Are You Neurotypical? Signs to Look For
Understanding Neurotypicality
Neurotypicality refers to the typical neurological functioning of individuals who do not exhibit developmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Essentially, a neurotypical person processes information, interacts socially, and responds to their environment in ways that align with societal norms. For instance, neurotypical individuals usually find reading social cues easier, engaging in reciprocal communication, and adhering to established behavioral expectations. These individuals are often seen as fitting into the mainstream categories of thought and behavior. In contrast, neurodivergent individuals may experience challenges with these same skills due to differences in brain functioning. To put it simply, neurotypicality is about conformity to expected cognitive, social, and emotional responses. It is important to note, however, that being neurotypical does not imply superiority or perfection; it means existing within a specific framework of behaviors and perceptions deemed ‘normal’ by society.
Comparison with Neurodiversity
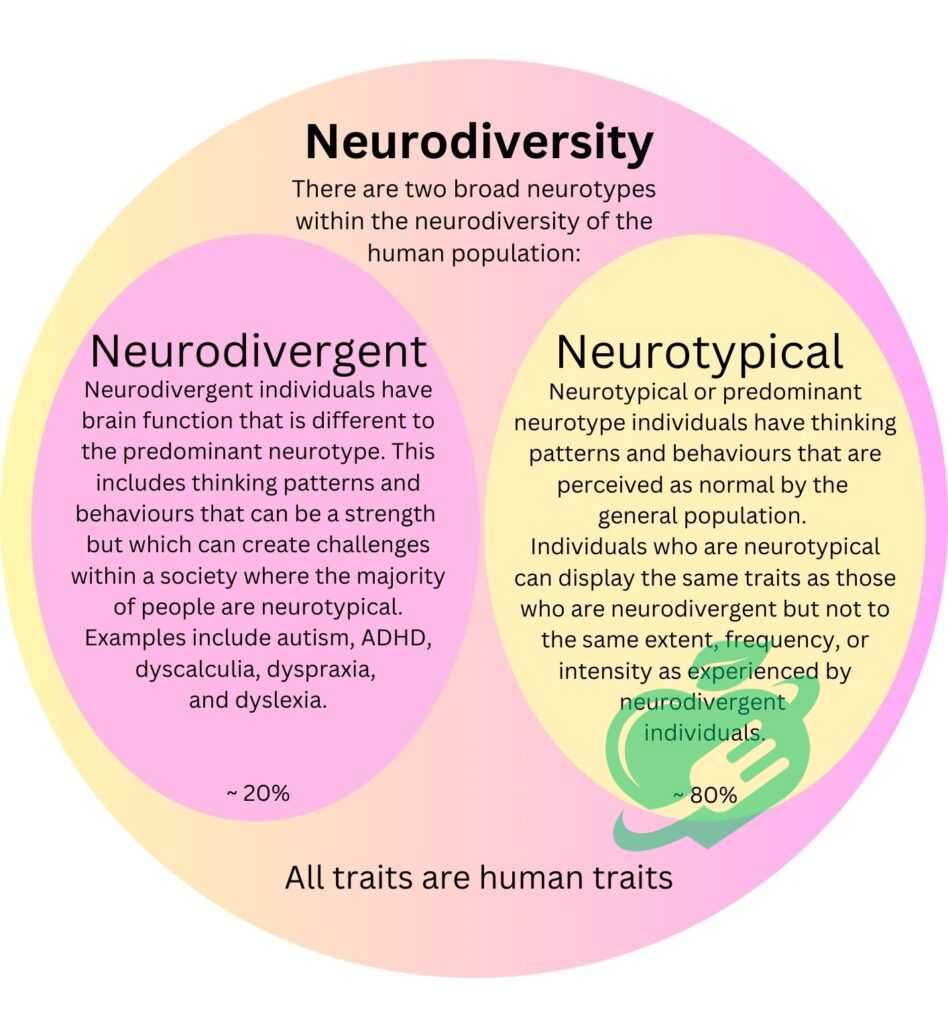
Neurodiversity is a broader concept that celebrates the variety of human brain functioning. While neurotypicality represents the most common form of neurological processing, neurodiversity encompasses everything from autism and ADHD to dyslexia and beyond. Here’s how they differ:
- Focus: Neurotypicality emphasizes conformity to standard neurological patterns, whereas neurodiversity advocates for recognizing and valuing differences.
- Cultural Perception: Neurotypical individuals often embody societal norms, making them more readily accepted in certain environments. In contrast, neurodivergent individuals may misalign with these expectations, making their experiences unique yet frequently misunderstood.
