Is the Belladonna Nightshade Plant Safe or Sinister?

Overview of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
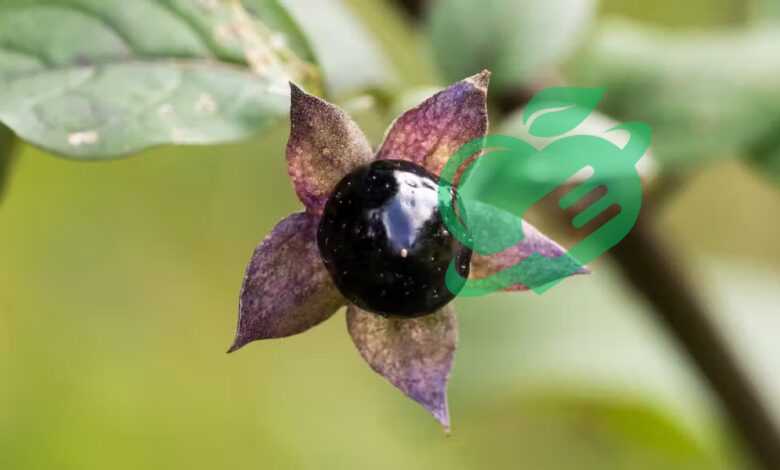
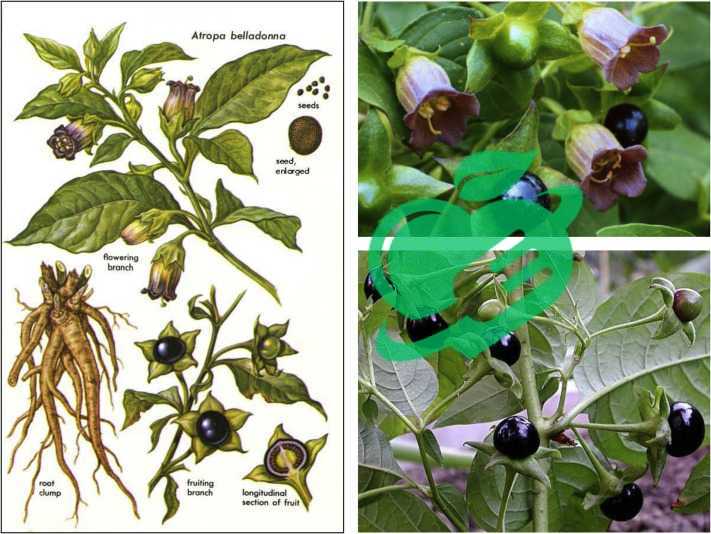
As we embark on this journey into the realm of Belladonna Nightshade Plant, or Atropa Belladonna, we encounter a plant steeped in complexity and intrigue. Known for its striking purple-black berries and lush green foliage, Belladonna symbolizes the duality of nature—its beauty is accompanied by a potent toxicity. This intriguing herb belongs to the Solanaceae family and is native to Europe, North Africa, and parts of Western and Central Asia.
- Key Features:
- Height: Typically grows between 2-4 feet tall.
- Flowers: Bell-shaped, purple flowers that bloom in late spring.
- Berries: Round, shiny black berries that are appealing yet deadly.
For many, Belladonna captures the imagination and raises questions. Why is it associated with folklore? How has it been utilized throughout history? Let’s dive into its historical significance.
Read also; Discover the Magic of the Mustard Seeds Tree.
The Historical Importance of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
The history of Belladonna is as rich and varied as the plant itself. From ancient civilizations to modern times, it has been revered, feared, and utilized in a myriad of ways.
- Roman and Greek Times:
- In ancient Rome, it was believed to be a remedy for various ailments. Romans used extracts as anesthetics and pain relievers during surgical procedures.
- Various sources suggest that the Greeks were aware of its toxicity, labeling it as a plant of the underworld.
- Medieval Europe:
- Fast forward to the Middle Ages, and Belladonna became associated with witchcraft. Many practitioners of herbal medicine used it in potions and spells, earning it a reputation as a “witch’s herb.”
- Cultural Reflections:
- Literary references abound, with Shakespeare and Chaucer including Belladonna in their works, often as a symbol of seduction or danger.
Reflecting on its historical paths, one can’t help but appreciate how Belladonna has shaped human understanding of both nature and medicine. It serves as a reminder 1
As we delve deeper into the fascinating world of the Belladonna Nightshade Plant, it’s important to understand not just its botanical profile and uses, but also the cultural lore and beliefs that have surrounded it. For centuries, this plant has captivated the imagination, leaving profound influences on literature, mythology, and even popular culture.
