DIY Fermented Foods Recipes You’ll Love

Overview of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods have captured the attention of health enthusiasts worldwide, and for good reason. From tangy yogurt to tangy kimchi, these culinary delights have been central to many cultures for centuries. Fermentation is a natural process that transforms food, breaking it down into simpler compounds while fostering the growth of beneficial microorganisms. This method not only enhances flavor but also preserves food, making it a practical solution for extending shelf life. As people become more health-conscious, the love for fermented foods is resurging, transitioning from a forgotten art to the forefront of modern nutrition. Some popular fermented foods include:
- Sauerkraut: Finely shredded cabbage that’s enjoyed for its crunchy texture and sharp flavor.
- Kombucha: A fizzy tea packed with probiotics that many people enjoy as a refreshing drink.
- Kimchi: A spicy blend of fermented vegetables that offers a punch to any meal.
These foods not only tantalize the taste buds but also contribute to overall well-being.
Benefits of DIY Fermented Foods
Making fermented foods at home can be a truly rewarding experience. Beyond the satisfaction of crafting something unique, DIY fermentation offers several notable benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Purchasing fermented foods at the store can be expensive. Making your own allows for substantial savings.
- Control Over Ingredients: Crafting your fermented treats means you know what’s going in, avoiding preservatives and additives commonly found in store-bought alternatives.
- Customization: Everyone has different tastes! DIY fermentation allows enthusiasts to experiment with flavors and adjust ingredients according to personal preferences.
- Freshness and Quality: Nothing beats the taste of fresh, homemade fermented foods. The quality is often superior to that of packaged options.
- Connection with Tradition: Engaging in this age-old practice helps revive cultural heritage, allowing individuals to reconnect with their food roots.
Embarking on a DIY fermentation journey encourages not only delicious results but also a deeper appreciation for the foods we consume.

Understanding the Fermentation Process
Now that we’ve explored the delightful world of fermented foods and the benefits of making them at home, it’s time to dive into the basics of fermentation. At its core, fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, or molds convert sugars and starches in food into acids, gases, or alcohol. This transformation not only preserves food but also enhances its flavor and nutritional value. Imagine the bubbling excitement as a batch of kombucha starts to ferment, filling your kitchen with a delightful aroma. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the fermentation process:
- Preparation: Select your ingredients and make sure they are clean and fresh.
- Inoculation: Introduce the right microorganisms, either through starter cultures or naturally present bacteria.
- Fermentation: Allow the mixture to ferment in a controlled environment, typically at room temperature. This can take anywhere from a few hours to several weeks, depending on what you are making.
- Finishing: Once fermented to your liking, the food is either transferred to storage or consumed right away.
Essential Tools and Ingredients
Before you embark on your fermentation journey, it’s essential to gather the right tools and ingredients. Below is a quick list of what you’ll need to kickstart your DIY endeavors: Essential Tools:
- Fermentation jars: Glass jars with airtight lids or specialized fermentation crocks are vital for monitoring the process.
- Weight: To keep submerged vegetables during fermentation (think clean stones or fermentation weights).
- Airlock: Helps to release gases while preventing contaminants from entering—ideal for beverages like kombucha.
Key Ingredients:
- Basic Vegetables: Cabbage for sauerkraut, carrots for pickles, or radishes for kimchi.
- Salt: Essential for creating a brine; the type can vary but use non-iodized sea salt or kosher salt.
- Water: Filtered or distilled, as chlorine in tap water can hinder fermentation.
- Optional Additives: Spices, herbs, or chili flakes for customized flavors.
With a bit of patience and these essentials, anyone can create fermented delights at home! Happy fermenting!
