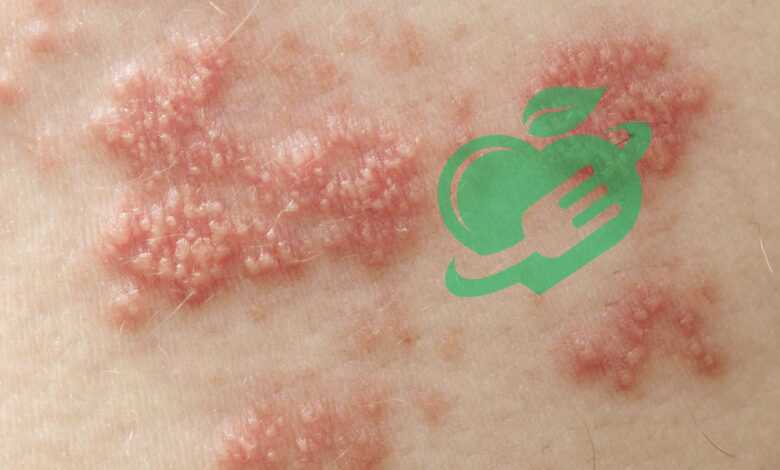
Overview of Skin Disorders
Skin disorders are an all-too-common issue that affects individuals of all ages, backgrounds, and skin types. From the occasional breakout to persistent conditions like eczema and psoriasis, these disorders can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Each skin condition presents its own unique set of symptoms, causes, and potential treatments. For instance, acne, the most prevalent skin issue, primarily affects teenagers but can also appear in adults. Conversely, conditions like vitiligo can affect anyone, leading to skin depigmentation and requiring various approaches to manage. Here’s a quick list of common skin disorder
- Acne: Inflammatory condition often leading to pimples or cysts.
- Eczema: Characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed skin.
- Psoriasis: Autoimmune disease resulting in scaly, patchy skin.
- Rosacea: Causes facial redness and visible blood vessels.
Importance of Awareness-Skin disorder
Raising awareness about skin disorders is crucial, not only for those suffering but for society as a whole. Understanding these conditions leads to empathy, better treatment, and proactive management strategies. Personal anecdotes highlight this importance. For example, a friend of mine struggled with acne throughout high school. It affected her self-esteem until she discovered effective treatments and support groups. Promoting awareness can help others feel less isolated and more empowered to seek help. In many cases, early detection can make a considerable difference in treatment outcomes. By becoming aware of the signs and symptoms, individuals can take charge of their skin health, leading to improved overall well-being.
Acne
Causes and Symptoms-Skin disorders
Acne is one of the most common skin disorders, often beginning during the teenage years but affecting people of all ages. So, what leads to those pesky breakouts? A variety of factors can contribute to acne development, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations during puberty, menstrual cycles, or hormonal disorders can cause the oil glands to produce excess sebum.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can increase one’s chances of developing it.
- Diet: Some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods and dairy can exacerbate acne in certain individuals.
- Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that lead to increased oil production.
Symptoms typically involve:
- Pimples: Red, inflamed lesions filled with pus.
- Blackheads and Whiteheads: Blocked pores that can appear on the skin’s surface.
- Cysts: Larger, painful lumps beneath the skin.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating acne, numerous options are available. Personal experience shows how effective a tailored approach can be. Treatment options include:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help clear pores.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe antibiotics or hormonal medications.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good skincare, and managing stress levels can also make a significant difference.
It’s important to remember that what works for one person might not work for another. For instance, my cousin tried several products before finding the right regimen, emphasizing the need for patience and persistence. Consulting a dermatologist can also provide personalized recommendations, ensuring a comprehensive approach to effectively manage and treat acne.