- Strengths and Challenges: Neurotypicality suggests a set of advantages in traditional social settings, whereas neurodiversity highlights that neurodivergent individuals often possess special strengths, such as heightened creativity or unique problem-solving abilities. 1
For example
A neurotypical student in a classroom may seamlessly follow lesson instructions and participate in group discussions. However, a neurodivergent peer might show exceptional creativity in projects, although they could struggle with conventional social interactions, such as making eye contact or understanding unspoken rules of engagement. Both neurotypical and neurodivergent individuals can contribute significantly to society, but they may do so in very different ways. Recognizing this diversity in thinking enables a richer tapestry of collaboration and innovation, where unique perspectives are valued and integrated.
The coexistence of neurotypicality and neurodiversity is essential for a balanced view of human variation. Society’s growing understanding of these terms encourages more inclusive discussions about cognitive differences. By appreciating what each neurological profile brings to the table, we foster a more compassionate and holistic view of human potential. In conclusion, while neurotypicality represents a standard frame of reference for brain function, neurodiversity underscores the importance of embracing cognitive differences. This broader perspective not only helps in personal interactions but also enriches workplaces, educational systems, and entire communities. Understanding and accepting both neurotypicality and neurodiversity creates a more inclusive environment for everyone, leading to better collaboration and innovation across all domains of life.
Read also: Unveiling the 75 Soft Challenge: Everything You Need to Know.
Characteristics of Neurotypical Individuals
Building upon the foundational understanding of neurotypicality and neurodiversity, it’s essential to delve deeper into the defining features of neurotypical individuals. This section will explore their social interactions and communication styles, as well as their behavioral patterns and responses, giving readers a comprehensive view of what it means to be neurotypical.
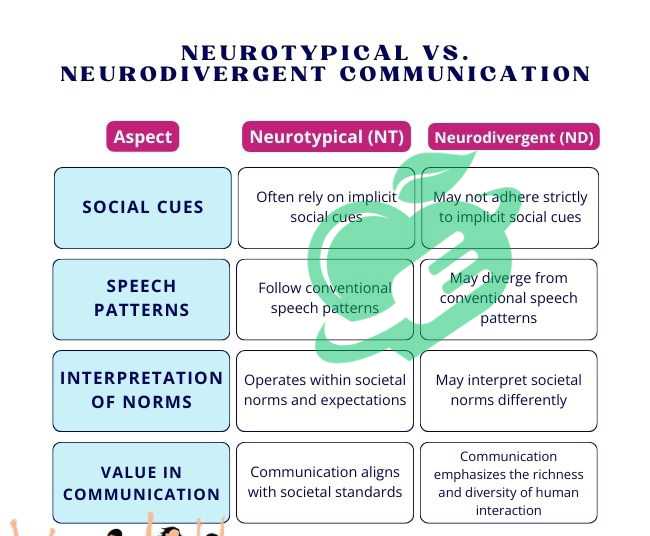
Social Interactions and Communication
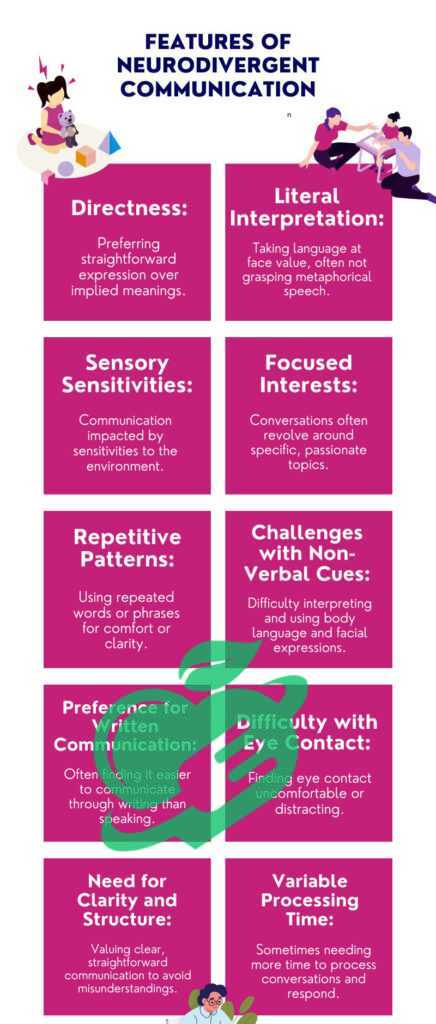
One of the hallmark characteristics of neurotypical individuals is their ability to navigate social situations with relative ease. Such individuals typically exhibit the following traits in their interactions:
- Understanding Social Cues: Neurotypical people are generally adept at interpreting non-verbal cues, including body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. For instance, when someone seems withdrawn at a party, a neurotypical person might instinctively approach them to check if they need company.