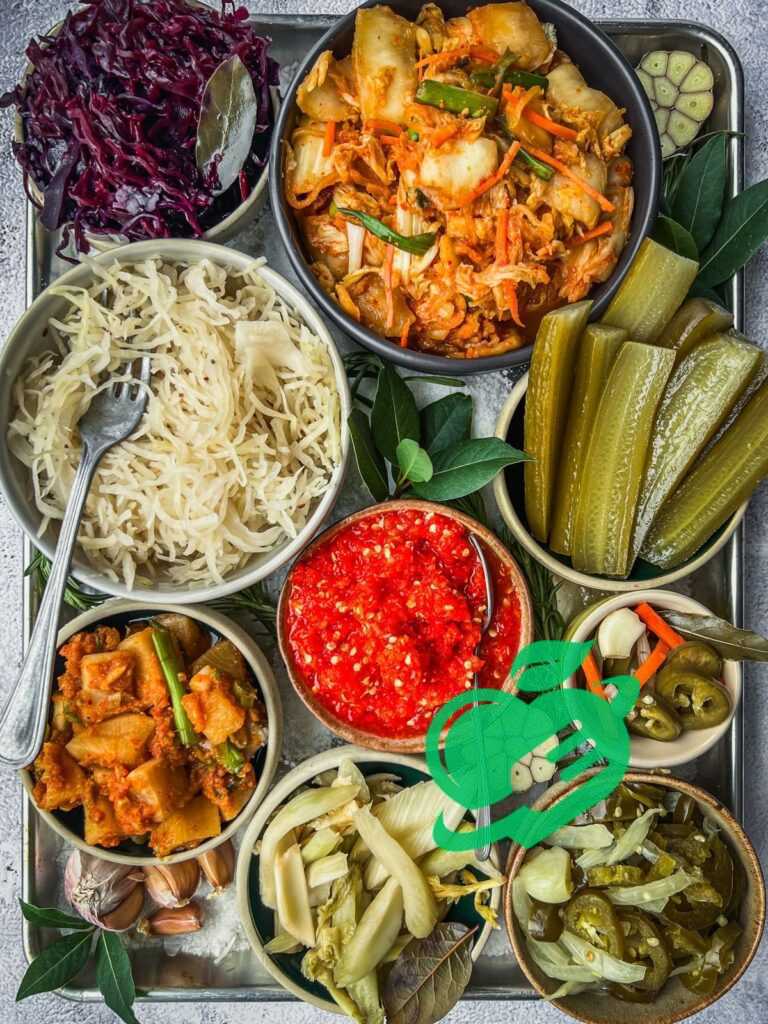

Popular DIY Fermented Foods Recipes
Having grasped the basics of fermentation, it’s time to explore some popular DIY fermented food recipes. These recipes are not only fun to make, but they also offer a delightful burst of flavor and countless health benefits. Here are four favorites to inspire your fermentation journey.
Sauerkraut
Making sauerkraut is one of the simplest ways to dive into fermentation. The crispiness of the cabbage combined with a tangy flavor makes it a perfect side dish or topping. Ingredients:
- 1 medium head of cabbage
- 2 tablespoons of sea salt
Instructions:
- Shred the cabbage finely and place it in a large bowl.
- Sprinkle the salt over the cabbage and let it sit for about 15 minutes.
- Massage the cabbage until it releases its juices.
- Pack the cabbage tightly into a fermentation jar, ensuring it’s submerged in the brine.
- Seal and let it ferment at room temperature for 2 to 4 weeks.
Kimchi
A staple in Korean cuisine, kimchi can be tweaked to suit your taste preferences. This spicy condiment bursts with flavor! Ingredients:
- 1 medium Napa cabbage
- 1/4 cup sea salt
- 3 cups water
- 5 radishes (sliced)
- 4 green onions (chopped)
- 2 tablespoons gochugaru (Korean chili powder)
- 1 tablespoon minced garlic
Instructions:
- Dissolve the salt in water and soak the cabbage for 2 hours.
- Combine radishes, green onions, garlic, and gochugaru in a bowl.
- Drain the cabbage, then mix it with the other ingredients, massaging well.
- Pack the mixture into a jar and let it ferment for about 1 week.
Kombucha
Kombucha, a fizzy tea loaded with probiotics, is bursting with flavor and is incredibly refreshing. Ingredients:
- 4 bags of black or green tea
- 1 cup sugar
- 1 SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast)
- 12 cups of water
Instructions:
- Boil 12 cups of water, steep the tea bags, and dissolve the sugar.
- Let it cool and transfer it to a fermentation jar.
- Add the SCOBY and cover with a cloth.
- Allow it to ferment for 1 to 2 weeks at room temperature, tasting periodically.
Yogurt
Homemade yogurt is creamy and customizable. A wonderful blank canvas for various toppings! Ingredients:
- 1 quart of milk (whole or low-fat)
- 2 tablespoons of plain yogurt with live cultures
Instructions:
- Heat the milk to just below a boil and let it cool to about 110°F.
- Stir in the yogurt and mix thoroughly.
