Preventing and Managing Brain Bleed: What You Need to Know
Preventing and Managing Brain Bleed: what causes a brain bleed
As we have explored earlier, understanding brain bleed is crucial in recognizing the signs of brain bleed and ensuring timely medical intervention. However, prevention and management strategies are equally significant in mitigating risks. With increased awareness, individuals can adopt lifestyles that reduce the likelihood of encountering what causes brain bleeding symptoms.
Preventive Measures at Home
Prevention begins at home, where simple lifestyle alterations can help protect against brain bleed and promote overall brain health:
- Healthy Diet: To support brain function, prioritize foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins. Include leafy greens, nuts, and fish in your meals.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities for at least 30 minutes daily. This boosts cardiovascular health, crucial for maintaining robust blood flow to the brain.
- Control Blood Pressure: Keep your blood pressure in check through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for brain bleeds.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both substances severely damage blood vessels and increase the risk of bleeding.
Risk Factors to Be Aware Of
Being knowledgeable about risk factors is essential:
- Age: Older adults are generally at higher risk.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and bleeding disorders can contribute significantly to brain bleeds.
- Traumatic Injuries: Protect your head during sports and activities by wearing helmets.
Importance of Regular Health Check-ups
Routine check-ups serve as a precautionary measure. Regular evaluations can identify hidden conditions that contribute to brain bleeding disease, allowing for proactive management. For example, Mr. Johnson, a 55-year-old man, took his health into his own hands after learning about the risks of brain bleed disease from a family friend. He started regular exercise and managed his cholesterol, leading to a healthier lifestyle and significantly reducing his risk factors. In conclusion, while one cannot eliminate the risk of brain bleeding, effective preventive measures and an understanding of personal health can significantly mitigate these risks.
Read also :Boost Your Health: Combatting Vitamin K Deficiency

Preventing and Managing Brain Bleed: What You Need to Know
Having discussed the signs, symptoms, and the urgency of addressing brain bleeding disease, it’s also vital to focus on prevention and effective management techniques. By understanding how to reduce the risk factors and knowing ways to cope should a brain bleed occur, individuals can take a proactive approach to their brain health.
Read also: Stroke TIA Attack: Warning Signs You Must Know
Simple Lifestyle Changes Can Make a Difference
Prevention starts at home, and anyone can implement simple, everyday changes to support their brain health. Consider these strategies:
- Nutrition: Adopt a balanced diet rich in:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colors on your plate.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, and fish.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice or quinoa promote cardiovascular wellness.
- Stay Active: Engaging in physical activity doesn’t mean hitting the gym every day. Try activities you enjoy, such as:
- Walking or biking in the park
- Dancing to your favorite songs
- Gardening to get your hands dirty and enjoy nature
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Both can contribute to various health issues, including those affecting blood pressure and vessel integrity.
Stay Informed About Risk Factors
Understanding your health conditions can significantly help in managing risks associated with brain bleed. Factors to pay attention to include:
- Hypertension: Monitor your blood pressure regularly.
- Diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels stable with diet and exercise.
- Head Injuries: Be cautious during activities that pose a risk of falls or impacts.
The Role of Regular Check-ups
Regular health check-ups can catch potential issues before they escalate. For instance, Sarah, a 48-year-old teacher, discovered she had high blood pressure during a routine physical. This motivated her to make necessary lifestyle changes, significantly lowering her risk of a brain bleed. In summary, while it may not be possible to eliminate the risk of brain bleeds entirely, taking proactive steps through lifestyle choices and regular medical consultations can greatly enhance one’s ability to manage and prevent this serious condition.
Read also: Unlocking the Benefits: How Veggies Can Lower Your Blood Pressure
Understanding Brain Bleed
Having discussed the importance of prevention and management, let’s delve deeper into brain bleeds themselves. Understanding what a brain bleed disease is, the various types, and what can cause it can empower individuals to recognize risks and seek timely help.
Definition of Brain Bleed
A brain bleed, medically known as a hemorrhagic stroke, occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks blood into surrounding tissues. This can create pressure on the brain and disrupt normal functions. Imagine it as a leak in a dam — if the pressure builds too high, it can cause serious damage not only to the structure but also to what’s behind it.
Types of Brain Bleeds
There are several types of brain bleeding disease each with different characteristics and implications:
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: This is the most common type, occurring within the brain tissue itself. It can result from high blood pressure or arteriovenous malformations.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: This type happens in the space between the brain and the tissues covering it. Often associated with aneurysms, it can lead to sudden and severe headaches.
