5 Key Benefits of Opting for a Birth Control Shot

Definition of Birth Control Shot
The birth control shot, often referred to as Depo-Provera, is a hormonal contraceptive that provides women with a reliable method to prevent pregnancy. Administered via an injection, this shot contains Depo-medroxyprogesterone acetate, a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. Its primary function is to inhibit ovulation, thereby preventing the ovaries from releasing eggs. For many women, the shot can be a convenient and discreet option. It eliminates the daily routine of taking a pill and can reduce the likelihood of unplanned pregnancies. Once receiving the injection, a woman is protected against pregnancy for three months, making it a favored choice for those seeking medium-term birth control solutions. Some key points about the birth control shot include:
- Method of Administration: It is administered via an intramuscular injection, typically by a healthcare provider.
- Frequency: The shot is required every three months to maintain its effectiveness.
- Mechanism of Action: The hormones in the shot work by thickening cervical mucus, thinning the uterine lining, and suppressing ovulation.
As we dive deeper into this topic, it’s essential to understand how the birth control shot fits into the larger spectrum of contraceptive options.
Brief History of Birth Control Shots
Birth control methods have evolved significantly over the years, with the birth control shot emerging as a notable advancement. The journey of the birth control shot began in the mid-20th century when significant strides were made in reproductive health.
- 1950s: The groundwork was laid with the development of hormonal contraceptives. During this period, researchers were actively exploring ways to manipulate hormones to prevent ovulation.
- 1960: The introduction of the first oral contraceptive pill marked a turning point in birth control options, paving the way for further innovations, including injectables.
- 1970s: The birth control shot debuted in clinical practice. Initially, it was available under different brand names, with Depo-Provera gaining popularity due to its relatively long-lasting effects and ease of use.
The shot was embraced rapidly for various reasons; it represented a significant shift from daily pills to a more user-friendly option. Women appreciated the autonomy that comes with having a contraceptive method that didn’t require daily remembrance.
Studies and research
Over the decades, more research confirmed its safety and effectiveness—reassuring women about its reliability. Early studies showed that the birth control shot effectively prevented pregnancy with a failure rate of less than 1% when used correctly. 1
This compelling evidence attracted many users looking for long-term solutions without the commitment of an IUD or multiple daily pills. In the 1980s and beyond, medical organizations and reproductive health advocates began to notice the broader implications of birth control, including its role in women’s health and empowerment.
Access to various contraceptive methods, including the birth control shot, became central to discussions about responsible family planning. Today, the birth control shot remains a popular choice among women worldwide.
It’s marketed as not only a contraceptive but also a versatile tool for addressing menstrual irregularities, such as heavy bleeding or painful periods, thereby serving dual purposes for many users. Overall, the birth control shot has evolved through rigorous scientific inquiry and societal changes, shaping it into the effective contraceptive solution it is today.
Understanding its definition and history helps contextualize its current role in women’s health and the accessibility of reproductive choices. As we explore the effectiveness of the birth control shot in the following sections, it is crucial to recognize its advantages, limitations, and how it compares with other methods to empower women to make informed choices about their reproductive health.
Read also: 10 Surprising Benefits of Cucumber You Need to Know.