- Pour the mixture into a jar, cover it with a cloth, and let it sit in a warm area for 6 to 12 hours.
- Refrigerate once set, and enjoy!
These recipes offer a fantastic gateway into the world of DIY fermented foods. Each one brings unique flavors that can be easily customized to suit your taste. Happy fermenting!
Read also: Discover the Benefits of Vitamin A for Shiny, Healthy Hair
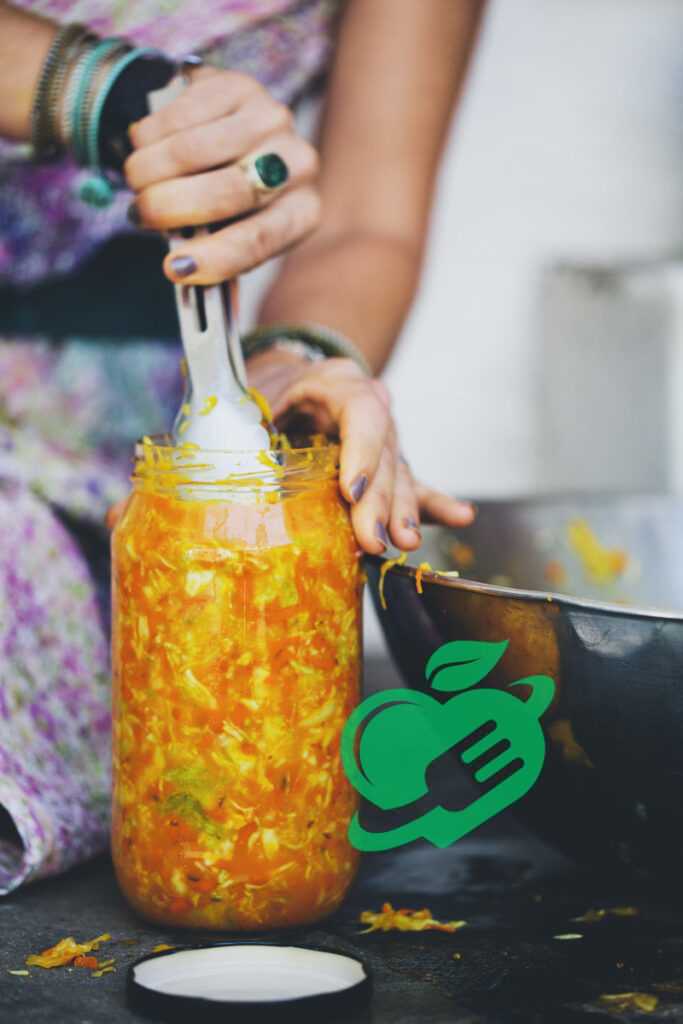

Advanced Fermented Foods Recipes
Now that you’ve mastered some popular fermented foods, it’s time to level up your fermentation skills with advanced recipes. These projects are a bit more involved but reward you with equally delicious results. Let’s dive into the world of sourdough bread, fermented pickles, and kefir!
Sourdough Bread
Sourdough bread is a fantastic staple that’s both tangy and hearty. The beauty of sourdough lies in its natural leavening process, using a starter that captures wild yeast and bacteria. Ingredients:
- 1 cup sourdough starter (active and bubbly)
- 1 cup water (room temperature)
- 3 cups all-purpose flour
- 1.5 teaspoons salt
Instructions:
- In a large bowl, combine the sourdough starter and water, mixing well.
- Gradually add the flour, followed by the salt, and mix until it forms a shaggy dough.
- Knead the dough on a lightly floured surface for about 10 minutes until smooth.
- Place it in a greased bowl, cover it with a towel, and let it rise for 4 to 6 hours.
- Shape the dough, let it rise for another 2 hours, and then bake at 450°F for about 30 minutes.
The result? A crusty loaf with a soft inside—perfect for sandwiches or toasted with butter!
Fermented Pickles
Fermented pickles are not only crunchy and tangy but are also a fantastic way to utilize seasonal vegetables. Ingredients:
- 4 cups cucumbers (small, pickling variety)
- 2 tablespoons sea salt
- 4 cups filtered water
- Spices (dill, garlic, mustard seeds, or peppercorns)
Instructions:
- In a pot, dissolve the salt in water to create your brine.
- Place cucumbers and spices in a clean jar, packing them tightly.
- Pour the brine over the cucumbers, leaving a little headspace.