- Subdural Hematoma: A collection of blood underneath the outer protective layer of the brain, usually resulting from head trauma. This can develop quickly or over weeks to months.
- Epidural Hematoma: This occurs between the skull and the outer layer of the brain, often due to a head injury. It’s known for rapid progression and requires immediate attention.
Causes of Brain Bleeding
Several factors can contribute to brain bleeding. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention:
- Hypertension: Often referred to as high blood pressure, it is one of the primary culprits.
- Trauma: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can lead to direct impacts causing bleeding.
- Blood Vessel Abnormalities: Conditions such as aneurysms or vascular malformations can increase the risk of blowing a vessel.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia can affect the blood’s ability to clot.
Consider the case of Lisa, a 60-year-old woman who suffered a brain bleed due to untreated hypertension. She initially dismissed her headache as stress-related but later learned the importance of monitoring her blood pressure. In conclusion, understanding the definition, types, and causes of brain bleeding disease can significantly impact awareness and response to this critical health issue, promoting proactive care and timely intervention when needed.
Read also: COVID XEC Symptoms: What You Need to Know
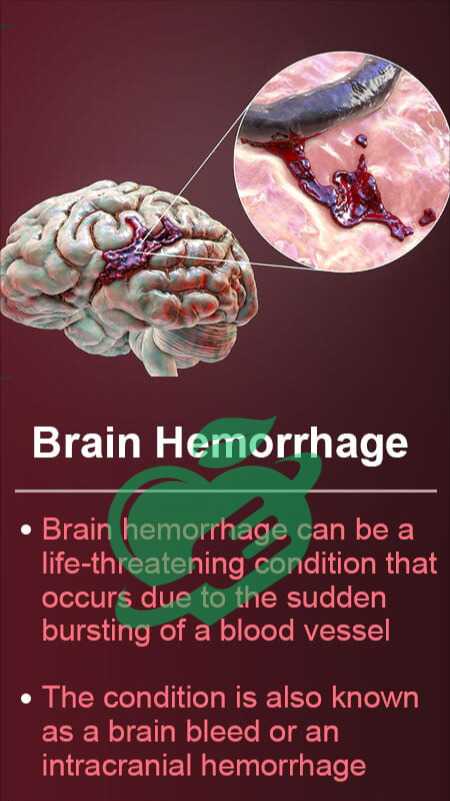
brain bleed symptoms
Now that we’ve built a foundation for understanding brain bleeds, recognizing the signs of brain bleeds and symptoms is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Being aware of what to look for can be life-saving, so let’s break down the symptoms of brain bleeding.
Common Symptoms of Brain Bleed
Brain bleed symptoms can manifest in various ways, and some common symptoms to note include:
- Headache: Often described as the worst headache of one’s life, it can come on suddenly and intensely.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may accompany headaches, increasing discomfort.
- Weakness or Numbness: Individuals may experience weakness or numbness on one side of the body, which can indicate that the brain is being affected.
- Confusion or Difficulty Speaking: Sudden confusion, trouble understanding, or difficulty expressing thoughts can signal a serious condition.
- Altered Consciousness: This might include dizziness, loss of balance, or even fainting.
You might recall a friend who called you in a panic because they suddenly couldn’t articulate their thoughts as clearly as before. This could easily be a sign that something is wrong.
Emergency Signs to Watch For-signs of brain bleed
Not every symptom is an emergency, but certain signs of brain bleed should prompt immediate action:
- Severe Sudden Headache: If someone experiences a headache that suddenly escalates, this requires urgent attention.
- Seizures: New-onset seizures can be a red flag for brain issues.
- Vision Changes: Sudden blurred or double vision can indicate a problem.
- Loss of Consciousness: Any episode of fainting or unresponsiveness warrants immediate medical evaluation.
When to seek medical help for a brain hemorrhage ?
Recognizing when to seek help can save lives. If you or someone you know experiences any combination of the above symptoms, it’s crucial to act quickly. Even if symptoms seem mild, getting a professional evaluation is always a good bet. For instance, Mark dismissed his initial headache and nausea, thinking it was just the flu. When he later experienced confusion, he was rushed to the hospital, only to find he had a brain bleed disease. Early intervention made all the difference in his recovery. In summary, being aware of the signs of brain bleed of brain bleeds and symptoms of brain bleeds can empower individuals to take swift action, ultimately leading to better outcomes in critical situations. Always prioritize health and don’t hesitate to seek medical advice when something feels wrong.