Comparison with Other Birth Control Methods
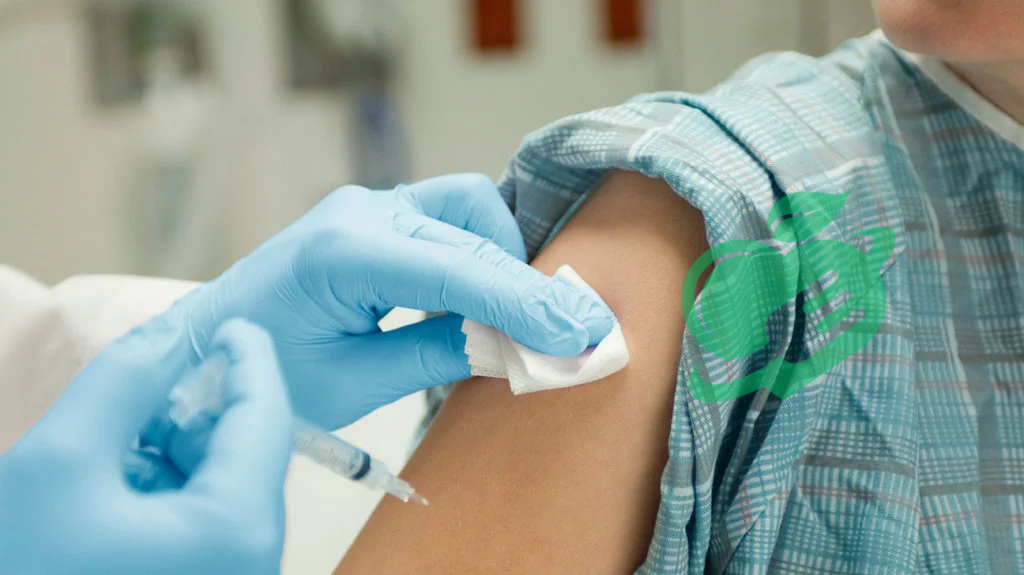
When considering contraception options, effectiveness is often at the forefront of a woman’s mind. The birth control shot stands out as one of the more reliable methods available. To better understand its efficacy, let’s compare it with other common birth control options:
- Birth Control Pill: The effectiveness of the birth control pill can reach up to 99% when taken correctly. However, typical use may drop that figure to around 91%, primarily due to missed doses or incorrect usage. In contrast, the birth control shot maintains an effectiveness of over 94%, regardless of daily habits, as long as it is administered on schedule.
- Intrauterine Device (IUD): IUDs are known for being one of the most effective contraceptive methods, with efficacy rates over 99%. They can prevent pregnancy for several years. However, they require a healthcare professional for insertion and may not be ideal for everyone due to individual comfort levels.
- Condoms: Male and female condoms are widely accessible and can offer protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in addition to preventing pregnancy. However, the typical use of condoms translates to an effectiveness of about 82%, due to the potential for breakage or improper use.
- Implants: Similar to the birth control shot, implants are highly effective, with an efficacy rate above 99%. They are inserted beneath the skin of the arm and can prevent pregnancy for up to three years. However, insertion requires a minor procedure by a healthcare provider.
In summary, while the birth control shot ranks favorably among various methods, its unique advantages lie in the ease of use and the convenience of not having to remember daily pills. Many women find that the shot offers a hassle-free way to manage their reproductive health.
Factors Influencing Effectiveness
While the birth control shot is generally effective, several factors can influence its efficacy. Understanding these factors can aid in ensuring that users get the best possible protection against unintended pregnancies.
- Timely Administration: As the shot is effective for three months, women must receive it on time. However, it’s essential to note that if the shot is administered late by more than a week, additional contraceptive methods should be employed for at least seven days.
- Body Weight: Studies have suggested that a woman’s weight can influence the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, including the birth control shot. Women who are significantly over the average weight range may experience decreased efficacy, though research is still ongoing in this area.
- Medications and Health Conditions: Certain medications, particularly anticonvulsants, and some antibiotics, may impact hormonal birth control methods. Women should always inform their healthcare provider of any medications they are taking to ensure continued efficacy.
- Initial Usage: If the birth control shot is administered within the first five days of the menstrual cycle, its effectiveness begins immediately. If it’s given at another time, protection against pregnancy may not be guaranteed until after a week.