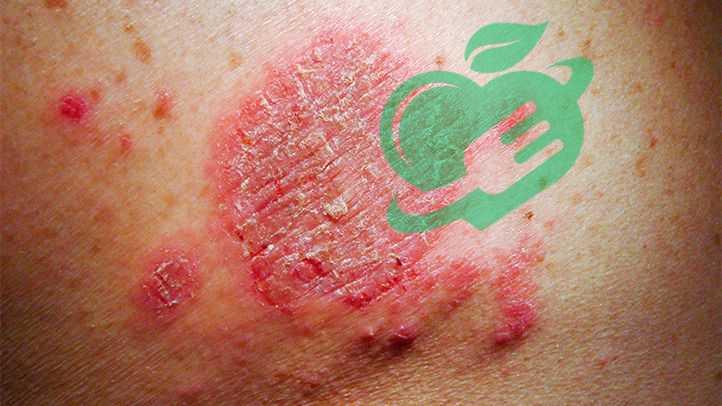
Eczema
Types of Eczema-Skin disorders
Eczema is an umbrella term for a group of conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed, itchy, and red. While various types exist, some are more common than others. Understanding these types can help individuals identify their specific issues and seek appropriate remedies. The most prevalent types of eczema include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: Often developing in childhood, this type is linked to allergies and asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by direct contact with irritants or allergens, leading to localized redness and itching.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small blisters on the hands and feet, often worsened by stress.
- Nummular Eczema: Presents as circular, coin-shaped patches on the skin and can be exacerbated by dry skin.
Each form can manifest differently, making it essential for individuals to pay attention to their symptoms.
Management and Prevention
When managing eczema, a multi-faceted approach is often the most effective. From personal experience, I found that consistency is key in maintaining skin health. Here are some tips for managing and preventing flare-ups:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated helps prevent dryness and irritation.
- Identify Triggers: Take note of foods, fabrics, or environmental factors that worsen symptoms.
- Use Gentle Products: Opt for fragrance-free soaps and shampoos to minimize irritation.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress can soothe itchy areas and reduce inflammation.
A friend of mine, who has struggled with eczema, started keeping a journal to track her triggers and found significant relief. It’s all about finding what works best for you and staying proactive in your skincare routine. Regular check-ins with a dermatologist can also provide valuable support and guidance for managing this often-challenging condition effectively.
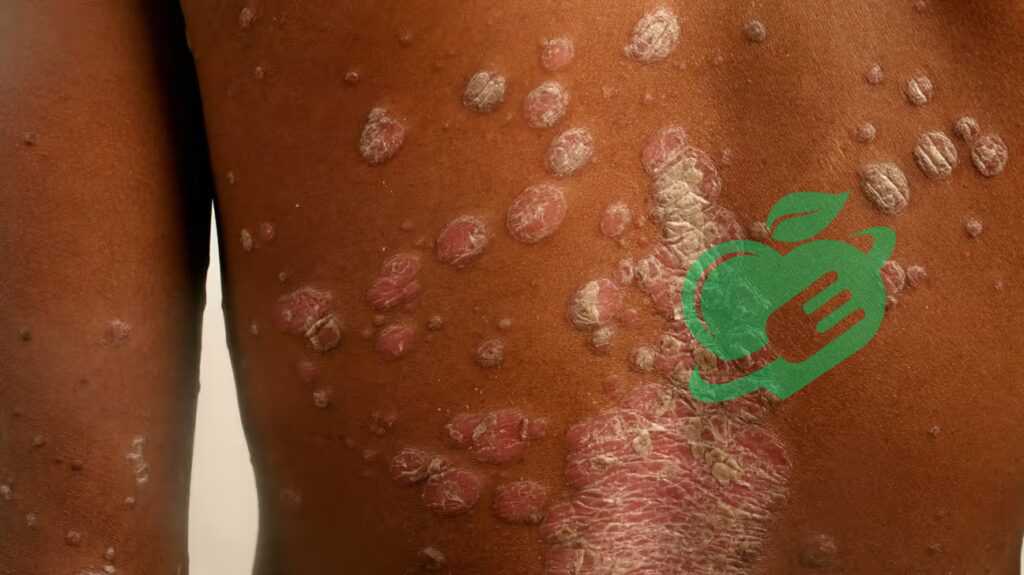
Psoriasis
Understanding Psoriasis-Skin disorder
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that accelerates skin cell production, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. It can appear anywhere but is commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp. Unlike other skin disorders, psoriasis is not just a surface issue; it’s linked to an overactive immune response that can cause discomfort and emotional distress. There are several types of psoriasis, including:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most prevalent form, marked by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Often starting in childhood, it appears as small, drop-shaped lesions.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Manifests as smooth, red patches in skin folds, often misdiagnosed due to its appearance.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin.
