Living with Diverticulum Zenker: What You Need to Know
Understanding Diverticulum Zenker
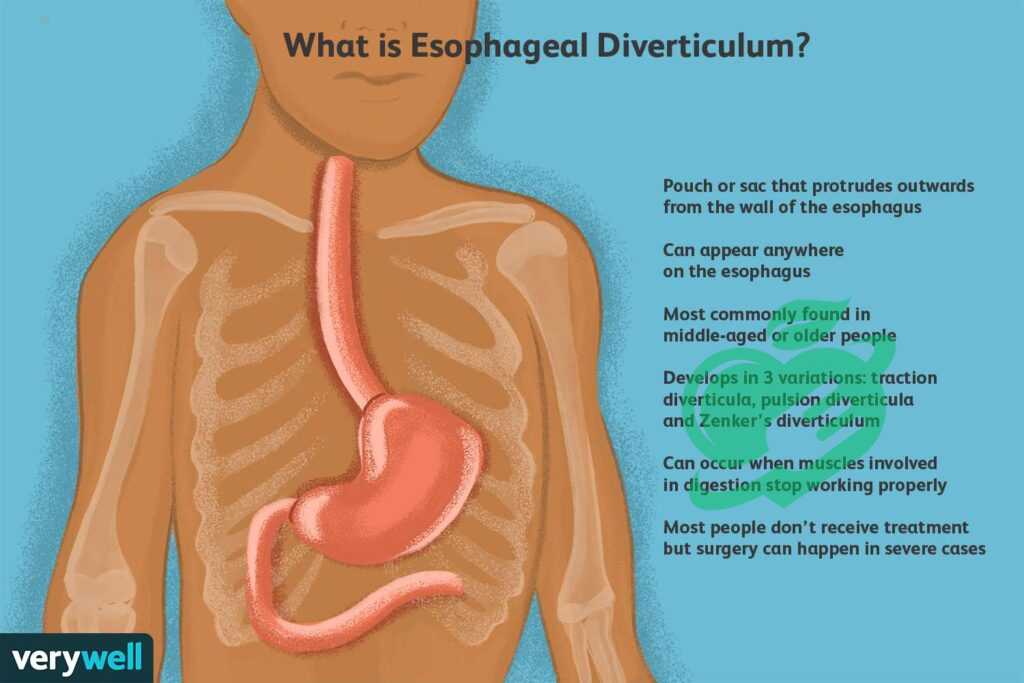
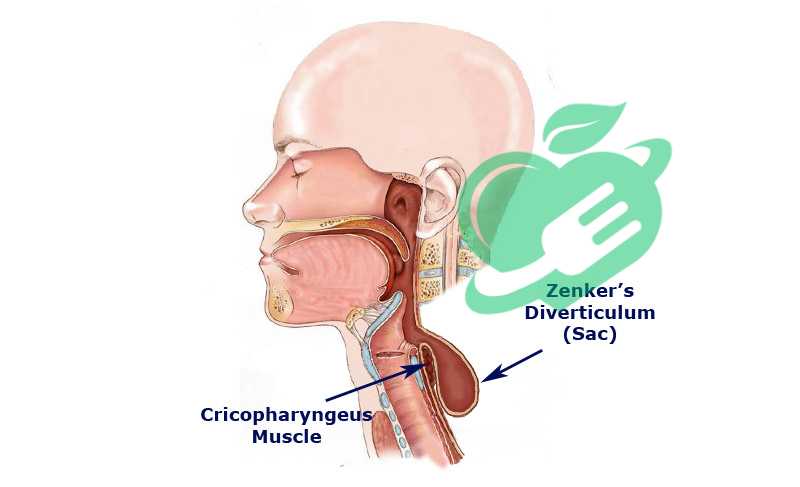
Zenker’s diverticulum, often referred to as Zenker diverticulum, is a condition characterized by the formation of a pouch in the upper esophagus, just above the esophageal sphincter. This pouch occurs due to a weakness in the esophagus’s muscular wall, leading to mucosal tissue protrusion. While it might sound a bit intimidating, many people are unaware that they have Zenker diverticulum until they experience symptoms. Often, this condition develops slowly over the years, typically affecting older adults, especially those aged 60 and above. Think of it as your body creating a little pocket where food can get caught, sometimes causing discomfort or swallowing difficulties. For some, this pouch can become a nuisance. It can collect food debris or even lead to halitosis, which can be quite embarrassing. However, not everyone with Zenker diverticulum will experience problematic symptoms.