- Individual Health: Each woman’s body may react differently to hormonal contraceptives. Factors such as hormonal balance, age, and overall health can influence how effective the shot will be.
a summary
Women should have a candid discussion with their healthcare providers regarding any specific considerations that may impact the birth control shot’s effectiveness. By understanding these influencing factors, they can take proactive steps to ensure reliable contraceptive coverage. In conclusion, while the birth control shot is highly effective in preventing pregnancy, comparing it to other methods and acknowledging the factors that can impact its efficacy allows women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health. With continued support and education, women can confidently use the birth control shot as a reliable method to manage their family planning needs. As we look towards the benefits of this method in the next section, it is essential to keep in mind how effectiveness plays into the overall picture of reproductive health options.
Read also: The Ultimate Vitex Agnus Castus Handbook: Tips and Tricks Revealed.
Benefits of Birth Control Shot
One of the primary benefits of the birth control shot is its effectiveness in preventing pregnancy. As discussed earlier, the birth control shot boasts a high effectiveness rate of over 94%, making it a reliable option for women who want to avoid unplanned pregnancies. What sets the shot apart is the convenience of not having to think about daily pills or other frequent routines.
Imagine living your busy life—balancing work, social activities, and self-care—without the added stress of remembering a daily medication. The three-month window of protection allows many women to plan their lives with confidence. For instance, Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer, shares her experience: “After struggling to remember pills with my hectic schedule, I switched to the shot. Now, I just schedule my appointment every three months, and I don’t have to worry about anything in between. It’s been a game-changer!” In addition to preventing pregnancy, the shot can also be an excellent fit for women who are looking for a birth control method that seamlessly integrates into their lifestyle.
Managing Menstrual Irregularities
Another significant benefit of the birth control shot is its ability to manage menstrual irregularities. Many women experience heavy periods, severe cramping, or unpredictable cycles, which can disrupt daily life and overall well-being. The hormonal components of the birth control shot help regulate these issues by thinning the uterine lining and reducing menstrual flow. This benefit can lead to healthier menstrual cycles for women who might traditionally struggle with discomfort or unpredictability. Here are some of the specific ways the birth control shot can help:
- Reduction in Menstrual Pain: Women often report experiencing fewer cramps, making their periods less distressing.
- More Predictable Cycles: Once initiated, many users enjoy more regular cycle patterns.
- Less Heavy Bleeding: The shot can significantly lessen the volume and duration of menstrual bleeding.
Consider Lucy, a 35-year-old teacher, who initially sought the shot for pregnancy prevention. “I had intense cramps each month that impacted my work,” she explains. “Now that I’m on the shot, my periods are not just lighter but manageable. It has improved my quality of life tremendously.” This aspect makes the birth control shot an appealing option beyond its contraceptive properties, offering real relief for women dealing with inconvenient menstrual symptoms.
Decreasing the Risk of Certain Cancers
Beyond preventing pregnancies and alleviating menstrual difficulties, research has suggested another notable advantage of the birth control shot: a lowered risk of specific types of cancers. Particularly, studies have indicated that long-term use of the shot may significantly reduce a woman’s chance of developing endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer.
By suppressing ovulation, the hormonal changes induced by the birth control shot could lead to fewer periods over a lifetime. This phenomenon could contribute to lower estrogen levels in the body, which has been linked to reduced risks of these cancers.
While this is a promising benefit, women must discuss this aspect with their healthcare providers, as individual health factors play an essential role. Moreover, regular preventive care and screenings remain paramount.
Birth control is just one piece of the larger puzzle of women’s health management. In summary, the benefits of the birth control shot go beyond pregnancy prevention. It also plays a vital role in managing menstrual irregularities and potentially lowering the risk of certain cancers.
Recognizing these advantages allows women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health. As we move forward, understanding the convenience and accessibility of the shot will help in assessing its overall impact on women’s lives.
By considering these factors, women can truly appreciate the multifaceted benefits that the birth control shot brings to their health journey.
Read also: 10 Surprising Benefits of Cucumber You Need to Know.