- Cover with a lid or a cloth and let them ferment at room temperature for 1 to 3 weeks.
Enjoying a homemade pickle adds a crunch to your sandwiches and burgers!
Kefir
Kefir is a creamy, tangy drink, known for its probiotic benefits. Making it at home fosters a deeper appreciation for this fermented treasure. Ingredients:
- 1 cup milk (whole or low-fat)
- 2 tablespoons kefir grains
Instructions:
- Combine the milk and kefir grains in a clean glass jar, leaving some space at the top for fermentation.
- Cover with a cloth or lid (not airtight) to let it breathe.
- Allow it to ferment at room temperature for 12 to 24 hours.
- Strain the kefir grains out using a fine mesh sieve and store the finished kefir in the fridge.
Sip on your homemade kefir as a refreshing drink or use it in smoothies and salad dressings. These advanced fermented foods not only expand your culinary skills but also pack a punch of flavor and nutrition. Enjoy the satisfaction that comes with creating something uniquely yours!
Read also: Unlocking the Secrets of Pickle: Tangy and Crunchy Delight.

Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
As we continue our exploration of fermented foods, it’s crucial to delve into the remarkable health benefits they offer. Understanding how these delicious creations can positively impact our well-being can motivate anyone to add them to their diet.
Probiotic Properties
One of the primary draws of fermented foods is their rich probiotic content. Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide numerous health benefits when consumed. Here’s why they’re so important:
- Gut Health: Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is essential for good digestion and overall health.
- Mood Enhancement: Believe it or not, a significant portion of your serotonin (the happiness hormone) is produced in the gut. A balanced gut microbiome can positively influence your mood and mental health.
I’ve noticed that including yogurt and kimchi in my meals has made a noticeable difference in how I feel day-to-day. It’s fascinating how something so simple can impact our overall well-being!
Improved Digestion
Fermented foods are powerhouses when it comes to aiding digestion. Here’s how they help:
- Enzymes: The fermentation process creates enzymes that assist in breaking down food, making nutrients more accessible to the body.
- Lactose Digestion: For those who are lactose intolerant, fermented dairy products like yogurt contain live cultures that can help digest lactose more effectively.
In my experience, since I’ve started fermenting my vegetables, I find they provide an added layer of flavor while contributing to my digestive comfort—hello, sauerkraut!
Boosted Immunity
A healthy gut equals a robust immune system. Most of our immune system resides in the gut, and fermented foods play a critical role in supporting it.
- Nutrient Absorption: The probiotics and enzymes in fermented foods enhance nutrient absorption, ensuring that our bodies get the most out of our diet.
- Fighting Infections: Probiotics can help protect against harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of infections.
Incorporating a variety of fermented foods into a daily routine can be a great way to help maintain health and resilience against common illnesses, making it easier to stay energized for the day ahead. With all these benefits, it’s clear that adding fermented foods to one’s diet isn’t just a trend; it’s a step towards a healthier lifestyle!
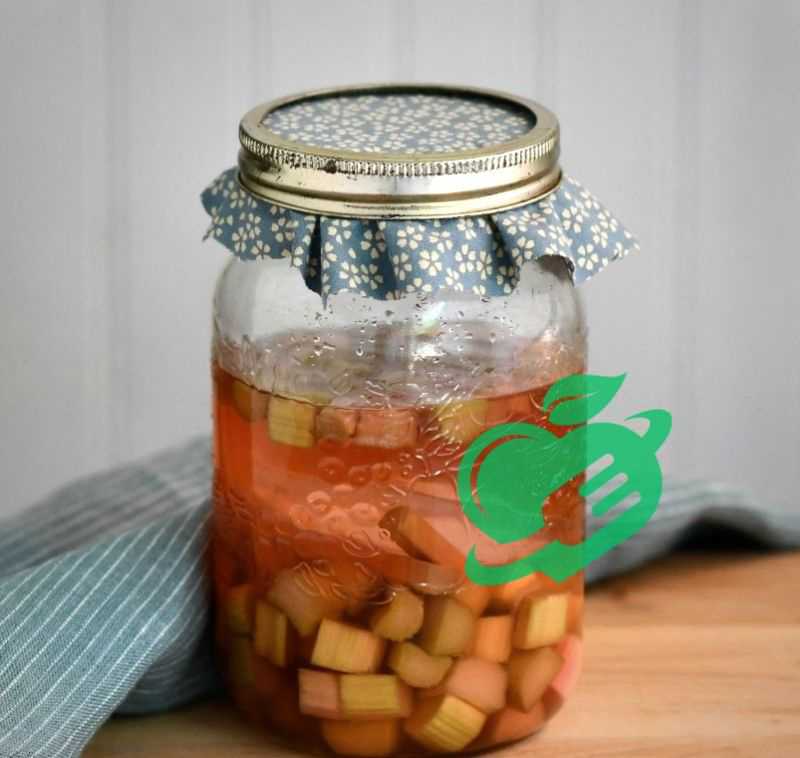

Tips for Successful Fermentation
Embarking on your fermentation journey can be exciting, but it’s essential to keep a few key tips in mind to ensure success. From creating the right conditions to troubleshooting any hiccups along the way, these insights will help you achieve the best results.