People often mistake psoriasis for simple eczema, but recognizing the differences is vital for effective treatment.
Treatment Approaches-Skin disorder
Managing psoriasis is about finding the right balance between treatment and lifestyle changes. I remember my neighbor’s struggles with flare-ups, trying various remedies until she discovered an effective regimen. Here are a few treatment options for psoriasis:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids can reduce inflammation and scaling.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can significantly decrease symptoms for some individuals.
- Systemic Medications: For severe cases, doctors may prescribe oral or injected medications that affect the entire body.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can help control flare-ups.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to tailor a treatment plan that suits one’s specific situation. With the right approach, living with psoriasis can be manageable, allowing individuals to focus on enjoying life rather than battling their skin condition.
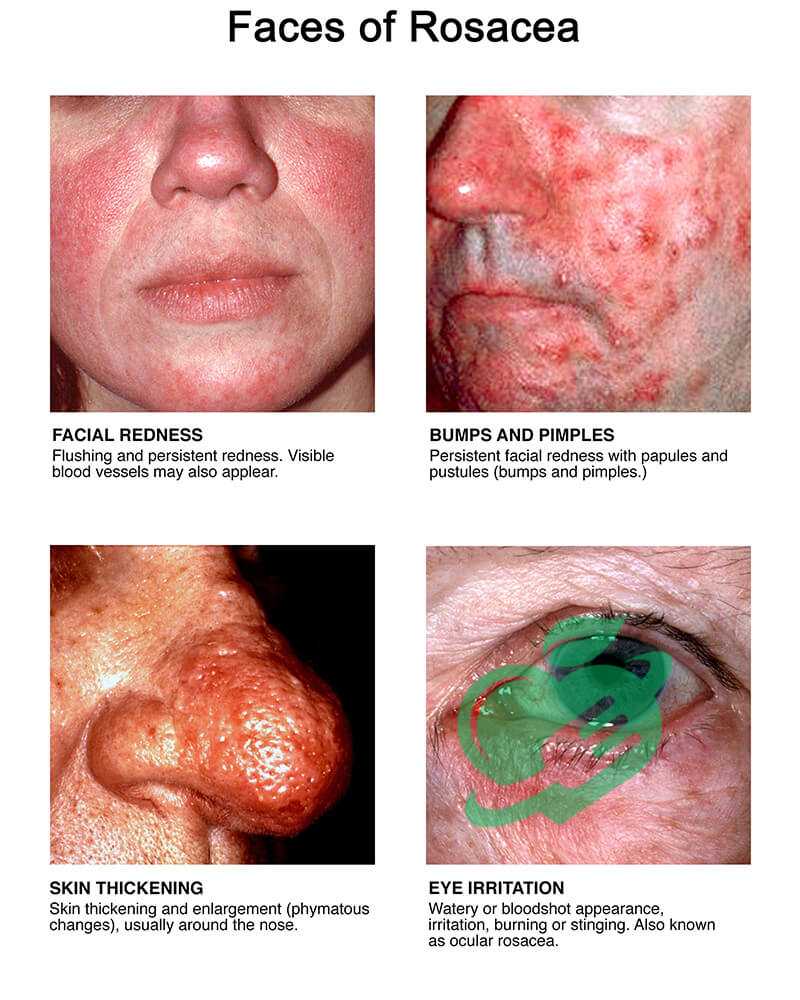
Rosacea
Triggers and Symptoms-Skin disorders
Rosacea is a common yet often misunderstood skin condition that primarily affects the face, resulting in persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like breakouts. Understanding its triggers and symptoms is essential for managing this skin disorder effectively. Common triggers for rosacea include:
- Heat: Hot weather or heated indoor spaces can exacerbate redness.
- Spicy Foods: Some individuals may notice flare-ups after consuming spicy meals.
- Alcohol: Particularly red wine, can trigger symptoms for many sufferers.
- Emotional Stress: High-stress situations may lead to rapid flushing and increased redness.
Symptoms of rosacea can vary widely but typically include:
- Facial Redness: A flushed appearance, often evolving into persistent redness.
- Pimples: Breakouts similar to acne may occasionally occur.
- Dryness and Sensitivity: Many affected individuals report a burning sensation or tenderness.
This condition often leaves individuals feeling self-conscious, as was the case for a colleague who faced teasing about her facial redness for years.