Convenience and Accessibility
Administration Process
One of the greatest advantages of the birth control shot is its straightforward administration process. Unlike some contraceptive methods requiring daily attention or complex insertion procedures, the shot is a simple, single-event experience that can be easily integrated into a woman’s routine. To receive the birth control shot, a woman typically visits her healthcare provider’s office. Here’s a quick overview of what the process generally looks like:
- Consultation: During the first appointment, a healthcare provider will discuss the woman’s medical history, preferences, and any possible contraindications. This ensures that the shot is the right choice for her.
- Physical Examination: A brief physical examination may be conducted to confirm eligibility.
- Administration: Once approved, the healthcare provider administers the shot as a deep intramuscular injection, usually in the arm or buttocks. The whole process is quick, often taking less than 15 minutes.
- Follow-Up: Scheduling follow-up appointments every three months becomes critical to maintain ongoing contraceptive effectiveness.
Many women appreciate the simplicity of this procedure. Emily, a 30-year-old nurse, shares her experience: “I get my shot during my lunch break while at work; it only takes a few minutes, and then I can go about my day without worrying again for three months.” This time-efficient process adds to the shot’s appeal, especially for women with busy schedules.
Duration of Effectiveness
The birth control shot’s duration of effectiveness is another significant convenience. Once administered, the shot protects against pregnancy for an impressive three months. This long duration allows women the flexibility to plan around their reproductive health without the daily reminder or routine associated with the pill. Here’s the effectiveness breakdown:
- Immediate Effectiveness: If the shot is given within the first five days of the menstrual cycle, it provides immediate protection.
- Delayed Effectiveness: If the shot is given at another time, the woman should use additional contraception for at least seven days before relying solely on the shot.
This three-month window is particularly beneficial for those who may find it challenging to remember daily pills or prefer to minimize the frequency of medical visits. It naturally falls in line with many women’s lifestyles, reducing stress and allowing for greater freedom.
Availability and Cost
When assessing the convenience of the birth control shot, it’s essential to consider its availability and cost. The shot is widely available in many healthcare settings—such as clinics, private practices, and family planning centers—making it an accessible option for many women. In terms of cost, the price of the birth control shot can vary depending on geographical location, the healthcare provider’s fees, insurance coverage, and other factors:
- Without Insurance: The shot typically costs anywhere from $30 to $150 per injection, which covers the administration and the medication.
- With Insurance: Many health insurance plans provide coverage for the birth control shot, often requiring minimal copays or possibly even none.
For those who may have financial constraints, community clinics often offer services on a sliding scale based on income, ensuring that access to contraception isn’t limited by affordability. All things considered, the birth control shot is a convenient, effective, and increasingly accessible contraceptive option.
By providing a simple administration process, a three-month duration of effectiveness, and widespread availability, it caters to a diverse range of women.
As we wrap up this section, it’s essential to recognize how the convenience and accessibility of the birth control shot empower women to take control of their reproductive health. This ease of use enhances compliance and allows women to focus on their daily lives while managing their birth control effectively.
Moving forward, it becomes crucial to address potential side effects and health considerations to provide a comprehensive overview of this contraceptive method.
Read also: Empower Your Health: Recognizing and Addressing 8 Triggers of Vaginal Pain.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While the birth control shot offers numerous benefits, like any medication, it can also come with potential side effects. Understanding these side effects is crucial for women to make informed decisions about their contraceptive choices. Some common side effects associated with the birth control shot include:
- Irregular Menstrual Bleeding: Some women experience changes in their menstrual cycle, which might include lighter periods, more frequent spotting, or even no periods at all after several months. This can be disconcerting, but it’s often considered a normal adjustment.
- Weight Gain: Some users report weight gain, sometimes attributed to hormonal changes that affect metabolism and appetite. This weight gain can vary significantly between individuals.
- Headaches: Hormonal fluctuations may lead to headaches in some women. While generally manageable, it’s advisable to discuss persistent or severe headaches with a healthcare provider.
- Breast Tenderness: Similar to symptoms experienced during menstrual cycles, some women notice breast tenderness or swelling shortly after receiving the shot.