Proper Fermentation Conditions
Creating the right environment for fermentation is vital. Here are some factors to consider:
- Temperature: Most fermented foods thrive at room temperature, typically between 68°F to 75°F (20°C to 24°C). A colder environment can slow fermentation, while a warmer one might lead to over-fermentation.
- Light: Direct sunlight can alter fermentation, so it’s best to keep your creations in a dark or shaded area during the process.
- Airflow: Some fermentation processes require air exposure, while others do not. For example, when making sauerkraut, you want to prevent air exposure to limit spoilage. An airlock or covering with a cloth can help manage this balance.
As my experience shows, finding the perfect corner of the kitchen that’s not too warm or cold can result in delicious and consistent fermentations!
Read also: Boost Your Health: Combatting Vitamin K Deficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even seasoned fermenters encounter issues from time to time. Here’s a quick guide to tackle some common problems:
- Off Smells: If your ferment has a pungent odor (not the delightful tang of fermentation), it could indicate spoilage. Discard the batch and ensure your tools and environment are clean for the next try.
- Mold Growth: A thin layer of mold on the surface is not uncommon, especially in vegetable ferments. If you notice this, carefully scrape off the mold, ensuring that the food underneath is still submerged in brine.
- Too Sour: If your ferment tastes overly sour, try fermenting for less time next round or using fewer starter cultures to slow the process.
Through patience and practice, even mistakes can lead to valuable learning experiences. By applying these tips, anyone can enjoy the art of fermentation and savor the fruits of their labor!
Read also: A Nutritional Face-Off: Greek Yogurt Versus Regular Yogurt
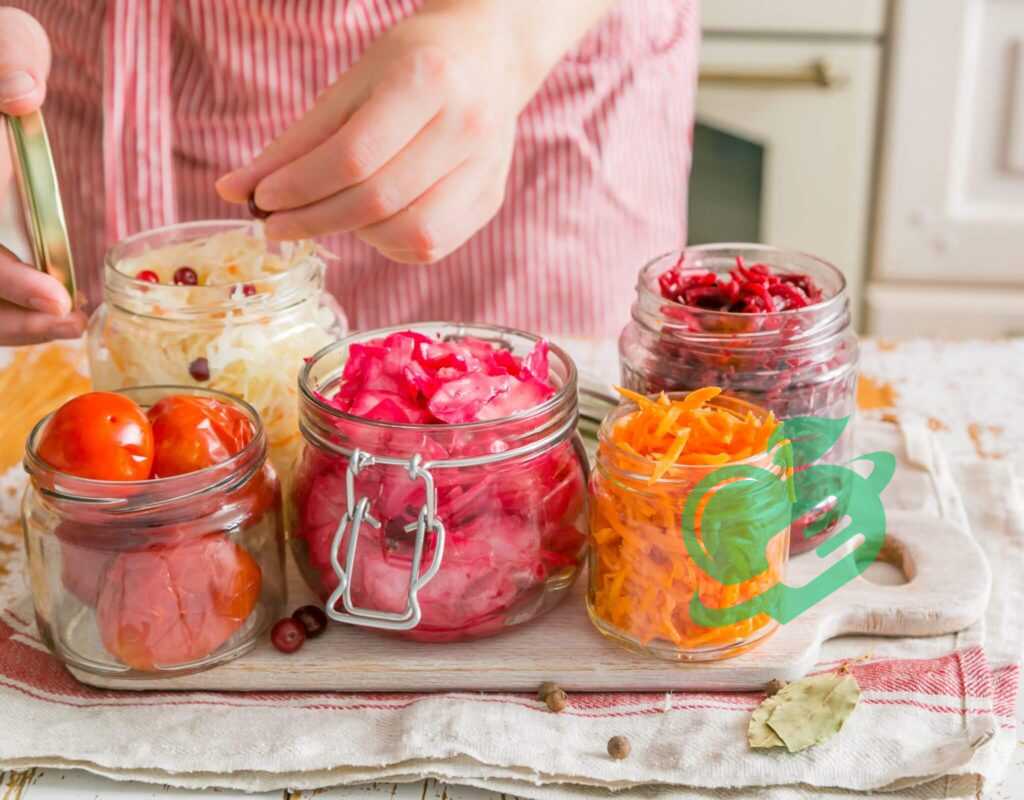

Safety Guidelines for Fermenting Foods
As you dive deeper into the world of fermentation, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Fermenting foods can be a delightful and rewarding process, but it requires careful attention to detail. This section will cover important safety guidelines, focusing on preventing contamination and proper storage to ensure your creations are both safe and enjoyable.