Read also : Safety First: Stay Updated on the Salmonella Egg Recall
Diagnosis and Treatment of brain bleed
Having recognized the signs of brain bleed and symptoms of brain bleeds, the next crucial step is diagnosis and treatment. Timely and accurate identification can significantly improve outcomes. Let’s explore the diagnostic procedures, available medical treatments, and potential surgical interventions.
Diagnostic Procedures for Brain Bleed
Doctors use a variety of diagnostic procedures to determine if a brain bleed is present. These methods typically include:
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): This is usually the first imaging test performed, as it quickly reveals any bleeding in the brain. It’s fast, which is critical in emergencies.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): If more detailed images are needed, an MRI may be used. While it takes longer, it offers a better view of the brain’s structure and blood vessels.
- Lumbar Puncture: Sometimes, a doctor may perform a lumbar puncture (or spinal tap) to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid. This can help detect bleeding not visible on imaging tests.
For example, when Maria started showing symptoms, her doctor quickly arranged for a CT scan. The results helped confirm that she had a small brain bleed, allowing for timely treatment.
Medical Treatments Available
Initial medical treatments focus on stabilizing the patient and controlling the bleeding. Options may include:
- Medications: To manage blood pressure, alleviate headaches, or reduce swelling in the brain. Common medications include antihypertensives and corticosteroids.
- Transfusion: In cases involving significant blood loss, transfusions might be necessary to restore blood volume.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring in a hospital setting is often crucial, as doctors observe for any changes or complications.
Surgical Interventions for Brain Bleed
In more severe cases, surgery may be required. Here are a few surgical options:
- Craniotomy: This procedure involves removing part of the skull to access the brain and relieve pressure caused by bleeding.
- Endovascular Procedures: Minimally invasive techniques can be used to treat aneurysms or vascular malformations via catheters inserted through blood vessels.
- Evacuation of Hematoma: If blood has pooled in one area, surgeons might need to remove it to alleviate pressure and prevent further damage.
Consider David, who had a significant subarachnoid hemorrhage. After a thorough evaluation, doctors performed a craniotomy, which allowed them to relieve the pressure and significantly improve his prognosis. In summary, the diagnosis and treatment of brain bleeds rely on rapid identification through imaging procedures, effective medical management, and appropriate surgical options when necessary. Swift action can greatly reduce the risks associated with this serious condition.
Read also: Brain Freeze Buster: Remedies for Instant Relief

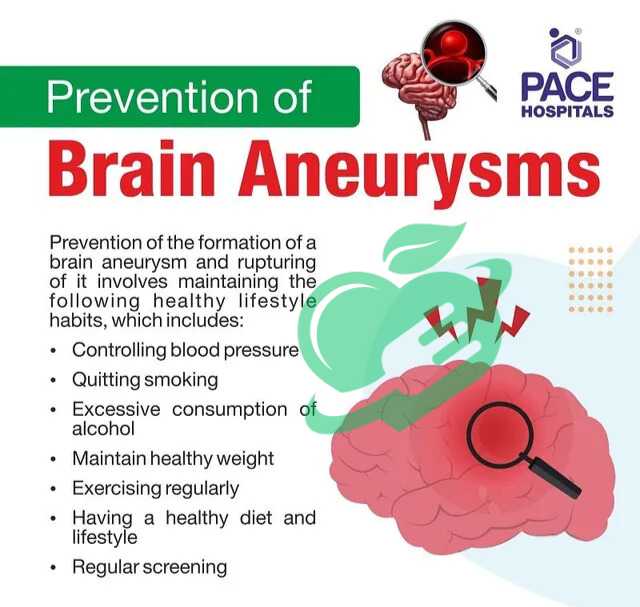
Preventive Measures
Now that we have covered the diagnosis and treatment options for brain bleeds, let’s shift our focus to prevention. Being proactive can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing a brain bleed later in life. It’s all about making informed lifestyle choices, understanding risk factors, and staying on top of your health.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Everyday habits can have a profound impact on brain health. Here are some effective lifestyle changes to consider:
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a rainbow on your plate for maximum nutrients.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate fish and plant-based proteins to support overall health.
- Healthy Fats: Opt for nuts, olive oil, and avocados to promote good circulation.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can keep your heart and blood vessels in shape.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect blood pressure. Practices such as meditation, yoga, or even spending time in nature can work wonders for mental well-being.
