proactive adjustments to diet, exercise, or medications before the next A1C test.
- Better Control: By reducing glucose variability, CGM can contribute to lower A1C results. Users often find that improved daily management translates to better A1C outcomes during routine tests.
- Personalized Adjustments: With the insights gained from CGM, individuals can tailor lifestyle changes and medical treatments to their specific needs, leading to more effective A1C management.
James, who had struggled with maintaining his A1C within target levels, saw remarkable improvement after incorporating a CGM into his routine. He could now recognize how different factors impacted his glucose and adjust accordingly. In conclusion, Continuous Glucose Monitoring not only provides immediate feedback on glucose levels but also integrates seamlessly into overall A1C management strategies. The combination of real-time data and personalized insights allows users to take charge of their diabetes care like never before.
Collaborating with Healthcare Providers
Effective management of diabetes and A1C levels often requires a collaborative effort between the patient and a dedicated healthcare team. This team can include doctors, nurses, dietitians, and diabetes educators. Each member plays a crucial role in ensuring comprehensive care.
- Physicians: They diagnose and create personalized treatment plans, adjusting medications based on regular assessments and lab results.
- Dietitians: These professionals help individuals develop healthy eating habits that align with their personal preferences and medical needs.
- Diabetes Educators: They provide valuable insights and training on how to use monitoring devices, understand medications, and adapt to lifestyle changes.
For example, Sarah found great success by working with a multidisciplinary team. With her dietitian’s help, she revamped her meal plans, and her patient educator taught her effective strategies for using her CGM. The synergy of knowledge and support empowered her to take control of her diabetes management.
Read also: How does diabetes affect your mood?
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are vital for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments to one’s treatment plan. These appointments ensure that:
- Blood Tests: Regular testing of A1C levels and other relevant biomarkers can help pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Discussion of Progress: Check-ups allow patients to discuss challenges and successes with their healthcare team, providing an opportunity for tailored advice.
- Preventive Care: Regular visits can also help identify complications early, enabling timely intervention.
John, who initially struggled with his A1C levels, made it a point to have quarterly check-ups with his healthcare team. With their support, he learned to anticipate changes in his health and adjust his strategies accordingly. In summary, a strong collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is essential for effective diabetes management. Regular communication and check-ups foster a proactive approach, ensuring that individuals have the tools and support they need to optimize their A1C levels and overall health. By leveraging the expertise of their healthcare team, patients can navigate the challenges of diabetes with confidence.

Long-Term Strategies for Maintaining Optimal A1C
One of the pillars of effective diabetes management is setting realistic goals for A1C levels and overall health. When individuals create achievable targets, they are more likely to remain committed to their care plans. Here’s how to establish those goals:
- Assess Current Levels: Understanding your current A1C level is imperative. For instance, if your A1C is 8% and your ultimate goal is 6.5%, consider setting intermediate targets—like aiming for 7.5% in three months.
- Break Down Goals: Instead of overwhelming yourself with a broad target, break it down into smaller, manageable milestones. Celebrate each achievement—like a successful month of maintaining a healthier eating pattern.
- Incorporate Flexibility: Life can be unpredictable, so it’s important to remain adaptable. Allow for adjustments based on personal circumstances or challenges.
Jessica, for example, found that by setting monthly goals around her meals and exercise, she remained motivated and saw her A1C drop gradually.
Behavioral Changes for Sustained Improvement
In addition to goal setting, making lasting behavioral changes can significantly enhance A1C management. Here are a few strategies that can lead to sustained improvement:
- Mindfulness Practices: Incorporating practices such as meditation or yoga can help reduce stress, which often impacts blood sugar levels.
- Consistent Monitoring: Keeping a daily log of food intake, exercise, and blood sugar levels encourages accountability and offers insights into patterns.
- Building a Support Network: Engaging with family or joining a support group can foster motivation and encouragement. Sharing experiences and advice can help in stay focused.
For instance, Tom started a small walking group with friends, leading to both increased physical activity and a supportive atmosphere where they encouraged one another. In conclusion, maintaining optimal A1C levels requires a combination of realistic goal-setting and sustainable behavioral changes. By taking small but meaningful steps, individuals can achieve long-term success in their diabetes management. With persistence and support, lasting improvements in health and quality of life are entirely within reach.