Preventing Contamination
Contamination can derail your fermentation journey, so taking steps to avoid it is essential. Here are key practices to follow:
- Clean Everything: Start by thoroughly washing your hands and cleaning all utensils, jars, and surfaces to remove any hazardous bacteria. Using hot, soapy water or running items through the dishwasher is a great option.
- Fresh Ingredients: Always select fresh, high-quality ingredients. Spoiled or overripe produce can introduce harmful bacteria into your ferments.
- Use Non-Reactive Containers: Opt for glass, ceramic, or food-grade plastic containers to avoid any chemical reactions that may occur with metals.
- Monitor the Conditions: Keep an eye on temperature, light exposure, and airflow during the fermentation process. Unruly conditions can lead to unwanted microbial growth.
When I first started fermenting, I encountered issues with mold due to improper sealing. A quick change to the environment helped me hone in on food-safe practices, making a world of difference!
Storage and Shelf Life
Once fermentation is complete, proper storage is essential for enjoying the fruits of your labor safely:
- Refrigeration: Most fermented foods should be stored in the refrigerator to slow down the fermentation process. Proper chilling will maintain flavor and prevent over-fermentation.
- Airtight Containers: Transfer your ferments into airtight containers or jars with secure lids. This protects them from outside contaminants and moisture loss.
- Shelf Life Awareness: Different fermented foods have varying shelf lives. For example, sauerkraut can last several months, while kombucha typically tastes best within a month. Always check for off smells, odd flavors, or changes in texture before consuming.
By adhering to these safety guidelines, you can ensure your fermentation endeavors are both successful and delightful, allowing you to confidently enjoy the health benefits of homemade fermented foods!
Read also: Exploring the Health Benefits of Sauerkraut: A Superfood for Gut Health.
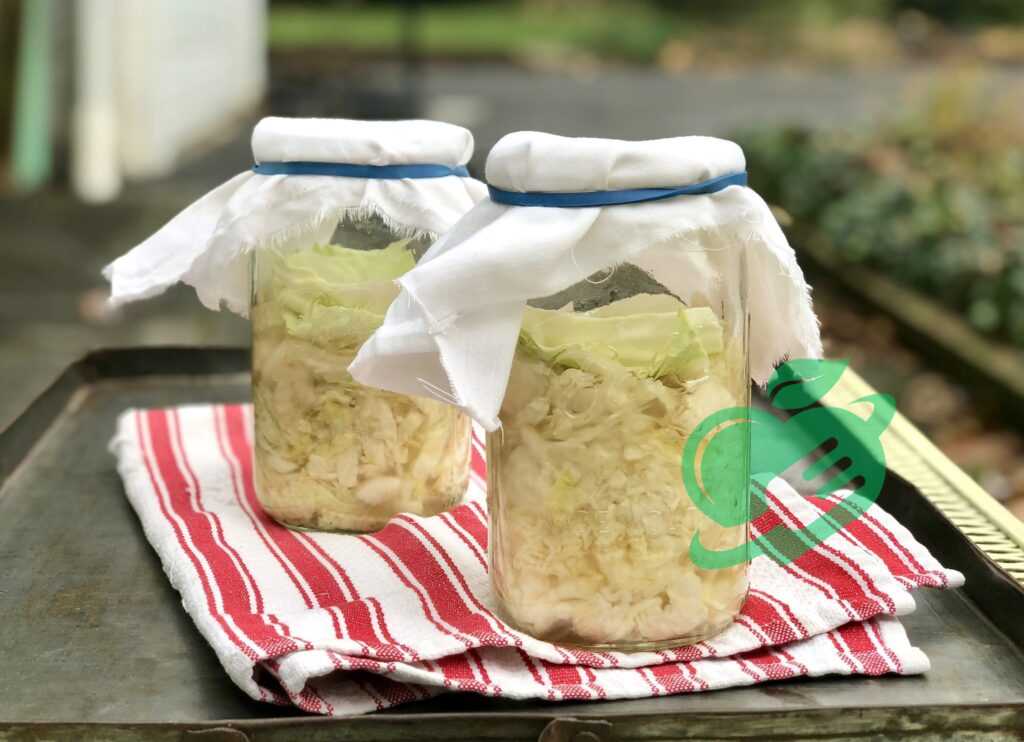

Recap of DIY Fermented Foods Benefits
As we wrap up this exploration into the fascinating world of DIY fermented foods, it’s worth revisiting the numerous benefits that come with engaging in this rewarding culinary practice.