Causes of Diverticulum Zenker
The exact causes of the Zenker diverticulum remain somewhat mysterious. However, a few contributing factors have been identified. Here are some key points to consider:
- Age: It primarily affects older adults and is rarely seen in individuals under the age of 40. The natural aging process can lead to muscular weakening and loss of tone in the esophagus.
- Muscle coordination issues: Conditions that disrupt normal muscle coordination during swallowing can increase pressure in the esophagus, leading to pouch formation.
- Chronic esophageal pressure: Factors that lead to increased pressure in the esophagus during swallowing may also contribute. These can include:
- Conditions like achalasia: A disorder that affects the ability of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, causing food to back up.
- Neurological disorders: Such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke, can disrupt normal swallowing mechanics.
Also, personal experiences often demonstrate that those who experience chronic inflammation or have had esophageal surgeries face greater risks. Knowing the causes helps in understanding the condition better, as awareness can be the first step towards managing it. For many, the diagnosis of Zenker diverticulum may initially evoke anxiety, but it’s essential to remember that it’s manageable, with various treatment options available. In summary, the Zenker diverticulum is a pouch that can form in the esophagus primarily due to age and muscle coordination issues, which leads to various symptoms. Understanding its causes enhances awareness and paves the way for proactive management and treatment in those affected.
Read also: Living with Friedreich’s Ataxia: What You Need to Know
Common symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum
Recognizing the symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum is essential, as they can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Many people may initially dismiss these signs as typical aging responses, but here’s a rundown of common symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum that could indicate the presence of this condition.
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing): One of the hallmark symptoms, individuals may struggle with swallowing solid foods or even liquids. They might feel as if food is stuck in their throat.
- Regurgitation of food: Some people may experience the sensation of food being brought back up after swallowing. Occasionally, this regurgitation can occur hours later or even lead to aspiration into the lungs, which can cause cough or choking.
- Halitosis (bad breath): As food particles accumulate in the diverticulum, they can lead to foul-smelling breath. This can be frustrating for patients and affect their social interactions.
- Weight loss: Over time, difficulty eating can result in unintentional weight loss as individuals may avoid solid foods to sidestep discomfort.
- Coughing or choking: Many people living with Zenker diverticulum report coughing fits or choking episodes, which can cause anxiety during meals.
Each of the symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum can vary in severity and may lead individuals to seek medical advice when they become more persistent or troublesome.
Diagnostic Procedures
If symptoms align with Zenker diverticulum, the next step is typically a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. Several diagnostic procedures may be employed to confirm the diagnosis:
- Barium Swallow Study: In this non-invasive test, the patient swallows a barium solution, which coats the esophagus and reveals its contours on an X-ray. This allows doctors to visualize any pouches or abnormalities.
- Endoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure in which a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to visually inspect the esophagus. This can show the presence of the diverticulum and assess its size.
- Esophageal manometry: This test measures the strength and coordination of esophageal muscles during swallowing. It can help identify muscle coordination issues that could be contributing to the diverticulum.
In combination, these diagnostic tools provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s condition. Navigating the symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum and diagnostic processes can seem daunting. However, knowing what to expect reassures individuals and encourages them to seek help sooner rather than later. Early intervention can significantly enhance outcomes and improve the quality of life. Recognizing the signs and understanding the diagnostic procedures serves as a crucial step toward the effective management of Zenker diverticulum.