For instance, Jane, who struggled with anxiety, found that regular Pilates sessions not only eased her mind but also helped her maintain a healthy weight and blood pressure.
Risk Factors to Be Aware Of
Understanding the risk factors associated with brain bleeds can be a game changer. Some key factors include:
- Hypertension: One of the leading causes of brain bleeds. Keeping blood pressure in check is vital.
- Heavy Alcohol Use: Excessive drinking can lead to liver disease and increase bleeding risks.
- Smoking: This habit affects vascular health and can heighten the risk of hemorrhages.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes can damage blood vessels over time, predisposing individuals to brain bleeds.
Importance of Regular Health Check-ups
Routine health check-ups are crucial in preventing brain bleeds. Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch risk factors like hypertension or high cholesterol early on, allowing for proactive management. For example, Tom decided to schedule annual health screenings after his father suffered a stroke. During one of his visits, he learned that his cholesterol levels were higher than normal. Making some dietary changes and getting more active led to significant improvements in his health. In summary, by adopting healthy lifestyle changes, understanding risk factors, and making regular check-ups a part of your routine, you can significantly lower your risk of brain bleeds and promote a healthier future. Taking these steps not only benefits the brain but overall well-being too!
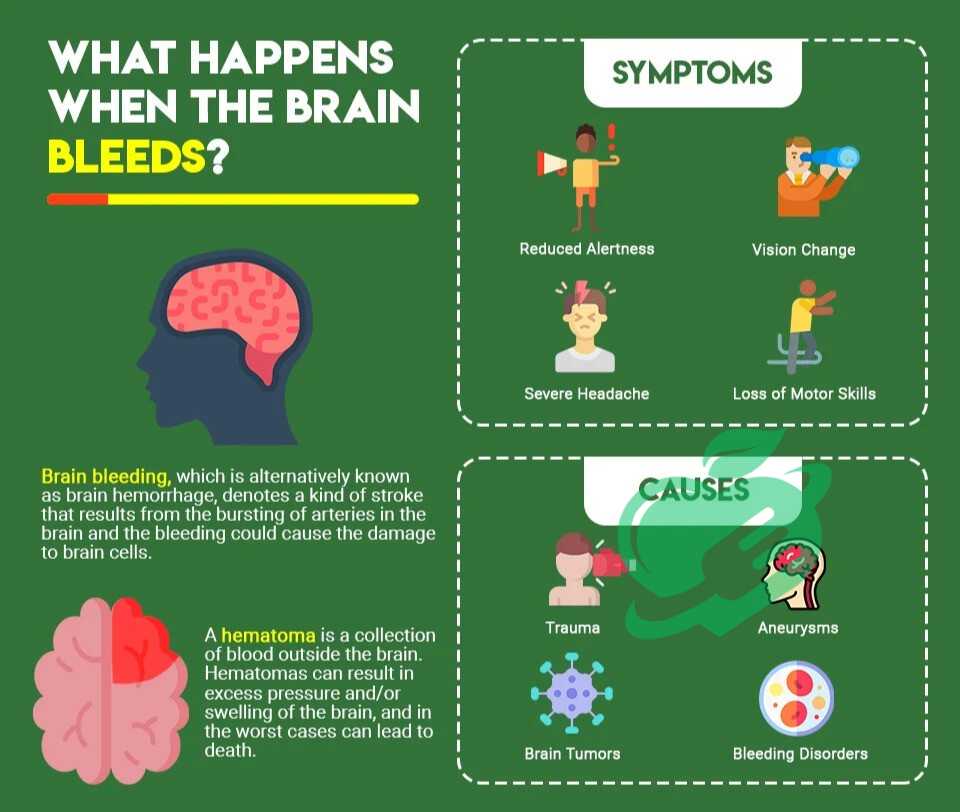
Rehabilitation and Recovery
After experiencing a brain bleed, the road to recovery is often a journey filled with hope and determination. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping individuals regain their independence and improve their quality of life. Let’s explore the rehabilitation techniques, long-term care plans, and the importance of support systems during this phase.
Rehabilitation Techniques Post Brain Bleed
Various rehabilitation techniques can be employed, tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Some effective methods include:
- Physical Therapy: This focuses on improving mobility and strength. Therapists work with patients to regain coordination and balance through targeted exercises.
- Occupational Therapy: This helps individuals relearn daily activities, like dressing and cooking, ensuring they can regain independence in their daily lives.
- Speech Therapy: Many individuals experience difficulties in communication and swallowing. Speech therapists utilize various strategies to rehabilitate these skills effectively.