enhancing flavor
From enhancing flavor to boosting health, the advantages of incorporating fermented foods into your diet are substantial. Here’s a quick recap of the key benefits:
- Probiotic Power: Fermented foods are packed with probiotics—those beneficial bacteria that support gut health and digestion.
- Better Digestion: The enzymes produced during fermentation can help break down complex nutrients, making them more accessible to our bodies.
- Immune Support: By fostering a healthy gut flora, fermented foods can bolster your immune system, helping you fend off common illnesses.
- Cost-Effective: Creating your fermented concoctions at home is often much cheaper than buying pre-packaged products.
Reflecting on my journey, I’ve found that not only have I saved money, but I’ve also explored my culinary creativity and embraced healthier eating habits.
Encouragement to Try Recipes
Now it’s time for you to roll up your sleeves and dive into the world of homemade fermented foods! Whether you start with the simplicity of sauerkraut or the more involved process of sourdough, each recipe is an opportunity to learn and experiment. To get started:
- Choose a Recipe: Pick one that intrigues you, and gather your ingredients and tools.
- Embrace Mistakes: Don’t be discouraged if things don’t turn out perfectly the first time. Fermentation is as much about the process as it is about the product.
- Share Your Journey: Consider documenting your experience! Taking notes or sharing with friends can make it even more enjoyable.
Frequently asked questions
What is the easiest fermented food to make?
Sauerkraut is among the easiest fermented foods to prepare. It consists of just two main ingredients: cabbage and salt, though caraway seeds may also be included at times. To create sauerkraut, simply shred the cabbage, sprinkle it with salt, and mix everything. 1
What’s the healthiest fermented food?
- Miso (refrigerated)
- Pickles (in salt, not vinegar)
- Sauerkraut (choose refrigerated)
- Kimchi.
- Kombucha (no sugar)
- Other sugar-free probiotic beverages include beet kvass and apple cider.
- Various other cultured products.
- You can effortlessly prepare fermented vegetables like sauerkraut at home! 2
What foods are best to ferment?
Vegetables like cabbage, beetroot, radish, turnip, and carrots are among the simplest foods to ferment at home since the natural bacteria present on their surfaces handle the fermentation process for you. 3
Who should not eat fermented foods?
- people with Histamine Intolerance.
- Individuals with Weakened Immune Systems.
- Children and Pregnant Women.
- People with Digestive Disorders.
- Individuals follow a rigid sodium-restricted diet.
- Gas and Bloating.
- Diarrhea.
- Allergic Reactions 4
What are the fermented Arabic foods?
The article examines fermented foods in relation to the traditional methods used in their production. This includes products such as sour milk, Karish cheese, Mish cheese, Laban Zeer, Kishk, Zabady, Shamsy bread, and various fermented foods from Sudan. 5
Your body is a mirror of what you eat, so make your food your source of strength and health. Choose with love and awareness what nourishes your body and soul, and be a friend of nature and its colors on your plate, because proper nutrition is the key to a life full of energy and wellness. Follow us constantly, as we strive to provide more useful articles and reliable information that make a difference in your daily life and help you achieve your health goals.
- restless ((↩))
- umassmed ((↩))
- heartfoundation ((↩))
- culturesforhealth ((↩))
- PubMed ((↩))