Managing Rosacea Flare-ups
Managing rosacea involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and treatment options tailored to individual needs. Drawing from personal experiences and observations, the following strategies can help reduce flare-ups:
- Identify Triggers: Keep a journal to track flare-ups and recognize what might be provoking them.
- Gentle Skincare: Use mild, fragrance-free products that hydrate and soothe the skin.
- Sun Protection: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to protect the skin from UV rays, which can aggravate symptoms.
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams or gels containing ingredients like metronidazole or azelaic acid can be effective.
For my friend, incorporating these practices significantly improved her skin condition over time. Consulting with a dermatologist remains invaluable, as they can provide personalized advice and treatment options ideally suited for managing rosacea, allowing individuals to regain confidence and control over their skin health.
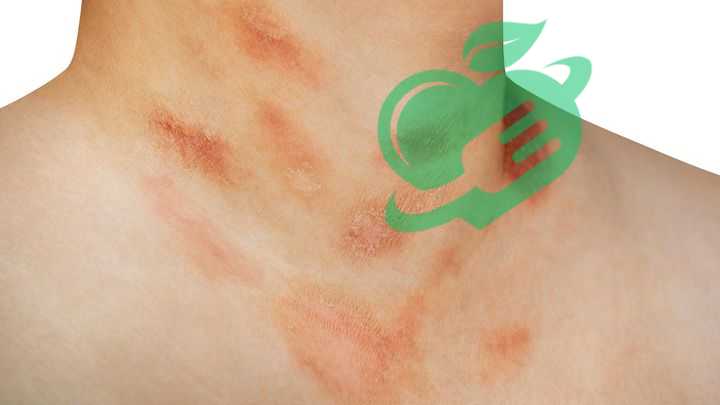
Dermatitis
Types of Dermatitis-Skin disorders
Dermatitis, an umbrella term for various skin inflammatory conditions, can cause discomfort and distress. It tends to manifest in different forms, each with unique triggers and symptoms. Understanding these types is vital for effective management and treatment. Here are the most common types of dermatitis:
- Atopic Dermatitis: Often seen in children, this eczema type is associated with allergies and asthma, leading to itchy, red patches on the skin.
- Contact Dermatitis: Occurs when the skin reacts to a specific irritant or allergen, such as poison ivy or harsh soaps, causing localized inflammation.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Characterized by flaky, greasy scales on the scalp (commonly known as dandruff), as well as other oily areas of the body.
- Stasis Dermatitis: This occurs when fluid collects in the lower legs, often due to poor circulation, leading to swelling and red skin.
Having dealt with contact dermatitis after a gardening mishap, I can personally attest to the frustration it can cause.
Treatment and Prevention
Managing dermatitis effectively often requires a combination of treatment strategies. Here are some practical tips for alleviating symptoms and preventing flare-ups:
- Identify Triggers: Maintaining a diary to note specific reactions to products, foods, or environmental factors can aid in recognizing triggers.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated helps reduce dryness and increases the skin barrier’s resilience.
- Gentle Skin Care: Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products to minimize irritation.
- Prescription Treatments: Dermatologists can prescribe topical steroids or other medications for severe cases, helping to reduce inflammation and itching.
For my sister, who has struggled with seborrheic dermatitis, consistent care and avoiding known irritants made a world of difference. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist can provide tailored advice, ensuring effective management and improving skin health. With proper understanding and care, individuals dealing with dermatitis can gain control over their skin and enhance their quality of life.