- Reciprocal Communication: Engaging in conversation is typically straightforward for neurotypical individuals. They understand the back-and-forth nature of dialogue, knowing when to listen and when to respond. A casual chat about weekend plans often flows easily with turn-taking.
- Empathy and Emotional Awareness: Neurotypical individuals often have a strong ability to empathize with others. They can sense when someone is upset and may offer comfort or express understanding, which helps establish deeper connections within relationships.
- Adherence to Social Norms: Often, neurotypical individuals are familiar with societal expectations, such as how to introduce themselves, how to greet others, and what topics are considered appropriate for conversation based on the setting.
However, it’s also important to recognize that not every neurotypical person will excel in all social situations. For example, some might feel awkward in large gatherings or struggle with small talk, much like any other group.
Typical behavioral patterns and neural responses
Neurotypical individuals also tend to display recognizable patterns in their behavior, which generally align with societal standards. Here are some of the common behavioral characteristics:
- Structured Routines: Many neurotypical people thrive on structure and predictability. Having a set routine can provide comfort and reduce anxiety. For example, someone might start their day with a morning run, a shower, and breakfast, expecting to follow that same pattern each day.
- Adaptability: While routines are appreciated, neurotypical individuals usually possess a degree of flexibility. When plans change, they can often adjust without experiencing severe distress. A friend might invite them to a last-minute event, and rather than hesitating, they might readily accept the invitation.
- Response to Stress: Neurotypical individuals often exhibit coping mechanisms that are broadly understood within their social circles. For instance, when faced with stress from work or personal relationships, they may turn to friends or family for support because they recognize this as a helpful practice.
- Conformity to Cultural Norms: Many neurotypical individuals align their thoughts and behaviors with the cultural and societal values they were raised with. For example, in a workplace, they may adhere to dress codes and professional etiquette, understanding that this aligns with organizational expectations. 2
Operate within familiar parameters.
In essence, neurotypical individuals tend to operate within familiar parameters when socializing and responding to their environments. These characteristics facilitate smoother interactions and more cohesive relationships in various contexts, be it in friendships, family dynamics, or the workplace. While these traits characterize many neurotypical individuals, it is vital to remember that people’s experiences can vary widely. Acknowledging these differences can foster empathy and understanding between neurotypical and neurodivergent perspectives, thereby enriching social interactions for everyone involved. In conclusion, understanding the social interactions, communication styles, and behavioral patterns inherent to neurotypical individuals not only highlights their experiences but also enhances the dialogue around neurodiversity. Embracing these characteristics allows society to appreciate the broad spectrum of human thought and interaction more fully.
Read also: Mental Health in Nursing: Challenges and Solutions
Neurotypicality in Society
As we continue to explore the significance of neurotypicality, it’s vital to understand how these characteristics are interwoven into the fabric of our society. In this section, we’ll examine cultural expectations and norms surrounding neurotypical individuals, as well as the dynamics they experience in workplace settings.
Cultural Expectations and Norms
Culture plays a pivotal role in defining what is considered ‘normal’ behavior in various contexts. Neurotypical individuals often find themselves aligning with these cultural expectations with relative ease. Here are some key points illustrating this relationship:
- Behavioral Conformity: Neurotypical individuals are generally expected to adhere to social norms, such as maintaining eye contact during conversations, participating in group activities, or showing interest in shared social events. These behaviors are often seen as markers of social competence, and those who perform them well are usually more accepted.
- Socialization Patterns: From a young age, neurotypical children are socialized to engage with their peers, learning communication skills through play and collaboration. For example, in school environments, children often learn to work in teams during class projects, which fosters essential social skills and prepares them for future communal activities.
- Media Representation: The portrayal of neurotypical individuals in movies, television shows, and literature often reinforces societal ideals of ‘normalcy.’ Characters who embody neurotypical traits frequently take center stage, which can further shape public perceptions of appropriate behaviors.
An everyday example of this can be seen at social gatherings. A neurotypical individual might easily navigate introductions, engage in conversations about trending topics, and participate in light-hearted banter. They often mirror the behavior of those around them, which aids in acceptance and belonging.
