Anxiety Disorder Zoloft : What You Need to Know
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
Defining Anxiety Disorders
anxiety disorder Zoloft are prevalent mental health conditions characterized by excessive worry and fear that can interfere with daily life. Individuals experiencing anxiety disorder Zoloft Zoloft often find themselves battling overwhelming feelings of dread, nervousness, or apprehension. The pivotal aspect of these disorders is that they go beyond typical anxiety. While it’s normal to feel anxious about significant life events—like a job interview or a first date—individuals with an anxiety disorder experience persistent, often irrational anxiety that doesn’t seem to fit the situation. Consider Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer who feels a wave of anxiety every time she steps into her office. What starts as a minor worry about meeting deadlines escalates into panic attacks, making it challenging for her to focus on her work. This is a classic example of how anxiety can impair an individual’s daily functioning. The symptoms can manifest in different ways and may include:
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Sleep disturbances
Understanding these aspects is vital in identifying and managing anxiety disorders Zoloft effectively.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
There are several types of anxiety disorders, each with its unique features and triggers. Recognizing the specific type can help in tailoring appropriate treatment options. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
- GAD involves chronic anxiety about multiple aspects of life, from daily responsibilities to health concerns.
- Individuals may feel overwhelmed even without specific triggers.
- Panic Disorder:
- Characterized by recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden periods of intense fear or discomfort.
- Symptoms can include a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and feelings of impending doom.
- Social Anxiety Disorder:
- This disorder involves an intense fear of social situations, leading to avoidance of interactions.
- Individuals may experience significant anxiety about being judged or embarrassed in social contexts.
- Specific Phobias:
- Phobias are irrational fears associated with particular objects or situations (like spiders, heights, or flying).
- The fear response is disproportionate to the actual threat posed.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
- OCD is characterized by obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors that the person feels compelled to perform.
- Individuals often recognize that their obsessions are irrational but feel unable to control them.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
- This can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event.
- Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety related to triggers that remind them of the trauma.
Each type of anxiety disorder requires a unique approach in treatment, emphasizing the need for accurate diagnosis and tailored therapeutic strategies. Understanding these disorders not only helps those affected but also fosters empathy and support from friends and family. It is important to remember that anxiety disorders are manageable, and help is available.

Overview of Zoloft
What is Zoloft?
Zoloft, generically known as sertraline, is a widely prescribed medication belonging to a class of antidepressants known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It is commonly used to treat various mental health conditions, including depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. For many individuals, Zoloft serves as a lifeline to a more balanced emotional state. Consider John, a 35-year-old teacher who struggled with anxiety for years; after starting Zoloft, he found that he could engage in social situations without feeling overwhelmed. Zoloft helped him reclaim his confidence. When prescribed, Zoloft is usually introduced in low doses, which can be gradually increased based on the individual’s response and tolerance to the medication. The versatility of Zoloft is one reason why healthcare providers often consider it as a first-line treatment option for anxiety disorder Zoloft . Some key points about Zoloft include:
- Administration: Typically taken once daily, with or without food.
- Onset of Action: It may take several weeks to feel the full benefits of Zoloft.
- Availability: Zoloft comes in tablet form and as an oral solution, making it convenient for patients.
How Zoloft Works for Anxiety
Understanding how Zoloft works helps demystify its role in managing anxiety. Zoloft primarily operates by increasing levels of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter linked to mood stabilization. All humans have serotonin receptors, which play a critical role in regulating emotional well-being. When anxiety strikes, often the serotonin levels are in flux, leading to heightened feelings of panic and distress. Here’s how Zoloft helps alleviate an anxious state:
- Enhancing Serotonin Levels: By preventing the reabsorption of serotonin, Zoloft increases the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic gap between neurons. This boost can help improve mood and promote a sense of calmness.
- Reducing Anxiety Symptoms: Patients frequently report a reduction in feelings of restlessness, irritability, and overall anxiety levels after starting Zoloft.
- Improving Functionality: As anxiety diminishes, many individuals notice improvements in their daily functioning—thinking more clearly, engaging in social activities, and performing better at work.
For instance, after a few weeks on Zoloft, Emily, who had avoided interactions due to social anxiety, felt empowered to join group events and even make small talk—transformations that significantly enhanced her quality of life. In summary, Zoloft stands out as a key player in treating anxiety disorder Zoloft . By promoting serotonin levels and alleviating anxiety symptoms, it opens doors for individuals to engage more fully in their lives, leading to a brighter outlook and healthier interactions.