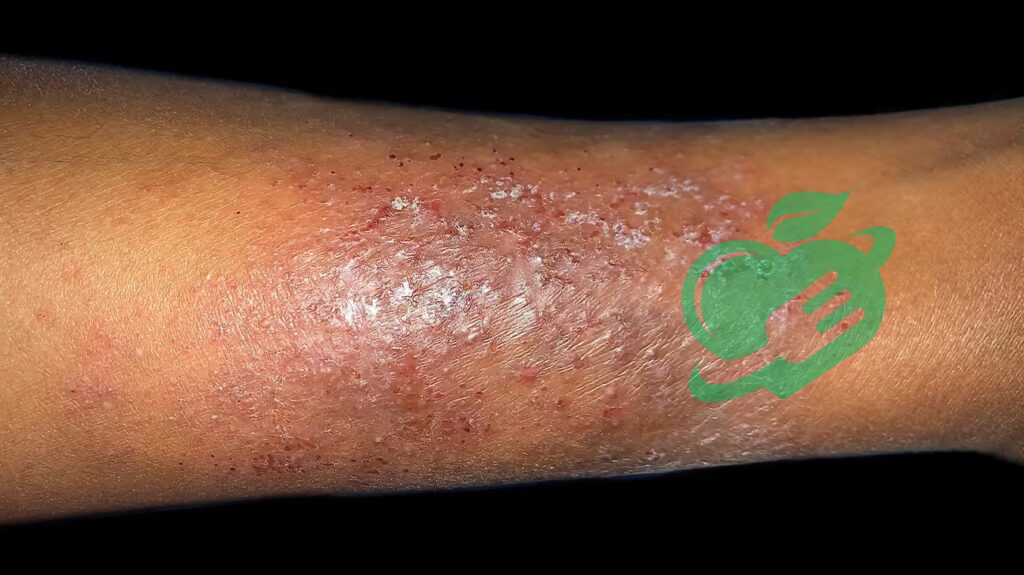
Hives
Causes of Hives-Skin disorder
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear suddenly and vary in size. They might look like small bumps or larger patches and can be a source of discomfort and concern. Understanding the causes of hives is crucial for effective management, whether they are acute or chronic. Common causes of hives include:
- Allergic Reactions: Foods (like nuts or shellfish), medications, insects, and pollen can trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
- Infections: Viral infections can prompt hives, particularly in children.
- Environmental Factors: Changes in temperature, humidity, or exposure to sunlight can lead to hives in some people.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can induce hives, highlighting the mind-skin connection.
Having experienced hives after trying a new skin product, I can relate to the unpredictability and irritation they bring.
Dealing with Acute and Chronic Hives
When it comes to managing hives, approaches differ based on whether they are acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting six weeks or longer). For acute hives, consider these methods:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines can help relieve itching and reduce swelling.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold pack can alleviate discomfort and minimize swelling.
For chronic hives, a more comprehensive approach may be necessary:
- Identification of Triggers: Keeping a diary of flare-ups and potential triggers can provide insights into manageable patterns.
- Consultation with a Specialist: Allergists can perform tests to identify underlying issues and establish a tailored treatment plan.
- Prescription Medications: In persistent cases, doctors may prescribe stronger antihistamines or corticosteroids.
My friend battled chronic hives for years, but with diligent tracking of her triggers and working closely with her allergist, she finally found relief. While managing hives can feel overwhelming at times, understanding their causes and implementing effective strategies can help individuals regain control and comfort in their skin.
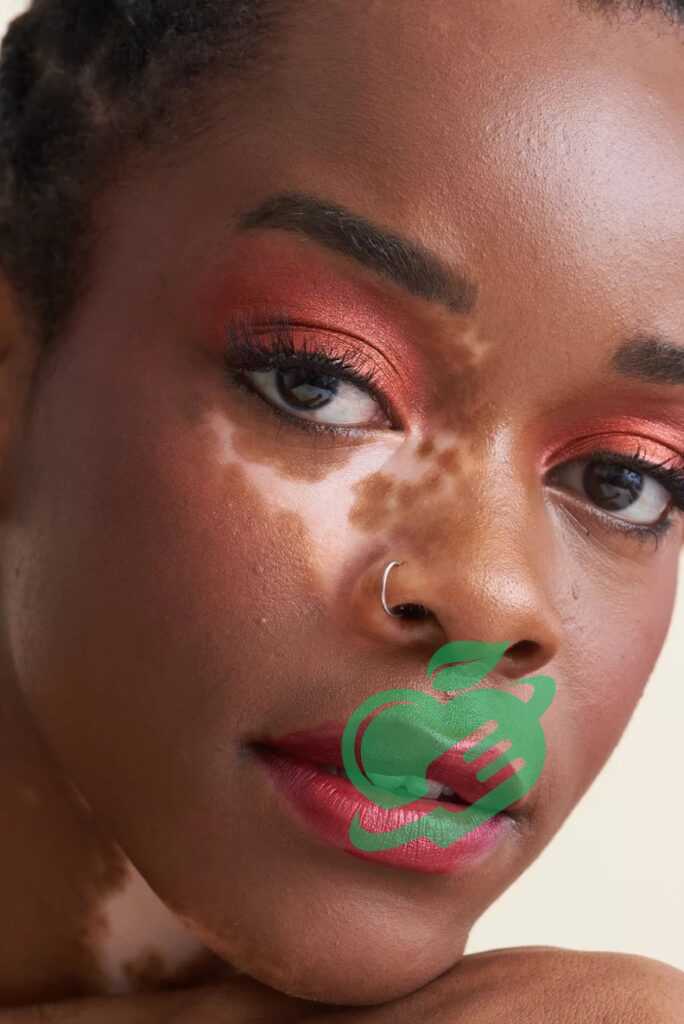

Vitiligo
Mechanism of Vitiligo-Skin disorders
Vitiligo is a skin disorder resulting in the loss of pigment in patches on the skin, leading to uneven skin tone. Understanding its mechanism can shed light on this often-misunderstood condition. At its core, vitiligo occurs when the melanocytes—cells responsible for producing melanin (the pigment that gives skin its color)—are destroyed or stop functioning. While the exact cause of this destruction remains unclear, several factors may contribute:
- Autoimmune Response: The immune system may mistakenly target and destroy melanocytes, similar to how it attacks invading pathogens.
- Genetics: A family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune disorders may increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Triggers: Factors such as sunburn, stress, or exposure to certain chemicals may precipitate the onset of the condition.
Witnessing a friend’s journey with vitiligo has shown me the emotional and physical challenges individuals face with this condition.
Treatment Methods-Skin disorder
While there is no definitive cure for vitiligo, various treatment methods can help manage the condition and restore skin color. Some effective options include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These can reduce inflammation and may help repigment the skin when applied early.
- Light Therapy: Controlled exposure to UVA or UVB light can stimulate melanocyte function, leading to improved pigmentation.
- Skin Camouflage Products: Specialized makeup can help conceal depigmented areas, providing a confidence boost for those affected.
- Surgery: In cases with extensive vitiligo, surgical options like skin grafting may be considered.
Throughout her journey, my friend found empowerment through support groups and learning about her options. Consulting with a dermatologist allows individuals to explore tailored treatment plans that suit their specific needs and skin type. Ultimately, understanding vitiligo and its management can greatly enhance the confidence and quality of life for those affected.
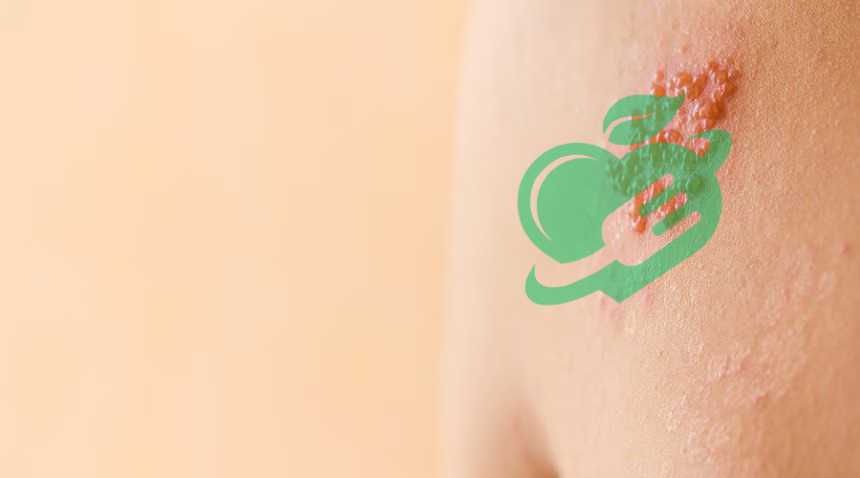
Shingles
Overview of Shingles-Skin disorder
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash and is a reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. This condition primarily affects adults who have previously had chickenpox, often lying dormant in the nervous system until something triggers its reactivation, such as stress or a weakened immune system. Key symptoms of shingles include:
- Painful Rash: Typically found on one side of the body, often resembling blisters or patches.
- Burning Sensations: Many people report intense pain or itching before the rash appears.
- Fever and Fatigue: General malaise and feeling unwell can accompany the onset.