Cultural Representations of the Belladonna Nightshade Plant
Belladonna, commonly known as deadly nightshade, finds its mention across various cultures, often symbolizing both beauty and danger. The name itself derives from Italian, meaning “beautiful lady,” due to its use by women who would instill the plant’s extract into their eyes to create a dilated pupil effect.
- Literature: The plant has also made notable appearances in works by Shakespeare and classical mythology, often representing a duality of allure and peril. In tales of fairies, it is often depicted as a favorite among otherworldly spirits.
- Art: In artistic representations, Belladonna is frequently portrayed alongside themes of death and seduction, emphasizing its toxic and beautiful aspects. 2
Recent References Belladonna Nightshade Plant
In contemporary culture, Belladonna has maintained its mystical aura, appearing in fantasy novels, films, and even video games. For example, in popular literature and fantasy lore, characters might brew potions or concoctions using the plant, reinforcing its association with magic and the supernatural.
Personal Anecdote: A Spirited Encounter
In my travels across Europe, I stumbled upon a quaint herb shop in the heart of Italy. As I perused the aisles filled with jars of dried herbs, I came upon Belladonna. The shopkeeper, adorned in bright traditional attire, recounted tales of its past—how it was feared and revered, collected and discarded, all in the same breath. Such personal connections to plants enrich our understanding and appreciation of their complexities.
Language: English
Transitioning from our discussion on the intricate uses and characteristics of Belladonna, it’s fascinating to explore how language shapes our understanding of this enigmatic plant. Language, particularly English, often encapsulates rich meanings, diverse interpretations, and cultural nuances surrounding the Belladonna Nightshade Plant.
Linguistic Roots and Etymology
The term “Belladonna” originates from Italian, translating to “beautiful lady.” This name highlights the plant’s duality: its aesthetic appeal versus its toxic nature. Reflecting on this:
- Beauty and Danger: The name has evolved into a cultural symbol of allure coupled with risk. For centuries, English literature has echoed this sentiment. Think of it as a metaphor for situations that are visually appealing yet hold potential threats.
- Folklore and Mythology References: Many English-speaking cultures have folklore that intertwines Belladonna with stories of witches and enchantments. This illustrates our tendency to use language as a vessel for conveying both reverence and caution.
Anecdote: Words That Spark Wonder
I remember a conversation with a friend during a lovely evening stroll in a botanical garden. We stumbled upon a vibrant patch of Belladonna. Intrigued, I shared its history, and she exclaimed, “It sounds like something out of a fantasy novel!” Words have immense power; they can awaken imagination and evoke curiosity.
Read also; Unveiling the Secrets of the Saffron Plant.
Modern Interpretations and Usage
In contemporary English, Belladonna frequently pops up in discussions about herbal remedies or toxicology. Here are some key points about its modern relevance:
- Health Discussions: In medical contexts, terms like “tropane alkaloids” often appear, detailing their chemical components and active properties.
- Cultural References in Media: Films, books, and even music incorporate Belladonna, using its name to portray themes of mystery and seduction.
Read also: What is ancient medicine?

Botanical Profile of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
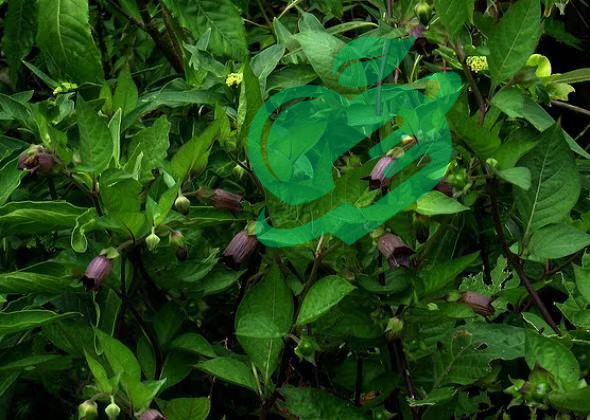
Transitioning from the historical significance of Belladonna, it’s time to delve into the intricate botanical profile of this captivating plant. Understanding its scientific classification, physical characteristics, and geographic distribution offers essential insight into its role in both natural ecosystems and human culture.
Scientific Classification of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
The scientific classification of Belladonna provides a lens through which to appreciate its place in the plant kingdom. It belongs to the Solanaceae family, which includes many other notorious plants, such as tomatoes and potatoes. Here’s a breakdown of its classification:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Clade: Eudicots
- Clade: Asterids
- Order: Solanales
- Family: Solanaceae
- Genus: Atropa
- Species: A. belladonna
Each level of this classification reflects Belladonna’s relationship with other plants, highlighting its shared characteristics within the family.
Physical Characteristics
Belladonna is not only visually striking but also exhibits unique physical traits that contribute to its enigmatic reputation. Here’s what to look for:
- Height: Grows up to 4 feet tall.