Treating Anxiety Disorders with Zoloft
Efficacy of Zoloft in Treating Anxiety
Zoloft has shown substantial efficacy in treating various anxiety disorder Zoloft , and its popularity among healthcare providers reflects this success. Clinical studies have revealed that approximately 60-80% of patients observe significant improvement in their anxiety symptoms when using Zoloft. Take, for example, Lisa, a 40-year-old mother of two who suffered from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). After consulting her doctor and starting Zoloft, she quickly noticed that tasks she once considered daunting—like attending school events or going to the grocery store—became manageable. Lisa’s story is quite common; many users report feeling a cloud of anxiety lift after weeks of consistent treatment. Research highlights some key benefits of Zoloft for anxiety, which include:
- Rapid Symptom Relief: Although it may take a few weeks to feel the medication’s full effects, many users report noticeable changes in anxiety levels within a couple of weeks.
- Long-term Management: Zoloft can be effective for long-term management, allowing individuals to lead fulfilling lives without the weight of constant anxiety.
- Low Risk of Dependency: Unlike benzodiazepines, which can lead to addiction, Zoloft is non-habit forming, making it a safer option over time.
Nonetheless, the efficacy of Zoloft can vary from person to person. It’s essential for individuals to monitor their responses and work closely with healthcare providers to tailor the treatment to their specific needs.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
When it comes to Zoloft, dosage and administration play a crucial role in optimizing treatment outcomes. Every individual’s situation is different, which is why healthcare providers usually start with lower doses and adjust according to each person’s unique needs. General guidelines for Zoloft dosage include:
- Initial Dose: The typical initial dose for adults is often set at 50 mg per day, especially for anxiety-related conditions.
- Adjustment Period: Depending on how well an individual responds, doctors may increase the dose in increments of 25 mg or 50 mg, with a maximum recommended dosage of 200 mg per day.
- Administration Tips: Zoloft is usually taken once daily, preferably in the morning or evening, and can be taken with or without food to enhance convenience.
For instance, Chris, a 27-year-old who started on 50 mg for panic disorder, found that after a month, he felt his anxiety diminish significantly. After discussing his progress with his doctor, they decided to increase his dosage to 75 mg, which helped him reach an optimal balance. Moreover, it’s important for users to take Zoloft consistently to maintain stable levels in the bloodstream. Skipping doses or inconsistently taking the medication can hinder its effectiveness. Monitoring any changes and communicating openly with healthcare professionals will ensure a tailored and effective treatment protocol. In conclusion, Zoloft offers a promising approach to managing anxiety disorder Zoloft. Through careful dosage and administration, many individuals can find relief from anxiety and reclaim their lives.
Read also : From Panic to Recovery: Dealing with Anxiety Attack Hangover

Managing Side Effects
Common Side Effects of Zoloft
Though Zoloft is effective for many individuals dealing with anxiety disorder Zoloft, like all medications, it can come with a set of common side effects. Understanding these potential reactions can play a vital role in managing expectations and approaching treatment proactively. Some of the most frequently reported side effects of Zoloft include:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, diarrhea, and dry mouth are common, particularly when starting the medication.
- Fatigue or Drowsiness: Some individuals may experience a sense of tiredness, affecting their overall energy levels.
- Insomnia: Troubling sleep patterns can arise, leading to difficulties in falling or staying asleep.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Issues such as decreased libido or difficulties achieving orgasm can occur, which may be distressing for some individuals.
- Weight Changes: Some people report weight gain or loss during treatment.
For instance, Mike, a 32-year-old software engineer, initially found relief from his anxiety with Zoloft. However, he struggled with fatigue and stomach upset for the first few weeks. Recognizing that these side effects were common, he felt more equipped to discuss them openly with his doctor. Most side effects tend to diminish as the body adjusts to the medication, typically within the first few weeks. Nevertheless, ongoing side effects should not be ignored, and addressing them is essential for a successful treatment journey.
Coping Strategies for Side Effects
Managing any side effects while remaining on Zoloft can feel daunting, but various strategies can help ease the process. Here are some effective coping methods:
- Gradual Dose Adjustment: If side effects are detrimental, talking to a healthcare provider about gradually adjusting the dosage can often yield better tolerability.
- Stay Hydrated and Nourished: Keeping up with hydration and maintaining a balanced diet can alleviate gastrointestinal issues. Foods like bananas, yogurt, and ginger tea may help settle an upset stomach.