Read also: Best Build Muscle Supplements You Need to Try Now
Treatment Options for Diverticulum Zenker
For many people diagnosed with Zenker diverticulum, non-surgical treatments can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Before considering surgery, healthcare providers typically explore conservative management options first. Here are some common non-surgical treatments:
- Dietary Modifications: A tailored diet can make a considerable difference. Individuals are often advised to switch to softer foods that are easier to swallow, such as pureed fruits, smoothies, or soups.
- Thickened Liquids: Some patients find that thickening their drinks with commercial thickeners improves swallowability, reducing the chances of choking or regurgitation.
- Postural Techniques: Changing the position during meals can help. For instance, leaning forward while swallowing may assist in guiding food past the diverticulum.
- Swallowing Therapy: Working with a speech-language pathologist can help individuals practice swallowing techniques that improve coordination and reduce the risk of aspiration.
For example, a patient named John found significant relief by incorporating smoother foods and focusing on swallowing techniques. He noted that consciously chewing his food more thoroughly and taking smaller bites made mealtime less stressful. While these non-surgical options may not eliminate the diverticulum itself, they can ease the symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum and empower individuals to enjoy their meals more comfortably.
Surgical Interventions for Diverticulum Zenker
In cases where non-surgical treatments are insufficient or if symptoms deteriorate, Surgical Interventions for Diverticulum Zenker may be necessary. The surgery aims to remove or correct the diverticulum and enhance swallowing function. There are a couple of common Surgical Interventions for Diverticulum Zenker procedures:
- Diverticulectomy: This procedure involves the complete removal of the diverticulum. Surgeons may use traditional open surgery or a minimally invasive approach, depending on the diverticulum’s size and location.
- Myotomy: In conjunction with diverticulectomy, a myotomy can be performed to cut the muscle at the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing better passage of food into the esophagus.
- Endoscopic Techniques: Recently, more advanced endoscopic methods have been developed. These minimally invasive procedures involve the use of an endoscope to cut the diverticulum, leading to reduced recovery times and minimized surgical risks.
It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of these surgical options with a healthcare professional. Patients like Linda, who opted for a diverticulectomy, reported remarkably positive results post-surgery. She described how her life changed dramatically, stating, “I finally relish eating without constant worry. It’s like a weight has been lifted!” Overall, whether through non-surgical means or surgery, there are effective treatment options available for those grappling with Zenker diverticulum. Each individual’s journey is unique, underscoring the importance of personalized healthcare decisions based on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health.
Read also: Headaches from MS? Discover the Best Remedies
Lifestyle Changes and Management
Navigating daily life with Zenker diverticulum can be challenging, particularly when it comes to food. Making thoughtful dietary choices can alleviate symptoms and make meals enjoyable again. Here are some dietary recommendations that can help manage the condition:
- Soft Foods: Emphasizing softer, easily chewable options is key. Foods such as mashed potatoes, yogurt, oatmeal, and cooked vegetables can minimize the risk of food becoming lodged in the diverticulum.
- Avoid Tough Textures: Steer clear of hard, coarse, or crunchy foods, like raw vegetables or tough meats, as they can aggravate swallowing difficulties.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. Water, broth, and herbal teas are great choices. Additionally, thickening beverages, as mentioned earlier, can enhance swallowability.
- Frequent, Smaller Meals: Instead of struggling through large meals, try having smaller, more frequent meals. This can reduce pressure and make the eating experience more manageable.
- Mindful Eating: Encourage a slower eating pace. Take smaller bites, chew thoroughly, and take breaks between bites to avoid overwhelming the swallowing mechanism.
For instance, Sarah, a long-time Zenker diverticulum patient, found success by preparing smoothies packed with fruits and protein powder. She shared that these nutritious options not only satisfied her hunger but also provided peace of mind during meals.
Tips for Living with Diverticulum Zenker
Living with Zenker diverticulum requires an adaptive mindset, but with the right strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some practical tips:
- Stay Informed: Knowledge is power. Understanding your condition and identifying potential symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum can empower you to seek help before complications arise.
