Is POTS Disease Hereditary? Find Out the Truth!

Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Overview of Pott’s Disease
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? Disease, also known as spinal tuberculosis, is a severe form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis that primarily affects the spine. It arises when Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the vertebrae, causing inflammation and sometimes leading to the destruction of spinal bones. ThisPOTS Disease can result in debilitating pain, deformity, and neurological deficits if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Many individuals might associate tuberculosis solely with lung infections, but Pott’s Disease highlights how this bacterium can manifest in various forms. It often presents with symptoms that include:
- Persistent back pain
- Fever
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
The unique aspect of Pott’s Disease is its slow onset. Unlike acute infections, the symptoms may develop gradually, making it easy for patients and even doctors to overlook the condition in its earlier stages. Personal experiences shared by patients often reveal a journey through misdiagnosis before receiving the correct treatment.
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Historical Background
The history of Pott’s Disease dates back several centuries. Named after the English surgeon Percivall Pott, who first described it in the 18th century, this disease has long been a challenge in both medical and social contexts. In Pott’s time, tuberculosis was notoriously prevalent and was often associated with poor living conditions and inadequate healthcare. Key points in the historical understanding of Pott’s Disease include:
- 18th Century: Percivall Pott’s descriptions laid the groundwork for recognizing spinal tuberculosis.
- 19th Century: The connection between tuberculosis and spinal deformities was firmly established.
- 20th Century: Advances in imaging and medical treatments began to transform how this disease was diagnosed and managed.
Over the years, societal perceptions of tuberculosis have evolved, influencing how Pott’s Disease is viewed today. Improved awareness and, importantly, understanding its genetic factors can significantly aid in prompt diagnosis and effective management.
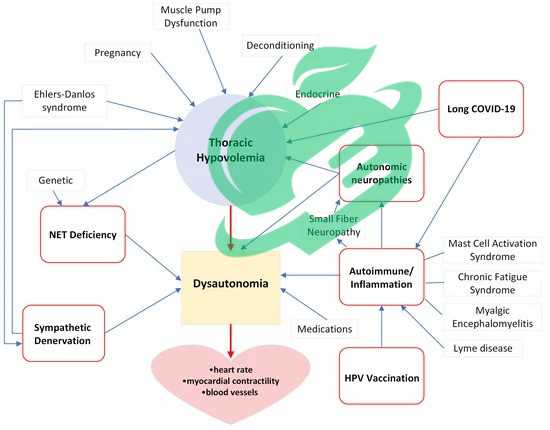
Genetics and Pott’s Disease
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Genetic Factors Involved
Understanding the genetic factors involved in Pott’s Disease opens up an intriguing aspect of this condition. While the primary cause remains the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining who develops the disease and its severity. Research has identified several genetic components that may contribute to the risk of developing Pott’s Disease, including:
- Immune Response Genes: Variants in genes that regulate immune responses can influence how effectively the body responds to tuberculosis.
- Cytokine Genes: Changes in cytokine production may enhance or diminish inflammation, affecting disease progression.
- Family History: Individuals with a family history of tuberculosis-related illnesses may be more susceptible, suggesting a hereditary component.
Personal anecdotes often highlight the importance of a family’s medical history. For instance, one individual might recall their grandmother suffering from tuberculosis, prompting them to be vigilant about potential symptoms or even seek genetic testing when experiencing back pain.
Role of HLA-B27 Gene
Among the various genetic markers associated with Pott’s Disease, the HLA-B27 gene has garnered particular attention. This gene is part of the human leukocyte antigen complex, influencing the immune system’s ability to recognize and respond to pathogens. In people carrying the HLA-B27 antigen, there is a higher likelihood of developing certain inflammatory diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis. Interestingly, research indicates that this genetic marker may also be linked to an increased susceptibility to Pott’s Disease. Some key points about HLA-B27 include:
- Increased Risk: Individuals with the HLA-B27 antigen may have a heightened risk of not just Pott’s Disease but also other related conditions.