- Leaves: Large, ovate leaves that are dark green and have a smooth texture.
- Flowers: Bell-shaped, purple flowers that bloom in late spring; they have a distinct, sweet fragrance.
- Berries: Shiny, black berries that resemble small cherries, each containing a toxic alkaloid.
These characteristics combine to create a plant that is both beautiful and treacherous, prompting careful consideration from those who might venture too close.
Geographic Distribution
Belladonna thrives in various environments, primarily across Europe, North Africa, and Western and Central Asia. This wide distribution speaks to its adaptability:
- European Forests: Prefers shady, wooded areas and can often be found near roads or in abandoned fields.
- Ecological Role: Functions as a crucial part of its ecosystem, providing habitats for various insects and animals, despite its toxicity.
Reflecting on my travels through European woodlands, I once encountered an untouched patch of Belladonna, nestled between trees. Its allure was undeniable; yet, the memory served as a reminder of the importance of understanding the balance between beauty and danger in nature. As we continue further, we will explore the toxicity and medicinal uses of Belladonna, unearthing its complex legacy in both traditional and modern contexts.
Read also: Top 10 High Phosphorus Foods to Boost Your Health

Toxicity and Medicinal Uses of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
Building on the fascinating botanical profile of Belladonna, it’s now time to explore the dual nature of this remarkable plant: its toxicity and the medicinal uses that have emerged alongside it. While Belladonna is well-known for its dangerous properties, it has also played a pivotal role in medical history. 3
Tropane Alkaloids in Belladonna
At the heart of Belladonna’s allure and danger lie its tropane alkaloids. These chemical compounds, primarily atropine, scopolamine, and hyoscyamine, are responsible for the plant’s lethal effects. Here’s a closer look:
- Atropine: Often used in medicine to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate) and as an antidote for certain types of poisoning.
- Scopolamine: Known for its use in motion sickness treatments, it can cause drowsiness and memory impairment at higher doses.
These alkaloids bind to acetylcholine receptors in the nervous system, leading to various physiological reactions.
Poisonous Properties of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
The toxic nature of Belladonna is not to be taken lightly. All parts of the plant contain toxic compounds, with the berries being particularly dangerous:
- Symptoms of Poisoning:
- Dilated pupils
- Blurred vision
- Rapid heartbeat
- Hallucinations
- In severe cases, it can lead to death.
Despite the risks, Belladonna’s dangerous reputation often sparks a sense of curiosity. I remember reading about a historical figure in my literature class who succumbed to its poison, intrigued as both a cautionary tale and a symbol of romantic tragedy.
Historical and Modern Medicinal Applications
Historically, Belladonna has had a complex relationship with medicine. In ancient times, it was used as a sedative and pain reliever. By the Middle Ages, it found its way into the hands of herbalists and midwives for various therapeutic purposes:
- Historical Uses:
- Pain relief and anesthetic during surgeries.
- Treatment for asthma and respiratory issues.
In modern medicine, scientists have refined these uses significantly. Today, Belladonna extracts are utilized in regulated preparations, such as:
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in medications to combat muscle spasms and motion sickness, and for dilating pupils in eye exams.
By understanding both its toxic and medicinal attributes, we appreciate Belladonna’s unique place in the historical fabric of herbal medicine. Our journey into the heart of this plant continues as we explore its cultural significance and how it’s perceived in contemporary society.
Read also: Purple Rice: Your Ticket to a Healthier Lifestyle.
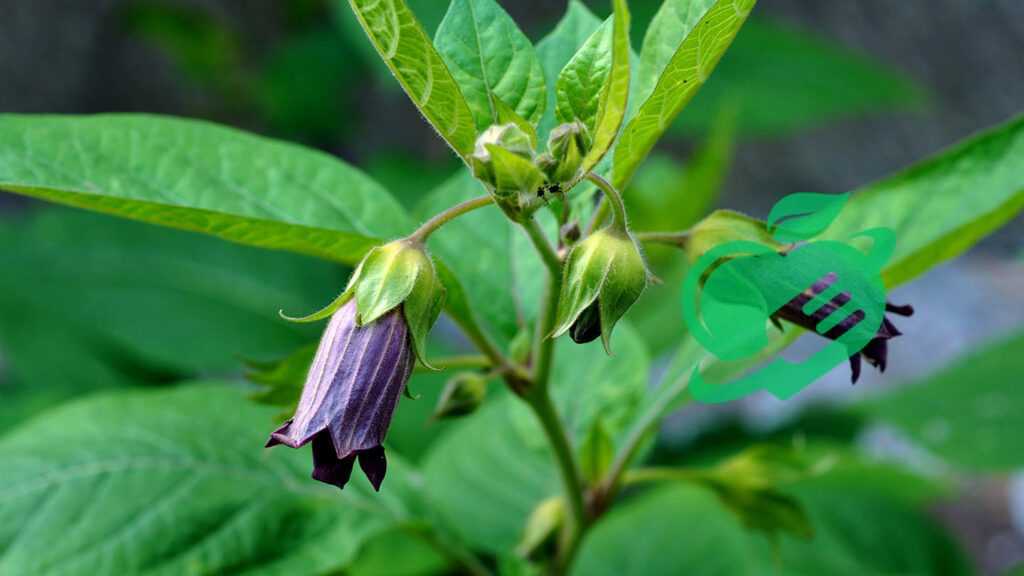

The Cultural and Symbolic Significance of the Belladonna Nightshade Plant
Having rich historical and medicinal roots, Belladonna also boasts a vibrant presence in mythology and folklore, making it a plant steeped in cultural significance. Its striking appearance and potent properties have inspired countless stories and beliefs that resonate through time.