Workplace Dynamics and Relationships
In professional settings, neurotypicality plays a significant role in shaping workplace cultures and interactions. The expectations and dynamics can be distinctly influential:
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Many workplaces promote a culture of teamwork. Neurotypical individuals usually find it easier to fit into collaborative environments where they are comfortable sharing ideas, accepting criticism, and providing feedback. Their ability to read social cues can enhance communication among team members.
- Communication Styles: In a corporate setting, clear and concise communication is often valued. Neurotypical employees may excel in providing updates during meetings or following up with colleagues via email, adhering closely to business etiquette. For instance, they may recognize when to dial it back in discussions and when to assert their opinions confidently.
- Performance and Recognition: Workplaces often reward neurotypical behaviors, such as initiative-taking, assertiveness, and adherence to hierarchies. Employees demonstrating these traits can receive promotions, raises, or accolades. However, this can pose a challenge for neurodivergent individuals who may exhibit unique strengths that don’t align with traditional metrics of success.
- Social Integration: Networking plays a critical role in career advancement. Neurotypical individuals often find informal interactions, such as coffee breaks or after-work gatherings, useful for building relationships and advancing their careers. They typically navigate these social landscapes more comfortably, allowing for natural alliances that can lead to professional growth.
a summary
Despite these advantages, it’s crucial to recognize that not all neurotypical individuals thrive equally. Factors like personality, cultural background, and personal circumstances can affect their experience in both social and workplace settings. In conclusion, the nuances of neurotypicality shape significant cultural expectations and norms that govern social interactions and workplace dynamics. Understanding these aspects not only fosters a deeper appreciation for the lived experiences of neurotypical individuals but also encourages a more inclusive atmosphere that recognizes the value of diverse cognitive approaches. As society moves toward celebrating neurodiversity, it is vital to honor the traditional pathways that have defined success and inclusion. By doing so, all individuals—regardless of their neurological framework—can contribute meaningfully to a more harmonious and productive society.
Read also: How to Manage and Reduce Relationship Anxiety.
Challenges Faced by Neurotypical Individuals
Although neurotypical individuals often navigate social environments and workplace dynamics with ease, they experience their own set of distinctive challenges. This section will delve into mental health issues and explore coping mechanisms and support systems that are crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
Mental Health Issues
Mental health is a universal concern, impacting individuals across all demographics, including those who are neurotypical. Despite their relative ease in social situations, neurotypical individuals are not immune to mental health struggles. Here are some prevalent issues they may encounter:
- Anxiety Disorders: Many neurotypical individuals experience anxiety at various stages of life. Whether it’s on the job during a big presentation or in social settings where high expectations exist, anxiety can surface frequently. For example, a person may find themselves feeling overwhelmed at the thought of networking at a corporate event, stressing over what to say or how to be perceived.
- Depression: Depression isn’t solely reserved for those with neurodivergent conditions; it can also significantly affect neurotypical individuals. Various life changes—such as job loss, the end of a relationship, or familial stress—can lead to feelings of hopelessness and sadness. An individual might struggle to sense joy in activities they once loved, leading to a diminishing sense of self-worth.
- Burnout: In today’s fast-paced society, neurotypical individuals might find themselves prone to burnout due to existing cultural demands. Juggling work responsibilities, social commitments, and personal goals can lead to mental fatigue. The feeling of always needing to perform at a high level can create a cycle of stress and exhaustion. 3
Overall, even though neurotypical individuals may possess the social skills often associated with traditional success, they are still subject to significant internal struggles, often masked by their outward confidence.
Typical coping mechanisms and neurological support systems
Recognizing the challenges of mental health is the first step to addressing them effectively. Many neurotypical individuals employ various coping mechanisms, along with support systems from their environments, to navigate these issues. Here are some notable strategies:
- Therapy and Counseling: Many individuals turn to mental health professionals to help process their emotions and develop healthy coping strategies. Whether through talk therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), or other modalities, professional guidance can provide invaluable tools for addressing anxiety, depression, or burnout.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practicing mindfulness—such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises—can significantly alleviate stress and anxiety. For example, a neurotypical person might take a few moments to breathe deeply or engage in a short meditation before facing a challenging situation, allowing them to calm their thoughts and refocus.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Fostering a healthy lifestyle can have a profound impact on mental health. Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep can help regulate mood and reduce stress levels. Engaging in physical activities like jogging, swimming, or even walking can be a great way to decompress after a long day.
- Strong Social Networks: Building and maintaining supportive relationships can also serve as an essential coping mechanism. Friends, family, and peers often help neurotypical individuals navigate their challenges by offering emotional support or constructive advice. A simple coffee catch-up with a close friend can provide moments of connection and comfort during tough times.