- Establish a Sleep Routine: To combat insomnia, creating a calming pre-sleep routine can work wonders. Techniques may include reducing screen time, practicing relaxation exercises, or reading a book before bedtime.
- Open Communication: Engaging in consistently open dialogues with healthcare providers about side effects is crucial. They may offer solutions or alternative treatments that suit an individual’s needs.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practicing mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can complement Zoloft’s effectiveness while also providing tools to manage anxiety and improve mental well-being.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who are navigating similar journeys can provide perspective and comfort. Support from peers helps individuals feel less isolated in their experiences.
As seen with Sarah, who took Zoloft and faced a mix of side effects, reaching out to her doctor and implementing some of these strategies led to a smoother experience. She discovered that taking Zoloft with food significantly lessened her stomach upset, and mindfulness practices helped her tackle fatigue. In summary, while side effects may pose challenges during treatment with Zoloft, a proactive approach involving various coping strategies can greatly enhance the experience and empower individuals to continue on their path to recovery.

Precautions and Considerations
Precautions Before Taking Zoloft
Before starting Zoloft, it’s essential to take specific precautions to ensure safe and effective treatment. Not every individual is suited for this medication, and being informed can help create the best possible outcomes. Here are several important considerations:
- Medical History: Be sure to discuss any pre-existing medical conditions with your healthcare provider. Conditions such as liver problems, epilepsy, or a history of bipolar disorder can influence whether Zoloft is appropriate for you.
- History of Suicidal Thoughts: There may be increased risks associated with suicidal thoughts, particularly among younger patients. Be candid about past mental health struggles to receive the right care.
- Pregnancy and Nursing: If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, discussing the implications of Zoloft with your doctor is critical. Zoloft can pass through breast milk, potentially impacting a nursing infant.
- Age Considerations: Children and adolescents should be monitored closely when taking Zoloft, given their heightened sensitivity to SSRIs.
- Allergic Reactions: Disclose any known allergies to medications to avoid adverse reactions. Signs of an allergic reaction can include rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
Sarah, a young mother contemplating Zoloft, took the time to discuss her family history and previous wellness issues with her doctor. This thorough conversation helped ensure Zoloft was the right fit for her. Keeping these precautions in mind empowers patients to engage in informed decision-making before beginning their Zoloft treatment journey.
Interactions with Other Medications
Another crucial aspect to consider before taking Zoloft is its potential interactions with other medications. Such interactions can lead to reduced effectiveness or even harmful reactions. Here are some key interactions to be aware of:
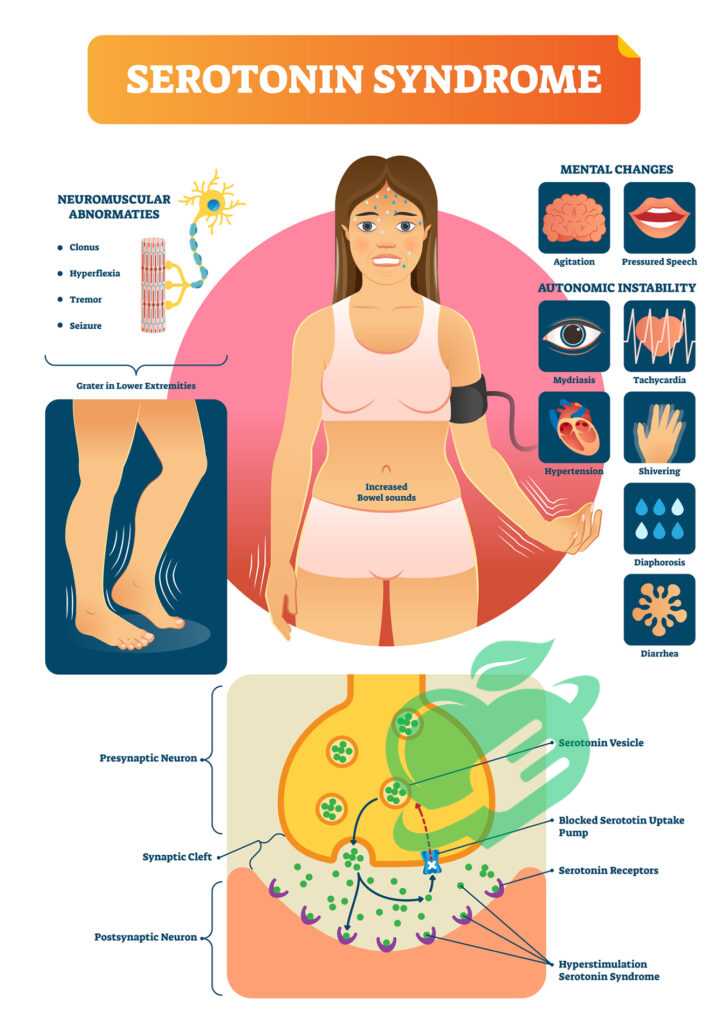
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Taking Zoloft with MAOIs (used for depression) can result in severe and dangerous reactions. It’s recommended to have a waiting period of at least two weeks between discontinuing MAOIs and starting Zoloft.