- Autoimmune Connections: The presence of this gene may indicate an underlying autoimmune dysfunction, which could exacerbate the effects of tuberculosis.
Ultimately, recognizing the implications of genetic factors, including the HLA-B27 gene, enriches the understanding of Pott’s Disease and may guide preventive strategies and treatment approaches tailored to individual patients.
Understanding the Pathogenesis
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Tuberculosis Infection
At the heart of Pott’s Disease lies the infectious bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a resilient pathogen that primarily targets the lungs but can wreak havoc elsewhere in the body as well. Understanding how tuberculosis infection leads to spinal involvement is essential for comprehending Pott’s Disease. When people are infected with M. tuberculosis, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream, spreading to various organs. Factors that influence this dissemination include:
- Immune Response: A person’s immune system can determine whether the infection is contained or spreads. Those with weakened immune systems—due to conditions like HIV or severe malnutrition—are at heightened risk.
- Chronic Inflammation: Ongoing inflammation may make the spinal tissues vulnerable, creating an environment conducive to infection.
Many patients recount their experiences of gradual health decline, with symptoms initially resembling a mild flu, only to discover later that their condition had escalated to Pott’s Disease.
Spinal Involvement
Once the bacteria infiltrate the body, they frequently take aim at the spine, leading to Pott’s Disease. The infection tends to localize in the vertebrae and can subsequently spread to adjacent structures. Understanding the mechanics of spinal involvement helps demystify the disease:
- Preferred Sites: The lumbar and thoracic vertebrae are the most commonly affected areas due to their rich blood supply and higher metabolic activity.
- Destruction of Bone: The bacteria trigger a pathological inflammatory response, leading to bone destruction and the formation of pus-filled abscesses that may impinge on the spinal cord.
Patients often describe excruciating back pain, which can limit mobility and affect daily life. This pain is often a hallmark symptom, prompting many to seek medical advice early in the disease progression. Pott’s Disease serves as a poignant reminder of how tuberculosis can extend beyond the lungs, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies. Understanding the pathogenesis behind this condition is critical for healthcare providers and patients alike to navigate its complexities effectively.
Read also : Unveiling the Secrets of ECG Readings for Better Health
Diagnosis and Genetic Testing
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Clinical Presentation
Diagnosing Pott’s Disease can be quite challenging, primarily due to its insidious onset and overlap with other conditions. Individuals typically present with a range of symptoms that can lead to confusion. Common clinical manifestations include:
- Back Pain: Often the most prominent symptom, patients describe it as persistent and localized. Sometimes, it radiates to the legs or involves muscle spasms.
- Systemic Symptoms: Fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss may accompany back pain, resembling other illnesses, including different forms of tuberculosis.
- Neurological Symptoms: In advanced cases, pressure on the spinal cord may lead to numbness, tingling, or even paralysis.
It’s not uncommon to hear stories from patients who initially thought their back pain was due to muscle strain or sedentary lifestyle, only to discover later that they were harboring an underlying infection.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
Once a healthcare provider suspects Pott’s Disease, a comprehensive diagnostic approach ensues. Several tools are at their disposal:
- X-rays: These are often the first imaging studies conducted. They can reveal vertebral destruction or changes in alignment.
- MRI and CT Scans: MRI is particularly effective at visualizing soft tissue involvement and can detect abscesses more readily than X-rays. These imaging techniques allow for a clearer picture of how deep the infection has penetrated into the spinal structures.
Accompanying imaging studies, laboratory tests are also crucial:
- Tuberculin Skin Test or IGRA: These tests detect exposure to M. tuberculosis. However, a positive result isn’t definitive for Pott’s Disease but can guide the clinician down the right diagnostic path.
- Blood Tests: Elevated inflammatory markers or specific cultures may provide additional information to confirm an active tuberculosis infection.