- Setting Boundaries: Learning to say no or establishing boundaries around work and social commitments can be crucial. Recognizing personal limits helps neurotypical individuals manage their stress and avoid burnout. For example, an individual might choose to limit their attendance at social events during a particularly busy work week.
Read also: Understanding the Importance of Mental Health First Aid.
In conclusion
While neurotypical individuals may experience advantages in social settings and workplaces, they are not without their mental health challenges. Addressing these challenges through effective coping mechanisms and supportive networks can enhance individual resilience. By fostering an environment where mental health is prioritized, neurotypical individuals can work toward building a more balanced and fulfilling life, ultimately leading to a healthier society as a whole.
Read also: Find Hope at a Leading Mental Health Hospital.
Embracing Neurodiversity
As we shift our focus towards embracing neurodiversity, it’s essential to recognize the importance of inclusivity and understanding in creating a more harmonious society. In this section, we will discuss how to foster inclusivity for neurodivergent individuals, as well as the significance of celebrating differences and unique perspectives.
Promoting Inclusivity and Understanding
Creating an inclusive environment necessitates a deliberate effort to understand and empathize with neurodivergent individuals. The benefits of promoting inclusivity extend far beyond the neurodivergent community; they enrich all members of society. Consider these effective strategies for fostering understanding and inclusivity:
- Education and Awareness: One of the most powerful tools for promoting inclusivity is education. Community workshops, school programs, and workplace training sessions can help bridge gaps in understanding. For instance, hosting seminars about neurodiversity can increase awareness about conditions like autism, ADHD, and dyslexia, allowing neurotypical individuals to better comprehend the experiences of their neurodivergent peers.
- Open Communication: Establishing an open dialogue is crucial in promoting understanding. Encouraging conversations about neurodiversity in schools, workplaces, and social groups fosters an atmosphere where individuals feel comfortable discussing their experiences and challenges. Creating safe spaces where people can share their thoughts and feelings is imperative to building trust.
- Policy Changes: Governments and organizations can implement policies that support inclusivity for neurodivergent individuals. Adjusting hiring practices, providing necessary accommodations, and ensuring a supportive environment can help create workplaces where everyone thrives. For example, offering flexible work hours may help individuals who need a different pace to excel. 4
As we lay the groundwork for understanding, it becomes apparent that fostering inclusivity greatly benefits society as a whole. Collective efforts lead to richer relationships and better cooperation across varying backgrounds, resulting in a stronger community.
Celebrating Differences and Unique Perspectives
When we embrace neurodiversity, we don’t just tolerate differences; we actively celebrate them. Each neurodivergent individual brings a unique perspective and set of skills, contributing to an innovative and dynamic society. Here are several ways to honor these differences:
- Highlighting Individual Strengths: Acknowledging and celebrating the talents of neurodivergent individuals can lead to increased confidence and self-worth. For example, an employee with ADHD may bring exceptional creativity or problem-solving abilities to the table, benefiting their team in unique ways. Sharing these experiences highlights the value of diverse cognitive styles.
- Fostering Diverse Collaborations: Encourage collaboration among individuals with different perspectives. Diverse teams often produce innovative solutions and creative ideas. In educational settings, group projects that draw on varied talents allow students to appreciate the unique input of their peers. This sense of appreciation can foster camaraderie, opening pathways to friendships and collaborations.
- Community Events and Celebrations: Organizing events that spotlight neurodivergent achievements can strengthen community ties. For instance, hosting a festival or art showcase that features the creative works of neurodivergent individuals invites everyone to celebrate their contributions. These events also serve as platforms for sharing stories and raising awareness about neurodiversity.
- Encouraging Advocacy: Empowering neurodivergent individuals to share their experiences fosters a sense of agency and belonging. Encouraging them to engage in advocacy initiatives helps raise awareness regarding neurodiversity. Whether through public speaking, writing blogs, or participating in discussions, their voices contribute to celebrating differences within society.
In conclusion
Embracing neurodiversity is a powerful movement that enriches our communities, workplaces, and societal interactions. By promoting inclusivity and understanding, as well as celebrating differences and unique perspectives, we create a more compassionate world. The journey toward a society that values every individual’s contributions is one marked by growth, understanding, and collaboration. Together, we can forge lasting connections, treat neurodiversity as a strength, and ultimately cultivate a future that values the incredible spectrum of human thought and experience.
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.
- Reference
- leafcare ((↩))
- sciencedirect ((↩))
- mayoclinic ((↩))
- ava ((↩))




One Comment