Mythology and Folklore
In the realm of mythology, Belladonna has been portrayed in various narratives, often embodying the themes of beauty, danger, and the supernatural. Different cultures have woven the plant into their folklore, perpetuating its rich symbolism.
- Greek Mythology: Belladonna was often associated with Hecate, the goddess of magic and witchcraft. Hecate’s connection to the dark arts further cemented Belladonna’s reputation as a plant that traverses the boundary between life and death.
- European Folklore: Many European legends speak of Belladonna as a key ingredient in potions used by witches. It was believed to confer various powers, making it a closely guarded secret among practitioners of folk medicine.
Reflecting on this, I often recall my grandmother telling me tales of witches gathering herbs under the cover of darkness, with Belladonna frequently mentioned as an essential component in their mystical brews. Such stories highlight the plant’s powerful allure throughout history.
Use in Witchcraft and Magic
Belladonna holds a prominent place in the practices of various magical traditions. Its toxic properties were not merely a warning but a source of fascination:
- Rituals and Spells: Witches and herbalists would often incorporate Belladonna in charms or spells aimed at protection, divination, or even enchantment. Its ability to induce hallucinations made it a favored plant in trance-inducing rituals.
- Craft and Culture: The plant features in modern witchcraft as well, used in potions and rituals that seek to enhance psychic abilities or promote healing.
Personal anecdotes from gatherings with fellow herbalists illustrate this well—discussions often turn to the magical properties attributed to Belladonna and its impact on cultural practices. As we delve deeper into the contemporary uses and regulations surrounding Belladonna, it’s clear that this captivating plant has not only carved out a niche in history and folklore but continues to shape perceptions and practices today.
Read also: 10 Surprising Uses of Turmeric Plant Beyond the Kitchen.
Contemporary Uses and Regulations of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
As we explore the modern landscape of Belladonna, it’s important to recognize not only its pharmaceutical applications but also the regulations governing its use. This plant, with its potent properties, has informed contemporary medicine while raising safety and legal concerns.
Pharmaceutical applications of Belladonna Nightshade Plant
In the medical field, Belladonna is valued for its potent extract, which has been refined and utilized in various pharmaceutical products. The active tropane alkaloids—atropine and scopolamine—play crucial roles in modern medicine:
- Atropine:
- Used in emergency medicine to increase heart rate during bradycardia.
- Administered as an antidote for nerve agents and insecticide poisoning.
- Scopolamine:
- Commonly prescribed for motion sickness and postoperative nausea.
- Available as a transdermal patch for effective delivery.
My experience volunteering in a community health clinic brought the importance of these applications to life. I would often see the impact of scopolamine patches on patients suffering from debilitating nausea; it was rewarding to witness how science harnesses the power of nature.
Read also: The Ultimate Guide to Bhringraj: How This Herb Can Transform Your Health.
Legal Status and Safety Concerns
While Belladonna holds medicinal value, its toxicity necessitates careful regulation. In many countries, the legal status of Belladonna is strictly controlled:
- Prescription Requirements:
- In the United States and many parts of Europe, Belladonna must be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider. Over-the-counter products containing it are often limited and specified.
- Safety Concerns:
- Misuse of Belladonna can lead to severe toxicity, necessitating public awareness and education about its dangers. Accidental poisonings, especially in children due to the appealing berries, have led to calls for strict handling and labeling guidelines.
I’ve often discussed these safety concerns with fellow herbal enthusiasts, where we emphasize the importance of education—understanding both the benefits and hazards of plants like Belladonna. As we conclude this section, it’s evident that while the Belladonna Nightshade Plant is a powerful tool in modern medicine, it also comes with a significant responsibility to ensure safety and promote informed usage, balancing its historical and cultural significance with contemporary needs.
Follow us for more updates and breaking news, as we provide you with everything new.



2 Comments