Ultimately, early diagnosis is pivotal, as it can radically affect the treatment outcome. As Pott’s Disease often masquerades as less serious issues, recognizing the signals and seeking timely medical advice is crucial for patients experiencing symptoms.

Treatment Approaches
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Antibiotic Therapy
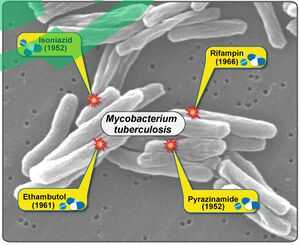
When it comes to treating Pott’s Disease, antibiotics play a central role in combating the underlying Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. The treatment protocol usually involves a combination of antibiotics to ensure efficacy and to prevent drug resistance. Standard Regimen:
- Initial Phase: Treatment typically starts with a combination of rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for the first two months.
- Continuation Phase: Following this, rifampicin and isoniazid are usually continued for an additional four to seven months.
Many patients share their experiences with antibiotic therapy, noting that while the initial side effects—like nausea or fatigue—can be challenging, the gradual relief from symptoms is often worth the struggle. It’s essential for patients to adhere strictly to the treatment regimen, as noncompliance can lead to complications or treatment failure.
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Surgical Interventions
In certain cases, particularly when there is significant spinal deformity or neurological compromise, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery can address structural issues while alleviating symptoms, ensuring the best possible quality of life for patients. Here are the most common surgical approaches:
- Decompression Surgery: This procedure helps relieve pressure on the spinal cord caused by abscesses or deformities.
- Spinal Stabilization: Surgeons may use instruments or bone grafting to stabilize the affected vertebrae, preventing further spinal damage.
- Abscess Drainage: If an abscess develops, it may need to be surgically drained to reduce pain and promote recovery.
Patients often recount their surgical journeys, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive discussions with their medical teams about potential risks and recovery expectations. The decision for surgery typically follows a careful evaluation of the patient’s overall condition and can offer significant relief when conservative treatments fail. Overall, the treatment approach for Pott’s Disease is multifaceted, often requiring a combination of antibiotics and surgery. The goal is always to manage the infection effectively while enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
Read also: From Panic to Recovery: Dealing with Anxiety Attack Hangover
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Prognosis and Genetic Counseling
Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals diagnosed with Pott’s Disease largely hinges on several factors, including prompt diagnosis, compliance with treatment, and the extent of spinal involvement. Many patients can achieve significant recovery if they adhere to the prescribed antibiotic therapy and, when necessary, undergo surgical intervention.
- Successful Treatment Rates: Around 80% of patients respond well to combined antibiotic therapy. Early intervention often leads to improved outcomes.
- Quality of Life: Beyond the elimination of the infection, effective treatment can result in substantial improvements in mobility and pain relief. Many patients share stories of regaining their ability to engage in everyday activities, such as returning to work or pursuing hobbies.
However, it’s important to note that some patients may experience long-term complications, such as residual back pain or spinal deformities, that require ongoing management. Personal accounts often reveal a mix of relief and the challenge of adjusting to life post-diagnosis, reinforcing the need for continuous support.
Genetic Risk Assessment
With advancements in genetic research, understanding the genetic predispositions that may influence Pott’s Disease has become crucial. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights, particularly for individuals with a family history of tuberculosis or those who carry high-risk genes like HLA-B27. Key aspects of genetic counseling include:
- Assessment of Family History: Counselors can help determine if a hereditary component may place individuals at heightened risk for developing the disease.
- Testing for Genetic Markers: For those with notable family histories, genetic testing may be recommended to identify specific risk factors.
Many families have benefited from genetic counseling, allowing them to embrace proactive healthcare strategies, such as routine screenings or early consultations with healthcare providers. Ultimately, the prognosis for Pott’s Disease can be quite favorable, especially with modern medical interventions. Genetic counseling enhances understanding and awareness, empowering patients and their families to make informed health decisions while navigating this complex disease.