- Other Antidepressants: Combining Zoloft with other SSRIs, SNRIs, or other antidepressants can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by confusion, rapid heart rate, and high blood pressure.
- Blood Thinners: Zoloft may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood-thinning medications like warfarin. Ongoing monitoring is vital in these cases.
- Certain Pain Medications: Opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also elevate bleeding risks when paired with Zoloft.
- Herbal Supplements: Natural products like St. John’s Wort can amplify the effects of Zoloft, enhancing the risk of serotonin syndrome.
For example, when Chris started Zoloft, he was already using over-the-counter pain relievers for chronic headaches. A comprehensive conversation with his healthcare provider helped him adjust his regimen safely. In conclusion, recognizing and addressing precautions before starting Zoloft, as well as being aware of potential drug interactions, are critical steps toward effective treatment. Informed patients who actively engage in discussions with their healthcare providers are better positioned to navigate their journey with Zoloft and ensure their safety and well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
When to Consult a Doctor or Psychiatrist
Knowing when to seek professional help is a crucial aspect of managing anxiety disorder Zoloft . While some individuals may experience mild anxiety that can be addressed through lifestyle changes or self-care techniques, others may need a more comprehensive approach. Recognizing the signs can make all the difference. Here are some indicators that it might be time to consult a doctor or psychiatrist:
- Persistent Symptoms: If anxiety is consistently affecting day-to-day life, impacting your work, relationships, or daily routines, it’s important to seek professional advice.
- Physical Symptoms: Experiencing frequent physical symptoms such as headaches, stomach upset, rapid heart rate, or difficulty sleeping without any apparent medical cause can be a signal that anxiety is at play.
- Increased Severity: If anxiety symptoms worsen over time or lead to panic attacks and overwhelming feelings of dread, this is a strong signal to reach out for help.
- Substance Abuse: Turning to drugs or alcohol to cope with anxiety symptoms is a concerning sign and could necessitate professional intervention.
- Thoughts of Self-Harm: If feelings of hopelessness or thoughts of self-harm arise, it is vital to seek immediate help from a professional.
Take the case of Emily, a college student who felt the pressures of academic life weighing her down. Initially, she tried to cope on her own, but when her anxiety escalated to the point where she couldn’t focus or enjoy activities she used to love, she recognized it was time to reach out. Consulting a psychiatrist provided her with the guidance she needed to begin her recovery journey.
Importance of Therapy Alongside Medication
While medication like Zoloft can play a pivotal role in treating anxiety disorder Zoloft , combining it with therapy often enhances the overall effectiveness of treatment. Therapy provides individuals with tools and strategies to address the underlying causes of their anxiety while medication helps manage symptoms. Here are several benefits of incorporating therapy into a treatment plan:
- Coping Strategies: Therapy equips individuals with coping mechanisms tailored to their specific triggers, which medication alone may not achieve.
- Understanding Triggers: Engaging with a therapist can help identify the root causes of anxiety and examine thought patterns, enabling individuals to address behavioral changes effectively.
- Supportive Environment: Therapy offers a safe space to express emotions and experiences, providing validation and understanding, which can be instrumental in the healing process.
- Building Skills: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can empower individuals with practical skills to manage their anxiety in real-time, reducing dependence solely on medication.
For instance, Michael, a 45-year-old office worker, found that while Zoloft helped him feel more stable, therapy consisting of CBT sessions allowed him to recognize and challenge irrational thoughts that contributed to his anxiety. This combination allowed him to lead a more fulfilling life, both personally and professionally. In conclusion, proactively seeking professional help when dealing with anxiety disorder Zoloft is essential for recovery. Understanding when to consult a healthcare provider and recognizing the importance of integrating therapy with medication can significantly enhance an individual’s path to well-being. It’s a journey that requires support, both from professionals and within one’s community.
Read also : Top 10 Uses of Magnesium Oil for a Healthier You