Read also: Unlocking the Secrets of Alzheimer’s and Diabetes 3: A Comprehensive Guide.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Tracking progress through regular monitoring is vital for anyone managing diabetes and striving to maintain optimal A1C levels. By consistently checking glucose levels, individuals gain essential insights that empower them to make informed decisions regarding their management plans.
- Identifying Patterns: Regular monitoring helps reveal patterns in blood sugar fluctuations, providing clues about how different foods, activities, and stressors impact glucose levels.
- Preventing Complications: Close monitoring allows for early detection of highs and lows, reducing the risk of severe complications and associated health issues.
- Building Accountability: Keeping a log of daily readings promotes accountability and encourages individuals to adhere to their management strategies.
For instance, Helen had been tracking her blood sugar levels for months and noticed a trend: her levels would spike during stressful work periods. Recognizing this pattern helped her implement stress management techniques.
Read also: Unpacking the Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Diabetics
Modifying Approaches Based on Results
Once individuals have a clear understanding of their glucose levels, it’s crucial to modify their approaches based on the information gathered. Here’s how to effectively adjust strategies:
- Reviewing Data Regularly: Set aside time each week or month to review glucose readings, meal logs, and physical activity to assess what works and what doesn’t.
- Adjusting Medication: Consult with healthcare providers to discuss potential adjustments to medications or insulin dosages based on observed patterns.
- Fine-Tuning Lifestyle Choices: If certain foods consistently lead to higher blood sugar, consider exploring alternative options or adjusting portion sizes.
For example, after reviewing her data, Lisa discovered that her afternoon snacks were pushing her glucose too high. By experimenting with healthier snack options and timing, she managed to stabilize her levels. In summary, tracking progress through regular monitoring and being open to modifying strategies based on results are essential components of diabetes management. By staying informed and flexible, individuals can optimize their A1C levels and enhance their overall health journey. Consistent evaluation and adaptation lead to empowered decision-making and better diabetes outcomes, paving the way for long-term success.
Read also: Understanding the New Diabetes Criteria: What You Need to Know.
Recap of Strategies
As we conclude this comprehensive dive into A1C optimization, it’s crucial to recap the strategies discussed throughout the journey. Each element plays a vital role in effectively managing diabetes and improving overall health.
- Understanding A1C Levels: Gaining a foundational knowledge of A1C, its significance, and how it impacts health is the first step towards effective management.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting healthy eating habits, committing to regular physical activity, and prioritizing quality sleep can have a profound effect on A1C levels.
- Medication and Treatment: Understanding available medications, from oral options to insulin therapy, enables personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
- Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) helps in diagnosing trends for better decision-making.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Engaging with a comprehensive healthcare team ensures effective management and support throughout the journey.
These strategies all interconnect, creating a robust framework for individuals managing diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good HbA1c by age?
| Diagnosis | HbA1c (%) | HbA1c (mmol/mol) |
| Optimal | 5 – 5.4 | 30 – 35 |
| Normal | 4 – 5.6 | 20 – 38 |
| Pre-diabetes | 5.7 – 6.4 | 39 – 47 |
| Diabete | 6.5 and above | 48 and above 1. |
What is an alarming A1C?
For individuals without diabetes, A1C levels must remain under 5.7%. A1C levels at 9.05% and above are considered hazardous. An A1C exceeding 9% heightens the likelihood of severe long-term complications from diabetes, such as blindness, nerve damage, and kidney failure. Maintaining an A1C below 7% is regarded as effective management of diabetes. 2.
What A1C is no longer diabetic?
Since reversal suggests a lasting cure, a more suitable term for this subject could be “diabetes remission.” This typically involves lowering the A1C to a level comparable to that of a non-diabetic individual (below 6.5%) and either completely stopping diabetes medications or restricting them to metformin. 3.
Because your health is the most valuable thing you have and the most precious thing we care about, we always recommend that you consult your specialist doctor in everything related to your health and daily life. Everything we provide here is for awareness purposes only and does not replace consulting a doctor. Every person has a unique condition that deserves special care, and we are here by your side, working passionately to provide the information you need. Always follow us, because we write for you with love and sincerity to remain a source that inspires you with hope and supports you on your journey towards a better life.



Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!