- Communicate: Inform friends and family about your condition so they can support you during meals. Having a buddy during mealtime can alleviate anxiety and encourage.
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals to ensure you have suitable options on hand. Stock your pantry with easy-to-prepare soft foods that align with your dietary recommendations.
- Practice Stress Management: Anxiety and stress can intensify symptoms. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation into your routine.
- Join Support Groups: Connecting with others experiencing similar challenges can offer emotional support and practical advice. Sharing stories helps normalize the experience and brings comfort.
Ultimately, living with Zenker’s diverticulum is about making informed choices and cultivating a support system. By embracing dietary recommendations and implementing simple lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly enhance their everyday experiences. Remember, while managing a chronic condition can be daunting, small adjustments and positive attitudes can lead to substantial improvements in quality of life.
Read also : Unraveling the Mystery of Sarcopenia: Causes and Treatment Options
Complications and Prognosis
While many individuals manage Zenker diverticulum successfully with lifestyle changes and treatments, it’s essential to be aware of potential complications that can arise if the condition is left untreated. Here are some of the most common complications to consider:
- Aspiration Pneumonia: When food or liquids enter the lungs instead of the esophagus, it can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This serious condition can result in cough, fever, and difficulty breathing, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Malnutrition: Persistent swallowing difficulties may cause individuals to avoid eating altogether, leading to significant weight loss and malnutrition. This can impact overall health and weaken the immune system over time.
- Diverticulum Inflammation: In some cases, the diverticulum can become inflamed or infected, resulting in pain, fever, and the need for antibiotics or more invasive treatment options.
- Esophageal Obstruction: If the diverticulum grows or remains untreated, it might obstruct the esophagus, making it increasingly difficult for food to pass through, which can lead to choking episodes.
A patient named Robert faced challenges when he experienced recurrent aspiration pneumonia, underscoring the importance of early intervention. He noted, “It was a wake-up call; I needed to take my condition seriously and seek proper treatment.” By understanding these potential complications, patients can remain vigilant and take proactive steps to prioritize their health.
Prognosis and Outlook & symptoms zenker’s diverticulum
The prognosis for individuals with Zenker diverticulum largely depends on the severity of symptoms and the treatment approach. With appropriate management, many people experience significant relief from symptoms. Here are some key points regarding the prognosis:
- Highly Treatable: Zenker diverticulum is generally considered a treatable condition. Whether through non-surgical methods or definitive surgeries, most patients see an improvement in their quality of life.
- Surgical Outcomes: Surgical interventions, such as diverticulectomy, boast high success rates, with many patients reporting substantial improvements in swallowing function and a reduction in symptoms of Zenker’s diverticulum post-operation.
- Long-term Management: Though some individuals may require ongoing lifestyle adjustments or dietary changes, many find that they can lead fulfilling lives after addressing their diverticulum.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are advisable, particularly for individuals who have undergone surgery, to monitor for any recurrence or complications.
In conclusion, while there are potential complications associated with Zenker diverticulum, the overall outlook is positive with timely intervention and appropriate management strategies. Educating oneself about the condition and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals play crucial roles in navigating challenges. As individuals like Robert have experienced, with vigilance and support, living well with Zenker diverticulum is entirely possible. Embracing the journey with informed choices can empower individuals toward a healthier and more enjoyable life.
Read also: Learn about the 5 most important health of teeth other than their traditional benefits
Support and Resources
Navigating life with Zenker diverticulum can feel isolating at times, but connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide much-needed encouragement and understanding. Support groups serve as a vital resource for individuals seeking community and shared experiences. Here are some advantages of joining a support group:
- Emotional Support: Sharing challenges and triumphs with others going through similar situations can foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Practical Tips: Members often exchange insights and strategies for managing symptoms, finding the best foods to eat, or navigating medical appointments.
- Inspiration: Hearing stories of recovery and adaptation from others can spark motivation and provide a positive outlook on life with the condition.