- Mood Changes: Hormonal contraceptives, including the shot, can influence mood due to hormonal fluctuations. Some women report feelings of anxiety or depressed mood, while others may not experience significant changes.
It’s essential to highlight that not every woman will experience these side effects, and for many, the benefits of the birth control shot will far outweigh any inconveniences. Carla, a 29-year-old marketing professional, shares her perspective: “Initially, I was worried about potential weight gain, but after talking to my doctor, I decided to give it a try. I had some spotting in the beginning, but now I feel great overall.” Understanding these possible side effects can ease concerns and enable women to better monitor their experiences.
Read also: 6 types of food to beware of during the first three months of pregnancy.y
Health Considerations
When considering the birth control shot, health history plays a critical role. Certain health considerations can impact the suitability of this contraceptive method. Women with the following conditions should discuss their options thoroughly with a healthcare provider:
- History of Blood Clots: Women with a history of blood clots, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or pulmonary embolism are generally advised against using hormonal contraceptives like the birth control shot, as they may increase the risk of clotting.
- Certain Cancers: A personal or family history of breast cancer may raise concerns. The shot is not typically recommended for those with breast cancer due to the influence of hormones on growth.
- Liver Disease: Known liver conditions can interfere with hormone metabolism, impacting safety and effectiveness.
- Undiagnosed Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: It’s important to rule out other significant medical conditions before starting hormonal contraceptives.
Women should have honest discussions with their healthcare providers about their health histories and any concerns they may have. This proactive approach ensures that they receive the best possible guidance tailored to their unique situations.
Read also: Choosing the Right Contraception: A Complete Overview.
Reversibility of the Birth Control Shot
One of the major advantages of the birth control shot is its reversibility. After discontinuation, most women regain their fertility relatively quickly, usually within a few months. Although it may take time for menstrual cycles to normalize, the return to fertility is generally swift compared to some long-term contraceptive methods like IUDs or implants. It can be useful to keep in mind:
- Timing of Return to Fertility: After the last injection, it may take up to 10 months for some women’s cycles to return to pre-injection patterns. Others may find that their cycles normalize more quickly.
- Pregnancy Planning: Women who plan to conceive should consider discussing their intentions with a healthcare provider. This can provide insights into optimizing timing and any necessary preparatory measures.
Many women appreciate this aspect of the birth control shot, knowing that they can maintain control over their reproductive health and can make changes as needed. In conclusion, while the birth control shot is a convenient and effective contraceptive option, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects and health considerations.
Understanding the reversibility of the shot can also empower women in their planning for the future. Every woman’s experience with contraceptives can differ; therefore, personalized medical advice is invaluable.
As we conclude this exploration of the birth control shot, it’s important to recognize how informed choices dramatically improve the journey of reproductive health management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the 3 month injection safe?
The contraceptive injection is a practical, safe, and very effective way to prevent pregnancy. One single injection can provide immediate protection, eliminating the concern of forgetting to take birth control pills or needing to use protection each time you engage in sexual activity. 2
Can Depo cause infertility?
Using Depo-Provera generally does not result in lasting infertility. It’s common for those receiving the injections to experience the absence of menstrual periods, and there is often a delay in the resumption of ovulation after stopping the injections. 3
What is the safest form of birth control?
Abstinence is the only method of birth control that is completely effective. It involves refraining from any sexual intercourse. Additionally, it is the only option for fully safeguarding yourself against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). 4
Because your health is the most valuable thing you have and the most precious thing we care about, we always recommend that you consult your specialist doctor in everything related to your health and daily life. Everything we provide here is for awareness purposes only and does not replace consulting a doctor. Every person has a unique condition that deserves special care, and we are here by your side, working passionately to provide the information you need. Always follow us, because we write for you with love and sincerity to remain a source that inspires you with hope and supports you on your journey towards a better life.
- PMC ((↩))
- intouchmedicare ((↩))
- verywellhealth ((↩))
- clevelandclinic ((↩))


2 Comments