A close family member of mine experienced shingles, and witnessing her pain and discomfort opened my eyes to the impact this condition can have.
Postherpetic Neuralgia and Complications
One of the most concerning complications of shingles is postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), characterized by persistent nerve pain in areas where the shingles rash occurred. This pain can last for months or even years after the rash has healed, significantly affecting one’s quality of life. Additional potential complications include:
- Vision Loss: If shingles affect the eye (ophthalmic shingles), it can lead to serious eye complications, including vision loss.
- Skin Infections: Secondary bacterial infections may develop in the areas where shingles blisters formed.
Managing shingles early with antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, mitigating the risk of complications like PHN. My family member found relief through prompt medical care, reminding us that timely intervention can make a significant difference. Vaccination is also an effective way to prevent shingles, especially in older adults, helping many avoid this painful condition altogether.
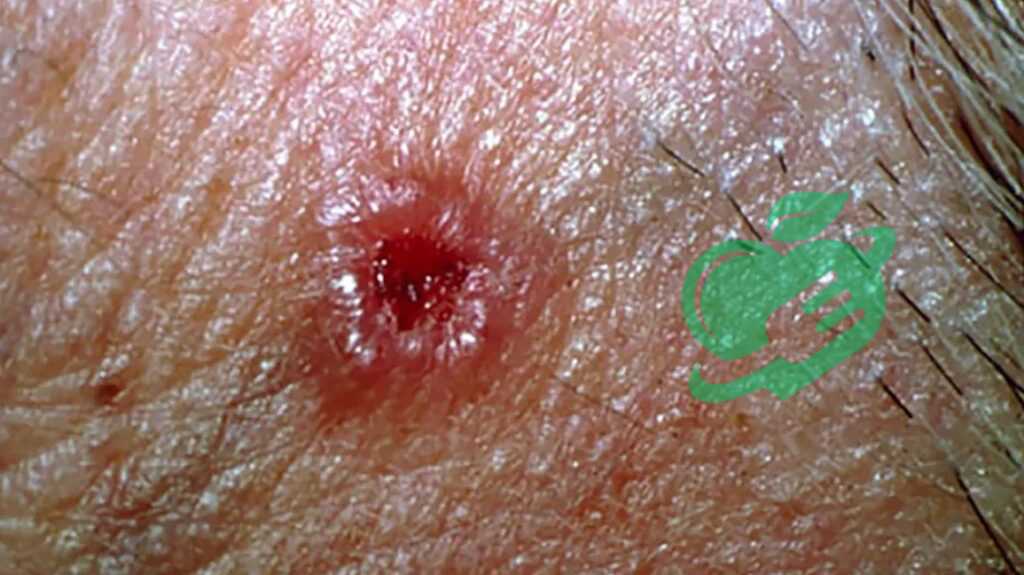
Skin Cancer
Types of Skin Cancer-Skin disorders
Skin cancer is a serious condition that arises when skin cells begin to grow uncontrollably. It is broadly categorized into three main types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This is the most common type of skin cancer, often appearing as a pearly bump or reddish patch. BCC usually develops in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face and neck.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): SCC may present as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore that won’t heal. Like BCC, it commonly arises in sun-exposed areas and is usually treatable when caught early.
- Melanoma: The most aggressive form of skin cancer, melanoma originates in the melanocytes. It can develop from existing moles or appear as a new dark spot. Melanoma requires prompt medical attention, as it can spread quickly to other parts of the body.
Having watched a friend battle melanoma, I understand firsthand the gravity of skin cancer and the importance of awareness.
Prevention and Early Detection-Skin disorder
Preventing skin cancer revolves mainly around protecting the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Here are key prevention tips:
- Sunscreen: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily, even on cloudy days.
- Protective Clothing: Wear wide-brimmed hats and clothing that covers your skin when outdoors.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds significantly increase the risk of skin cancer, especially in younger individuals.
Early detection remains crucial in successfully treating skin cancer. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are essential. Look for changes in moles or skin appearance, using the ABCDE method for melanoma:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color variations
- Diameter over 6mm
- Evolving changes
By staying vigilant and educating ourselves about skin cancer, we can take proactive steps to protect our skin and enhance our chances of early detection. As I learned from my friend’s journey, awareness and regular check-ups can truly save lives.