For example, during a support group meeting, Jane shared how she transformed her meals by using recipes exchanged among members. “It was refreshing to hear everyone’s stories, and I picked up so many great meal ideas I hadn’t thought of before!” she remarked. Support groups can be found both in-person and online, offering flexibility for those with busy schedules or mobility challenges. Websites like Meetup often list local gatherings, and many health organizations also host virtual platforms for discussion.
Useful Resources for Individuals with Zenker Diverticulum
In addition to support groups, various resources can aid individuals in managing Zenker diverticulum effectively. Here are some valuable options to consider:
- Health Organizations: Organizations like the American Gastroenterological Association provide reliable information about Zenker diverticulum, management strategies, and lists of knowledgeable healthcare professionals.
- Educational Websites: Websites such as the Mayo Clinic 1)and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) 2 offer detailed articles on symptoms, treatments, and living with diverticulum conditions. These resources can empower patients to make informed decisions.
- Nutrition Guides: Specialized dieticians who understand esophageal conditions can help create personalized meal plans. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics has a wealth of resources to aid in this regard.
- Online Forums: Joining forums and discussion boards focused on esophageal disorders can provide ongoing support and a broader community. Sites like PatientsLikeMe allow individuals to share experiences and ask questions in an accepting environment.
Frequently asked questions
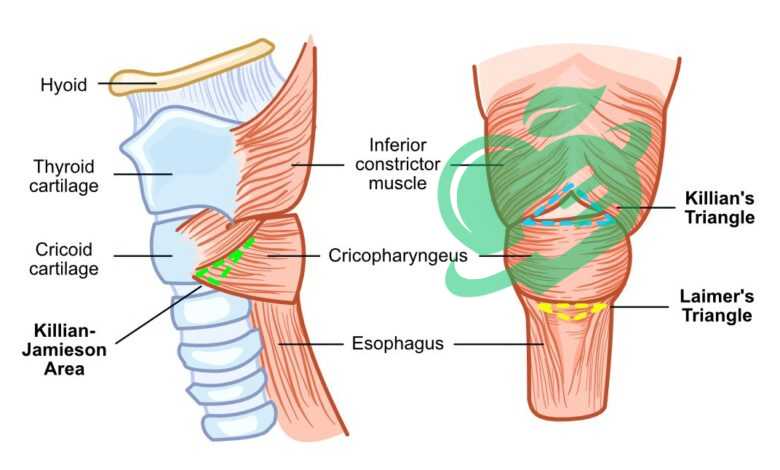
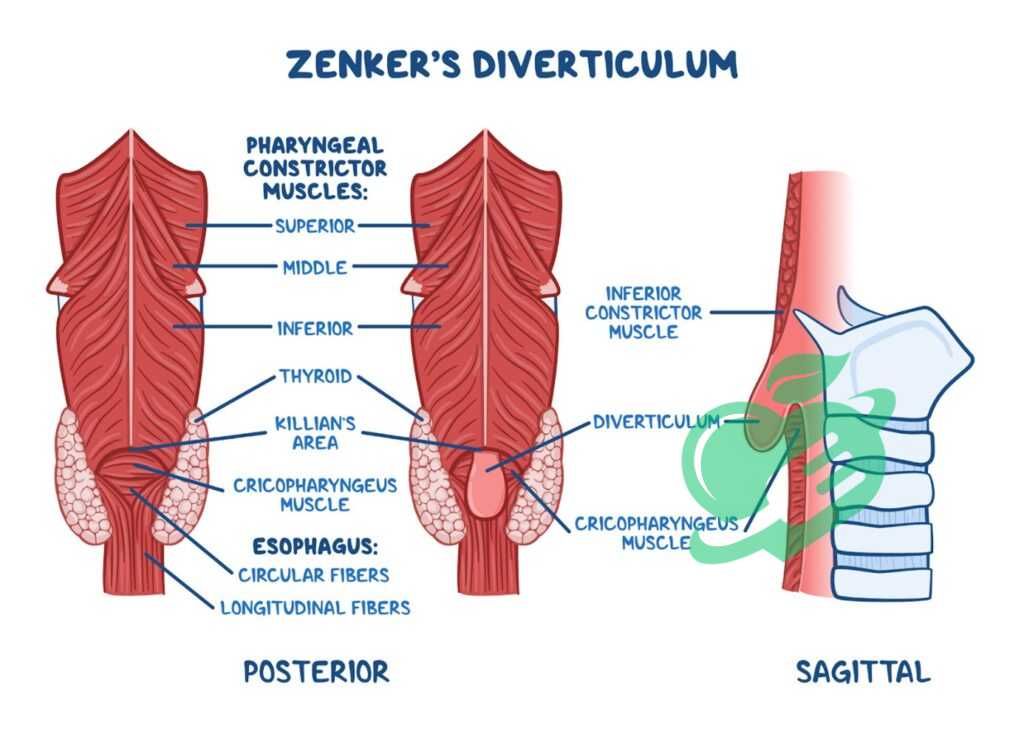
What is the difference between Killian Jamieson and Zenker’s diverticulum?