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Research and Future Directions
Emerging Studies
As the medical community continues to advance its understanding of Pott’s Disease, several emerging studies offer promising insights into its treatment and pathogenesis. Researchers are focusing on various aspects of the disease, including the interplay between genetics and environmental factors that contribute to infection susceptibility.
- Genetic Research: New studies are exploring the genetic mechanisms that may increase a person’s risk of developing Pott’s Disease. Understanding these factors can lead to tailored prevention strategies.
- Immunological Studies: Researchers are investigating the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis to identify potential vulnerabilities in the bacteria. This could pave the way for novel immunotherapies that enhance the body’s ability to fight off infections.
For instance, a recent study indicated that individuals with specific immune profiles might respond differently to traditional treatments, highlighting the need for personalized medical approaches. Patients often express hope when they hear about new research, as they believe it may lead to more effective treatments and better outcomes.
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Potential Genetic Therapies
The future of Pott’s Disease treatment could be significantly impacted by advancements in genetic therapies. As researchers delve deeper into the genetic factors associated with susceptibility, several innovative approaches are on the horizon:
- Gene Editing Technologies: Techniques like CRISPR could potentially be used to modify genes linked to increased risks of developing Pott’s Disease, effectively reducing susceptibility.
- Targeted Therapies: As more is understood about the relationship between specific genes and tuberculosis infection, targeted therapies might emerge, complementing traditional antibiotic treatments.
Many patients and families are understandably excited about these potential innovations. Living with Pott’s Disease can be challenging, but the prospect of genetic therapy offers a glimpse of hope for not just better treatment but also a possible preventive measure. As research continues to evolve, the burden of Pott’s Disease may one day diminish, paving the way for a future where the fear of this condition can be significantly lessened through advanced genetic understanding and intervention. This ongoing commitment to research underscores the medical community’s dedication to improving patient outcomes and enhancing overall quality of life.
Read also : Empowering Your Health Journey with an Endocrinologist’s Care
Is POTS Disease Hereditary?
Importance of Genetic Understanding
The journey through Pott’s Disease is not just a medical journey; it’s a path of self-discovery and understanding the intricacies of genetics and infection. Recognizing the genetic influences that contribute to the disease equips patients and healthcare providers with the tools to better manage and prevent future occurrences.
- Empowerment Through Knowledge: Patients who understand their genetic predispositions can make informed decisions about their health. This knowledge can guide screening practices, lifestyle choices, and even family planning.
- Advancements in Personalized Medicine: A genetic understanding fosters the development of personalized treatment plans, leading to improved outcomes for individuals diagnosed with Pott’s Disease.
Many patients share transformative experiences where gaining insight into the genetic aspects of their condition has allowed them to take control of their treatment journey, effectively changing how they perceive their overall health.
Is POTS Disease Hereditary? -Summary of Key Points
In summary, Pott’s Disease, while challenging, can be effectively managed through a combination of antibiotic therapy, surgical interventions, and a profound understanding of genetic predispositions. Key points include:
- Prognosis: Early diagnosis and treatment greatly enhance long-term outcomes, with an 80% success rate for antibiotic therapy.
- Genetic Factors: Studies indicate that genetic markers, such as HLA-B27, play a significant role in susceptibility, guiding the importance of genetic counseling.
- Research Trends: Emerging studies and potential genetic therapies hold promise for more effective treatments in the future.
As the landscape of medicine evolves, the focus on genetics is becoming increasingly paramount. The hope is that with continued research and public understanding, we can rewrite the story of Pott’s Disease—transforming it from a condition marked by fear and uncertainty into a manageable and understood health issue. Overall, embracing genetic comprehension is essential, not just in terms of individual health but also in enhancing societal awareness and promoting proactive healthcare. Through shared knowledge and ongoing research, the future looks optimistic for those navigating the complexities of Pott’s Disease.