For instance, when Mark had his brain bleed, he initially struggled with walking. Regular physical therapy sessions helped him regain his strength, allowing him to walk independently after several months.
Read also: Brain Damage Posturing: What You Must Know
Long-Term Care Plans
Long-term care planning is essential for individuals recovering from a brain bleed. This may include:
- Regular Follow-up Appointments: Routine visits to healthcare providers can help track recovery and address any ongoing challenges.
- Medication Management: Keeping medications organized and ensuring they’re taken as prescribed is vital for preventing future incidents.
- Adaptive Equipment: Depending on needs, items such as grab bars in bathrooms or stairlifts can enhance safety and independence.
Support Systems for Recovery
The importance of having a strong support system cannot be overstated. This may include:
- Family and Friends: Their encouragement and assistance can help motivate individuals throughout their recovery journey.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have gone through similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical strategies.
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling can be beneficial for both patients and families as they navigate the emotional challenges following a brain bleed.
Frequently asked questions
What is the survival rate after a brain bleed?
Bleeding in the brain, known as brain hemorrhage, can pose serious risks to life, with an estimated 5-year survival rate of approximately 26.7%. The outlook for recovery is influenced by the severity and location of the bleeding, as well as the degree of swelling it causes. 1 .
What causes bleeding in the brain?
The primary causes of a brain hemorrhage include head trauma and high blood pressure. Head injuries are the most frequent cause of brain hemorrhages in individuals under 50. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can weaken the walls of blood vessels, potentially resulting in a brain hemorrhage. 2
Can you live a normal life after a brain bleed?
After experiencing a brain bleed, you might require rehabilitation. The extent of the bleed could lead to brain damage, which may impact your ability to carry out everyday activities. Rehabilitation can assist you in recovering the necessary functions for daily life and reduce the risk of future brain bleeds.
Can you live a normal life after a brain bleed?
After experiencing a brain bleed, you might require rehabilitation. The extent of the bleed could lead to brain damage, which may impact your ability to carry out everyday activities. Rehabilitation can assist you in recovering the necessary functions for daily life and reduce the risk of future brain bleeds. 3
What were your first signs of a brain bleed?
The signs of a brain hemorrhage differ depending on the type, but may include:
- Unexpected tingling, weakness, numbness, or paralysis in your face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of your body.
- Sudden, severe headache.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Confusion.
- Dizziness.
- Slurred speech.
- Lack of energy, sleepiness.
- In addition, you may experience:
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Vision loss.
- Stiff neck.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Loss of balance or coordination.
- Difficulty breathing and irregular heartbeat.
- Seizures.
- Loss of consciousness and coma. 4
How long can you have a brain bleed before you know it?
Subacute. Symptoms may take time to emerge, sometimes appearing days or weeks following a head injury. Chronic. This type of hematoma, resulting from less severe head injuries, can lead to gradual bleeding, with symptoms potentially taking weeks or even months to manifest.5
How do they fix a brain bleed?
Surgery: In certain situations, conventional surgical procedures may be required to remove blood from the brain or to mend injured blood vessels. Removing the fluid that encases the brain: This allows the hematoma to grow without harming brain cells. Medication: Medications are administered to manage blood pressure, seizures, or headaches. 6
Can a brain bleed heal on its own?
Surgery: In certain situations, conventional surgery might be required to remove blood from the brain or fix injured blood vessels. Removing the fluid around the brain allows space for the hematoma to grow without harming brain cells. Medication: Medications are administered to manage blood pressure, seizures, or headaches.6
Is surgery for a brain bleed serious?
As with any surgical procedure, the operation for a subdural hematoma involves potential complications. Although many of these complications are rare, they can be quite serious. One possible issue that may arise following surgery for a subdural hematoma is additional bleeding in the brain.7
Because your health is the most valuable thing you have and the most precious thing we care about, we always recommend that you consult your specialist doctor in everything related to your health and daily life. Everything we provide here is for awareness purposes only and does not replace consulting a doctor. Every person has a unique condition that deserves special care, and we are here by your side, working passionately to provide the information you need. Always follow us, because we write for you with love and sincerity to remain a source that inspires you with hope and supports you on your journey towards a better life.
- medicinenet (((↩))
- nyp ((↩))
- my.clevelandclinic ((↩))
- clevelandclinic ((↩))
- mayoclinic ((↩))
- aurorahealthcare ((↩))((↩))
- NHS ((↩))