Killian-Jamieson diverticula are relatively rare and smaller in size compared to Zenker’s diverticulum. They are also less prone to causing symptoms and are less frequently linked to overflow aspiration or gastroesophageal reflux than Zenker’s diverticulum. 3
What is the difference between esophageal diverticulum and Zenker’s diverticulum?
A diverticulum is an irregular bulge or pocket that develops from the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. Zenker’s diverticulum is a specific pouch that appears in the throat, located at the start of the digestive system, just above the upper esophageal sphincter (UES). 4
s Zenker diverticulum anterior or posterior?
The practical features of Zenker’s diverticulum.
It is a diverticulum located at the back that can fill up during or after swallowing, and if it is large enough, it may shift to one side, typically leaning toward the left. 5
What muscles are derived from the 4th pharyngeal arch?
The fourth arch is responsible for the formation of the thyroid and cuneiform cartilages, along with the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles and the cricothyroid and levator veli palatini muscles. 6
What is the most common presentation of a patient with a zenker diverticulum?
Diagnosis. Zenker’s diverticulum presents with distinct symptoms and signs. The primary and most prevalent symptom is a progressive difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia). As a result of regurgitation, there may be aspiration of food into the bronchial tree, which can lead to difficulty breathing (dyspnea) due to Mendelson’s syndrome. 7
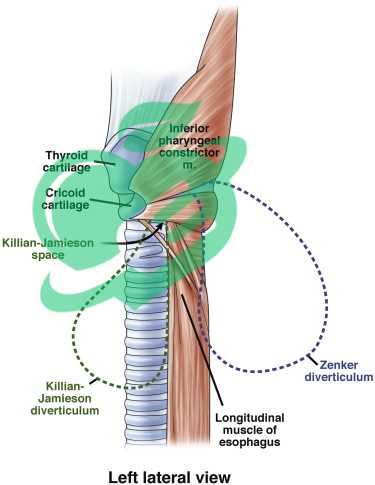
What muscles are Zenker diverticulum?
Zenker diverticula forms in a muscular gap that is typically found between the diagonal muscle fibers of the inferior constrictor muscle and the transverse fibers of the cricopharyngeus muscle. 8
What is the Killian’s triangle in Zenker’s diverticulum?
Killian’s dehiscence, or Killian’s triangle, is a triangular region in the pharyngeal wall located between the cricopharyngeus and thyropharyngeus muscles, which are components of the inferior constrictors (refer to Pharyngeal pouch for more information). This area can be considered a site of decreased resistance. 9
What is the most common location for a Zenker diverticulum?
Zenker’s diverticulum is typically found on the back wall of the pharynx at the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), situated between the lower pharynx and the esophagus. It can also develop above the UES at the suture line of the lower pharyngeal sphincter muscle, though this is less common, as is its occurrence in the lateral or posterolateral walls of the esophagus. 10
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.